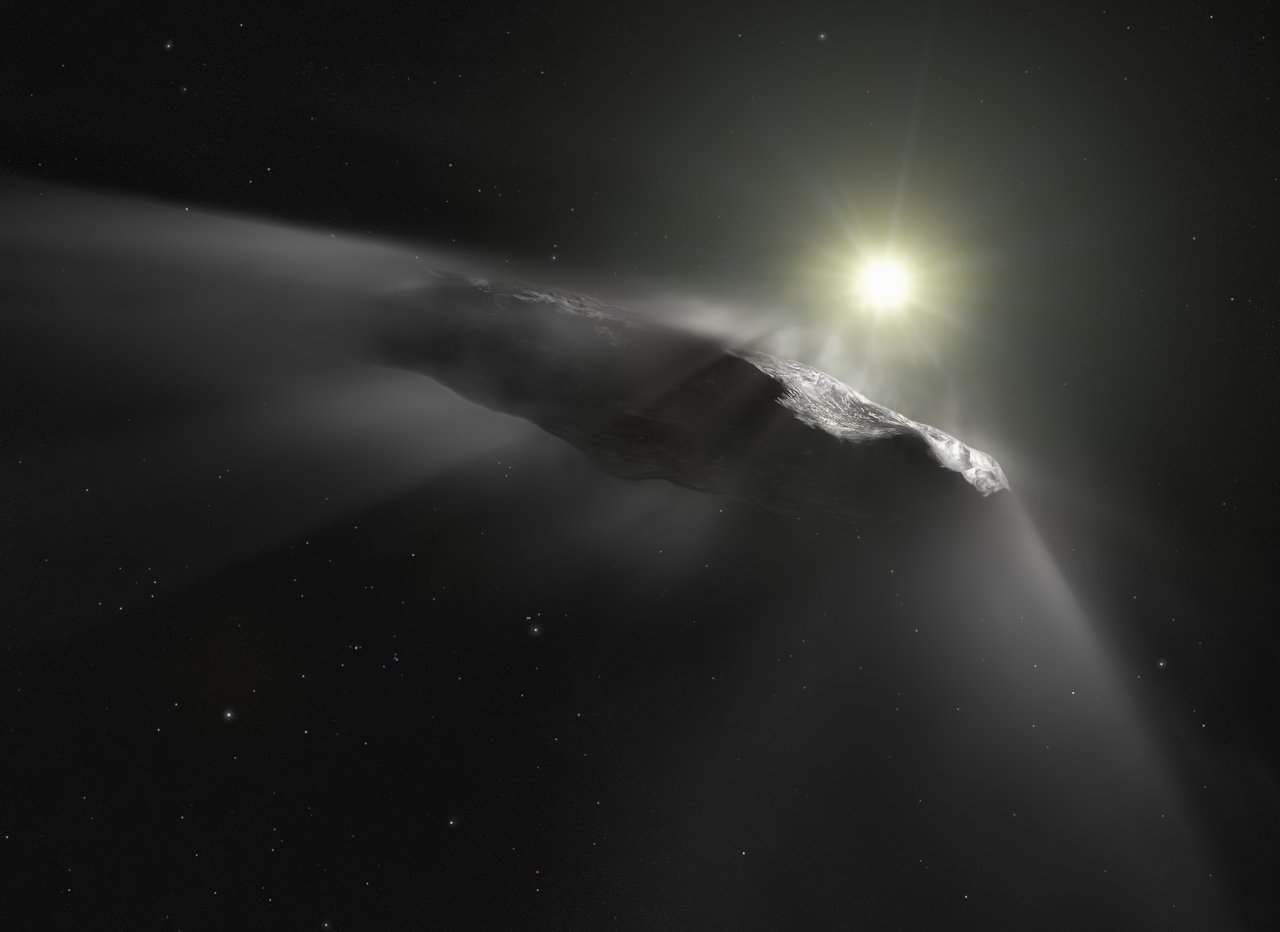
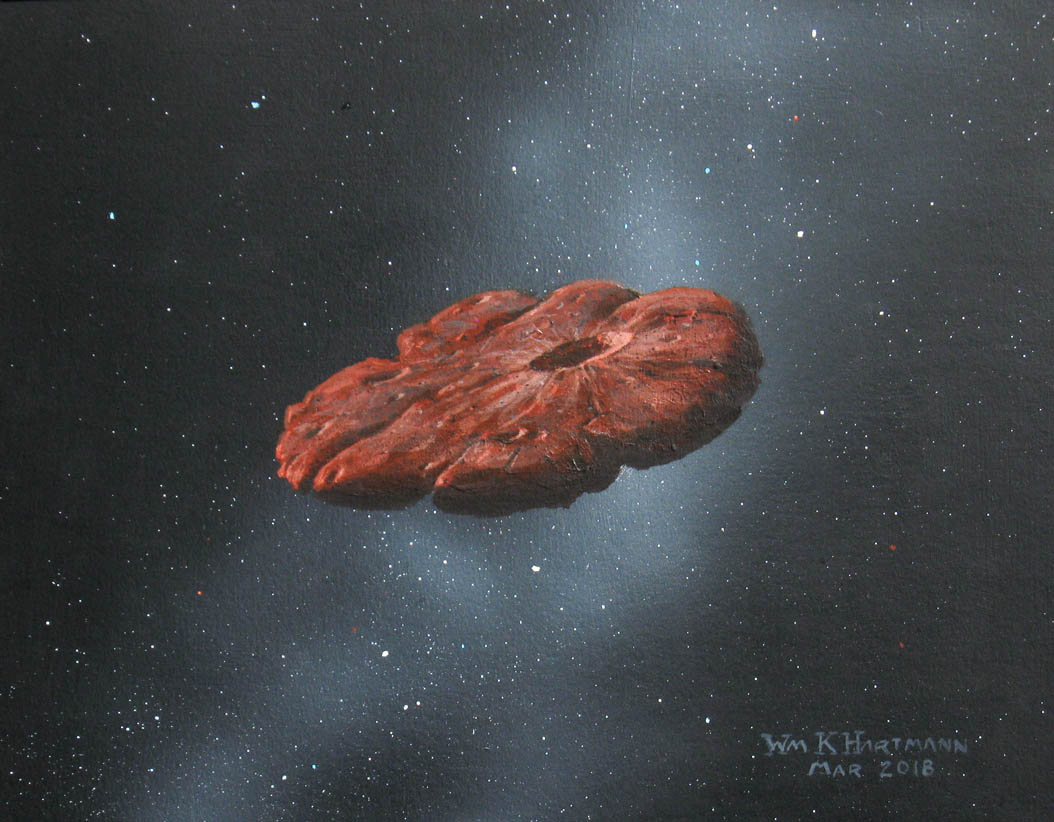
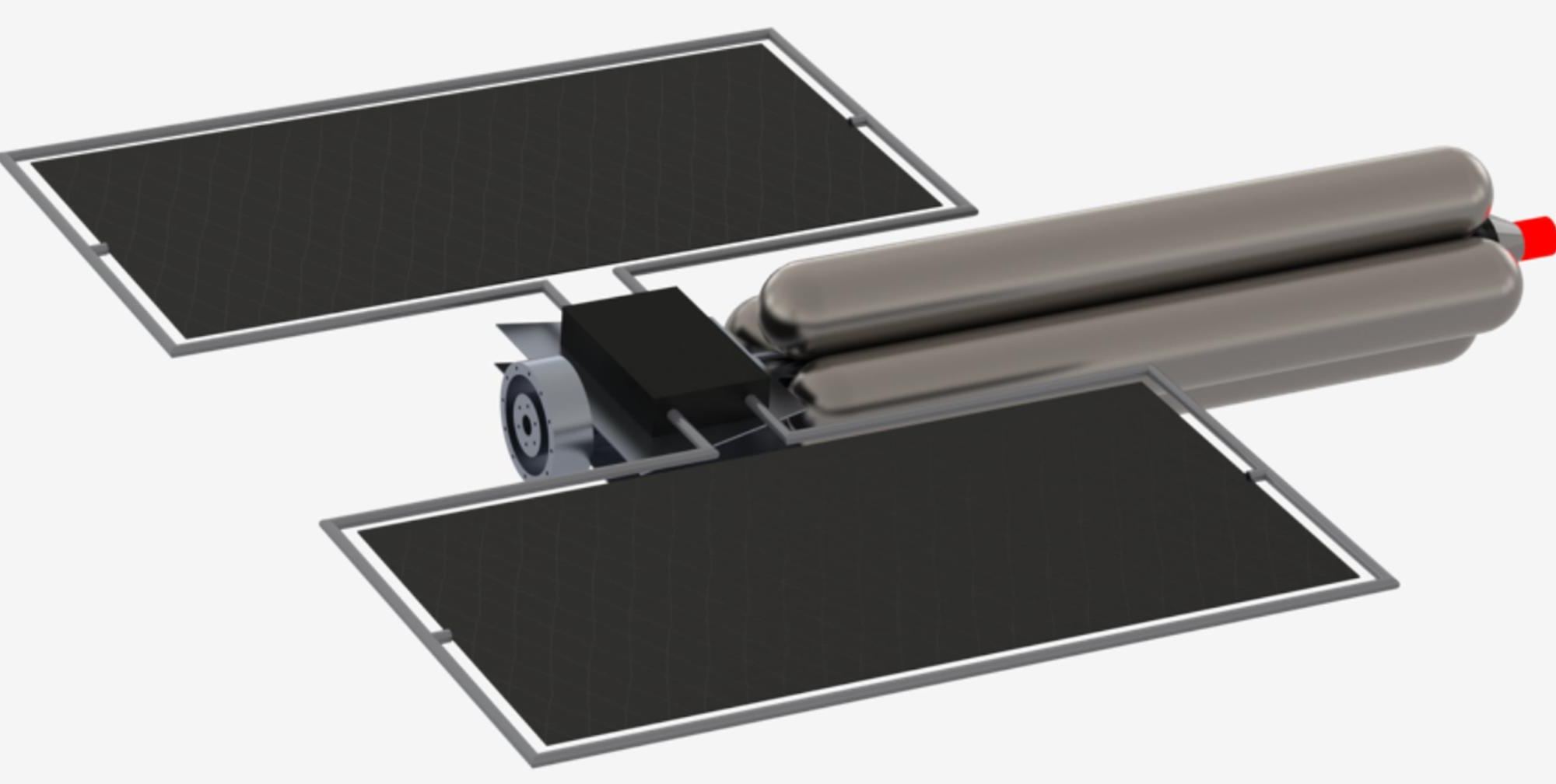
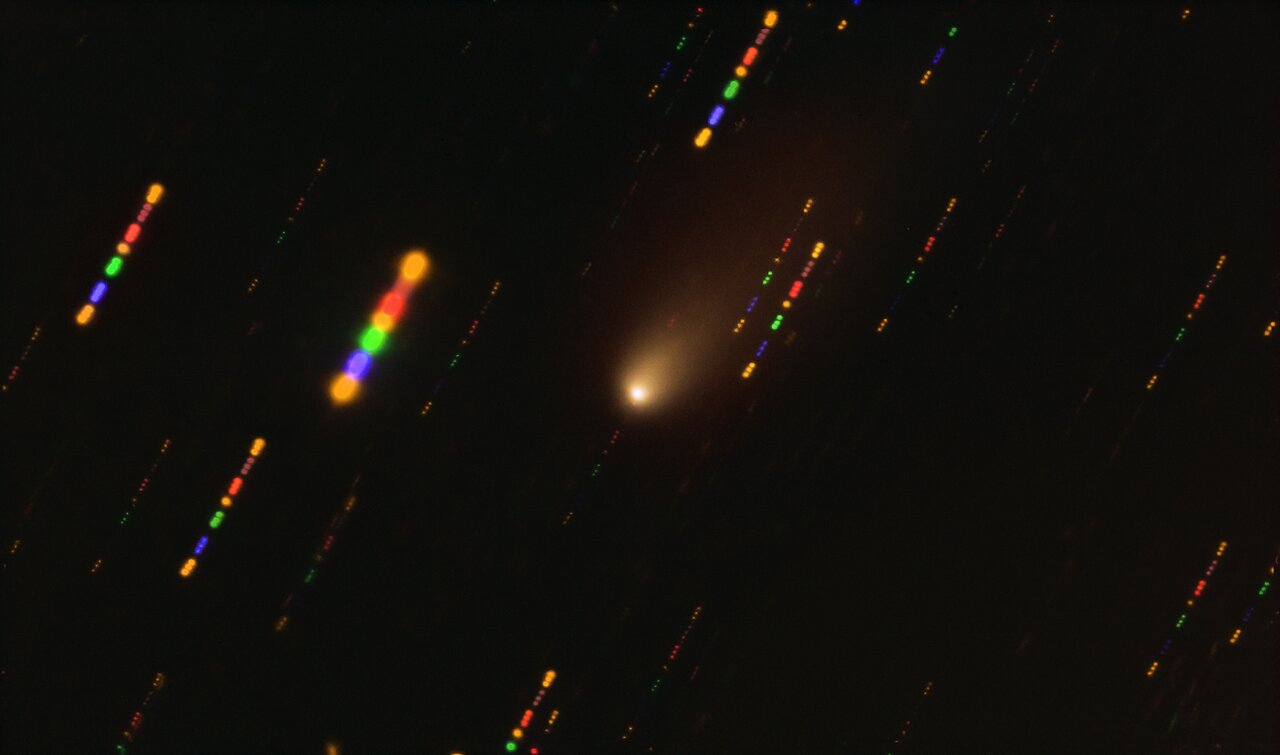
What if we had the ability to chase down interstellar objects passing through our Solar System, like Oumuamua or Comet Borisov? Such a spacecraft would need to be ready to go at a moment’s notice, with the capacity to increase speed and change direction quickly.
That’s the idea behind a new mission concept called the Extrasolar Object Interceptor and Sample Return spacecraft. It has received exploratory funding from NASA through its Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program.
“Bringing back samples from these objects could fundamentally change our view of the universe and our place in it,” says Christopher Morrison, an engineer from the Ultra Safe Nuclear Corporation-Tech (USNC-Tech) who submitted the proposal to NIAC.
Continue reading “Extrasolar Object Interceptor Would be Able to Chase Down the Next Oumuamua or Borisov and Actually Return a Sample”