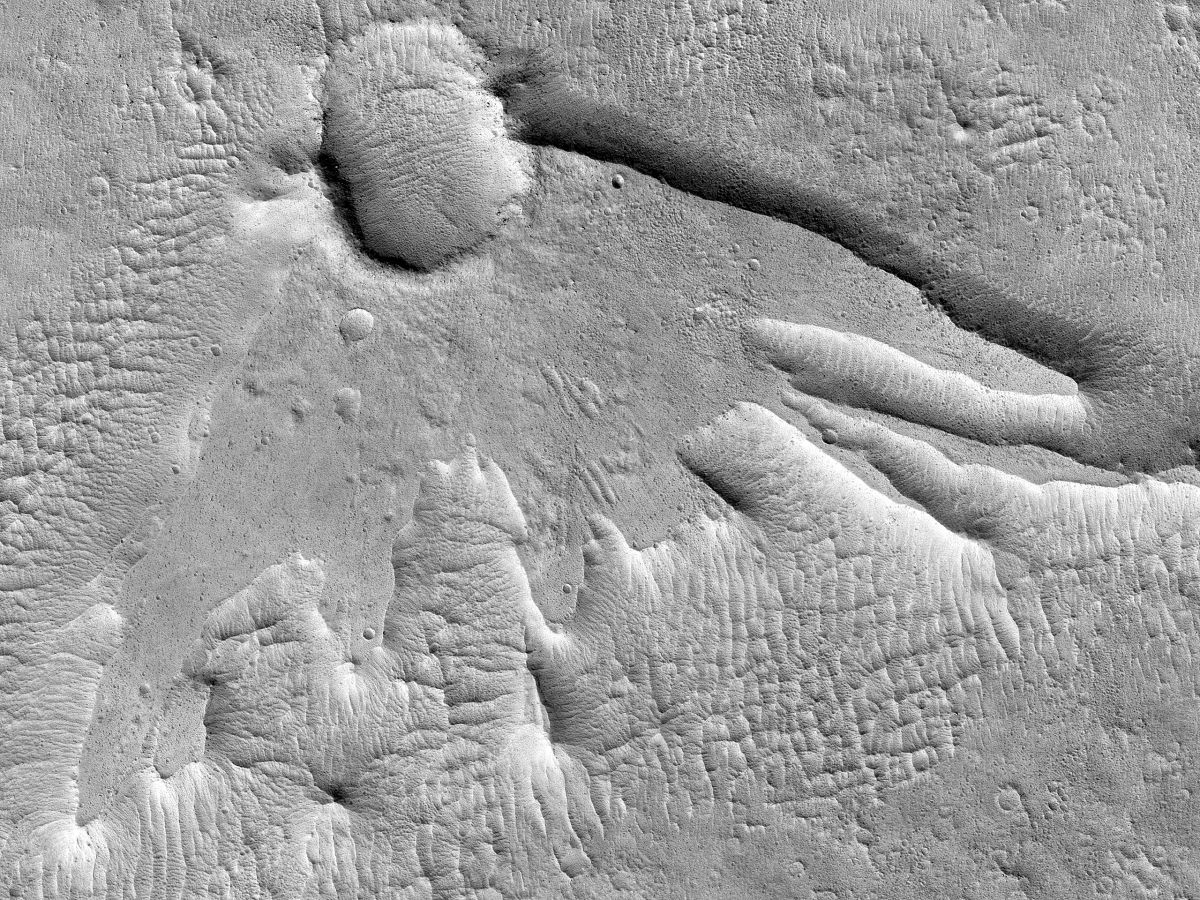
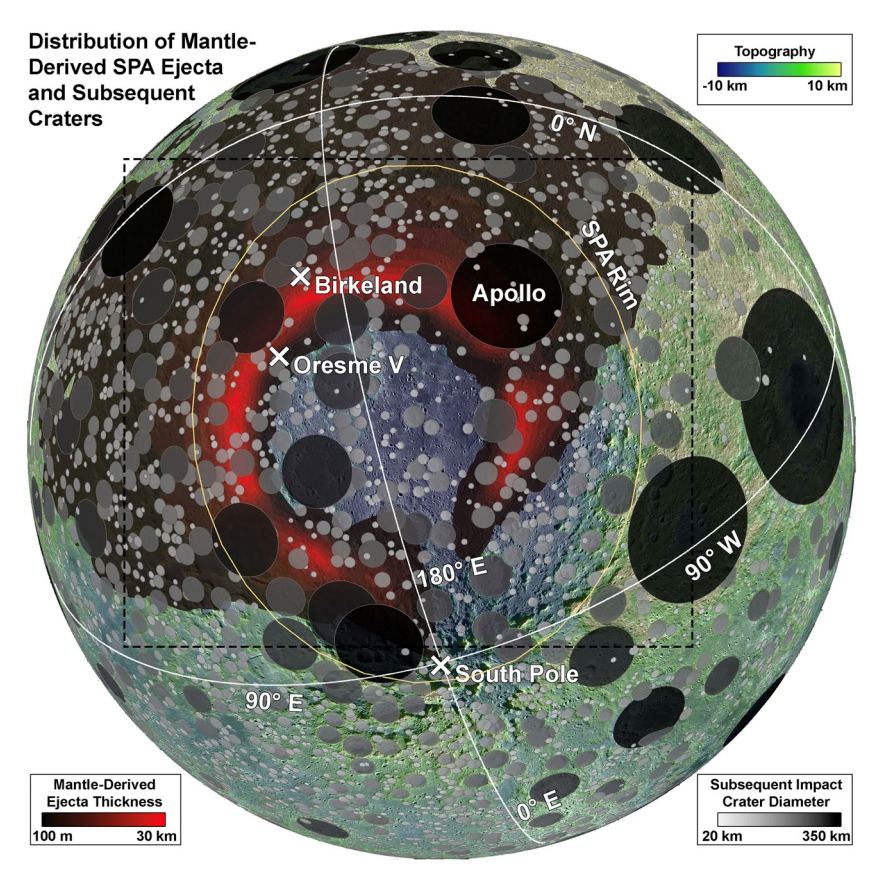
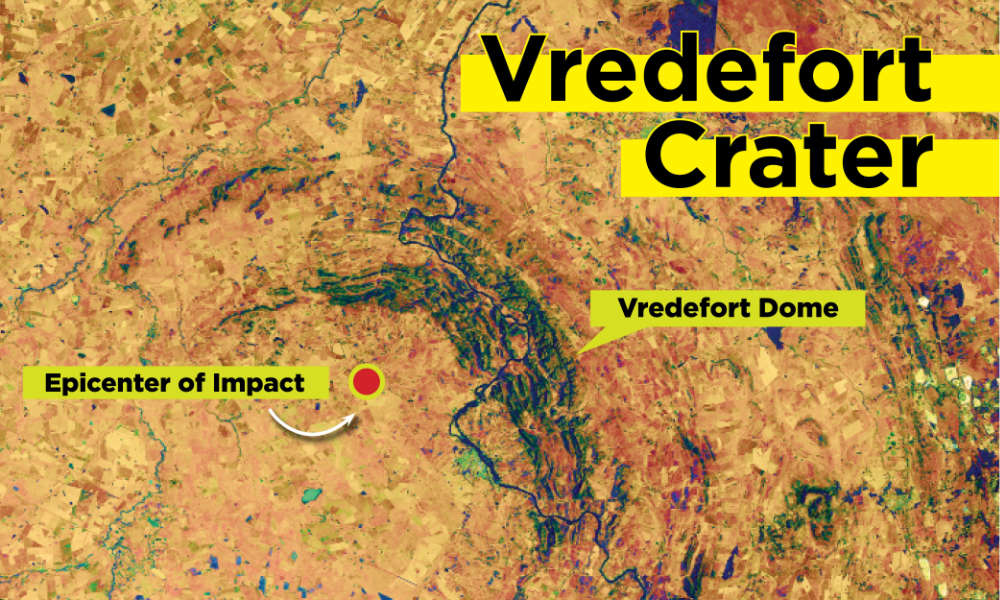
Impact craters are nature’s signature from a more chaotic time in our Solar System’s history. A quick glance at the Moon’s disfigured surface makes that clear. Same with Mars, though a telescope is needed to examine it. Or better yet, an orbital spacecraft with a powerful camera.
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and its HiRISE camera have been examining Mars’ surface for years, cataloguing the planet’s menagerie of impact craters. One of them, recently chosen as the HiRISE Picture of the Day (HIPOD,) looks like a Thunderbird. Or a dinosaur footprint left in the mud.
Continue reading “Not All Craters are Circular. Sometimes They Look Like This”