Update: Hubble took its first picture since it went into safe mode on June 13th! More info here.
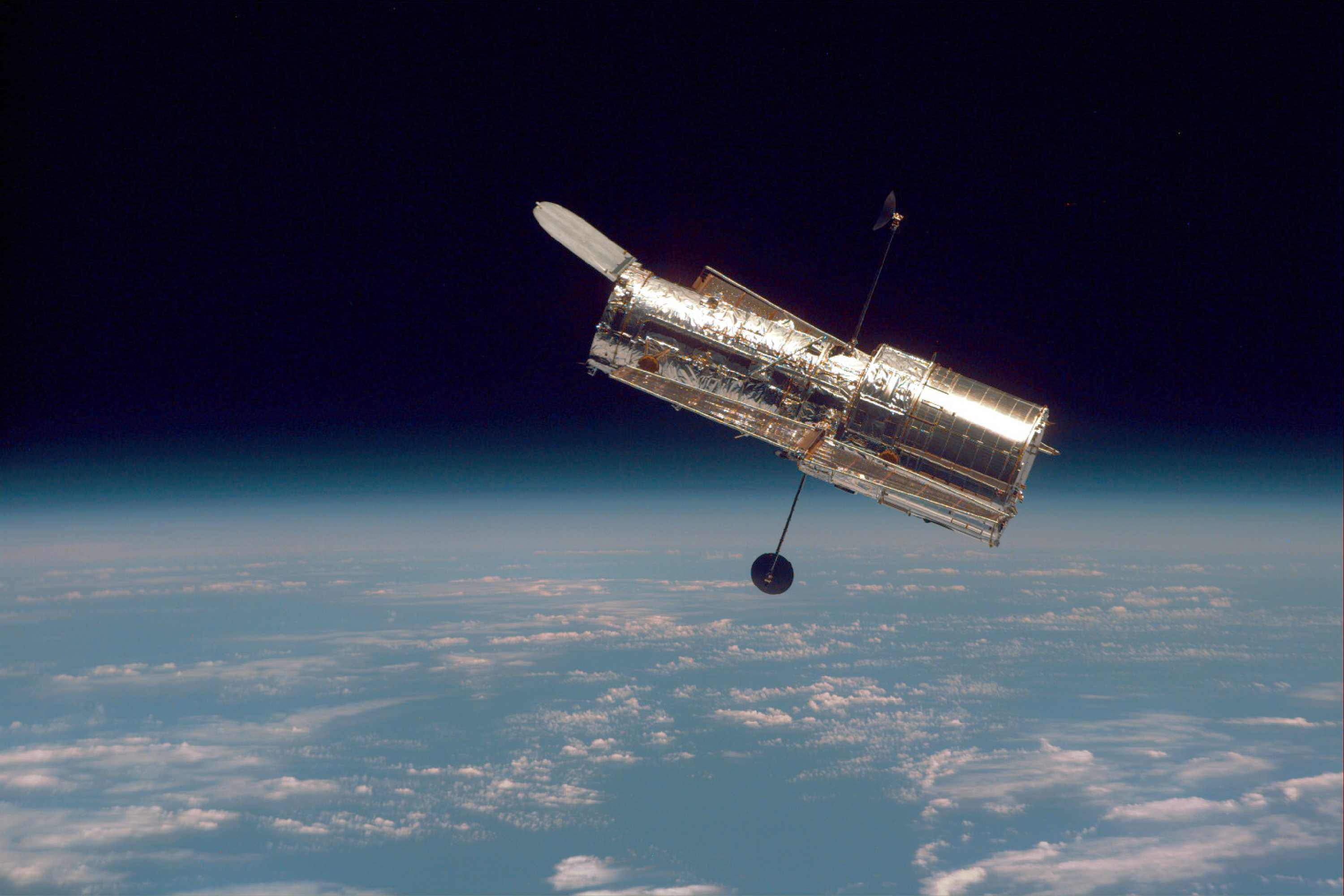
On Sunday, June 13th, the Hubble Space Telescope gave the astronomical community a fright when its payload computer suddenly stopped working. This prompted the main computer to put the telescope and its scientific instruments into safe mode. What followed was many tense weeks as the operations team for the HST tried to figure out what the source of the problem was and come up with a strategy for turning Hubble back on.
On Friday, July 17th, after more than a month of checking, re-checking, and attempted restarts, the operations team for Hubble identified the root of the problem and restored power to the telescope’s hardware and all of its instruments. Science operations can now resume, and the pioneering space telescope that gave us over thirty years of dedicated astronomy, cosmology, and astrophysics, still has some life in her!
Continue reading “Good News! NASA Announces that they have Fixed Hubble!”