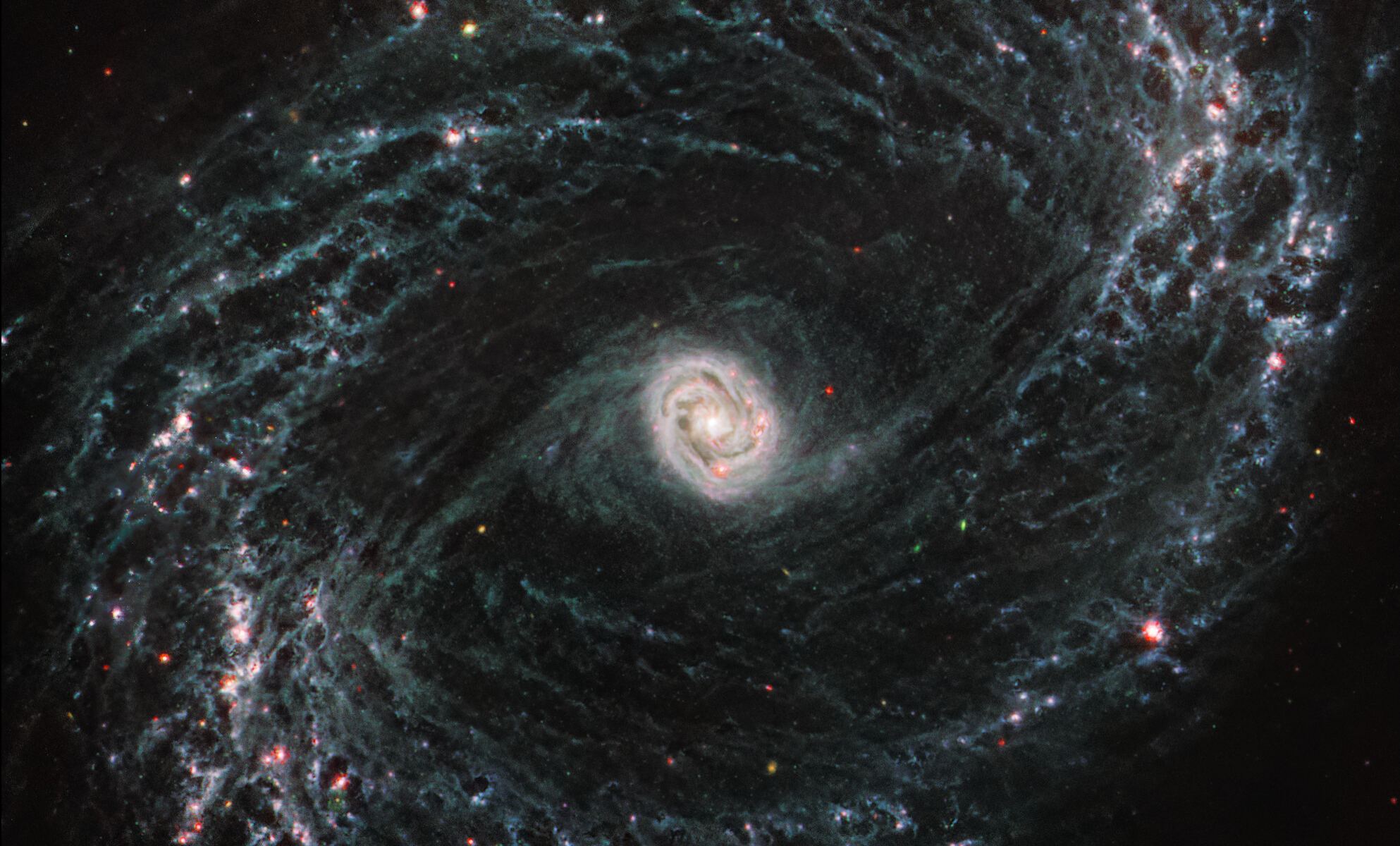
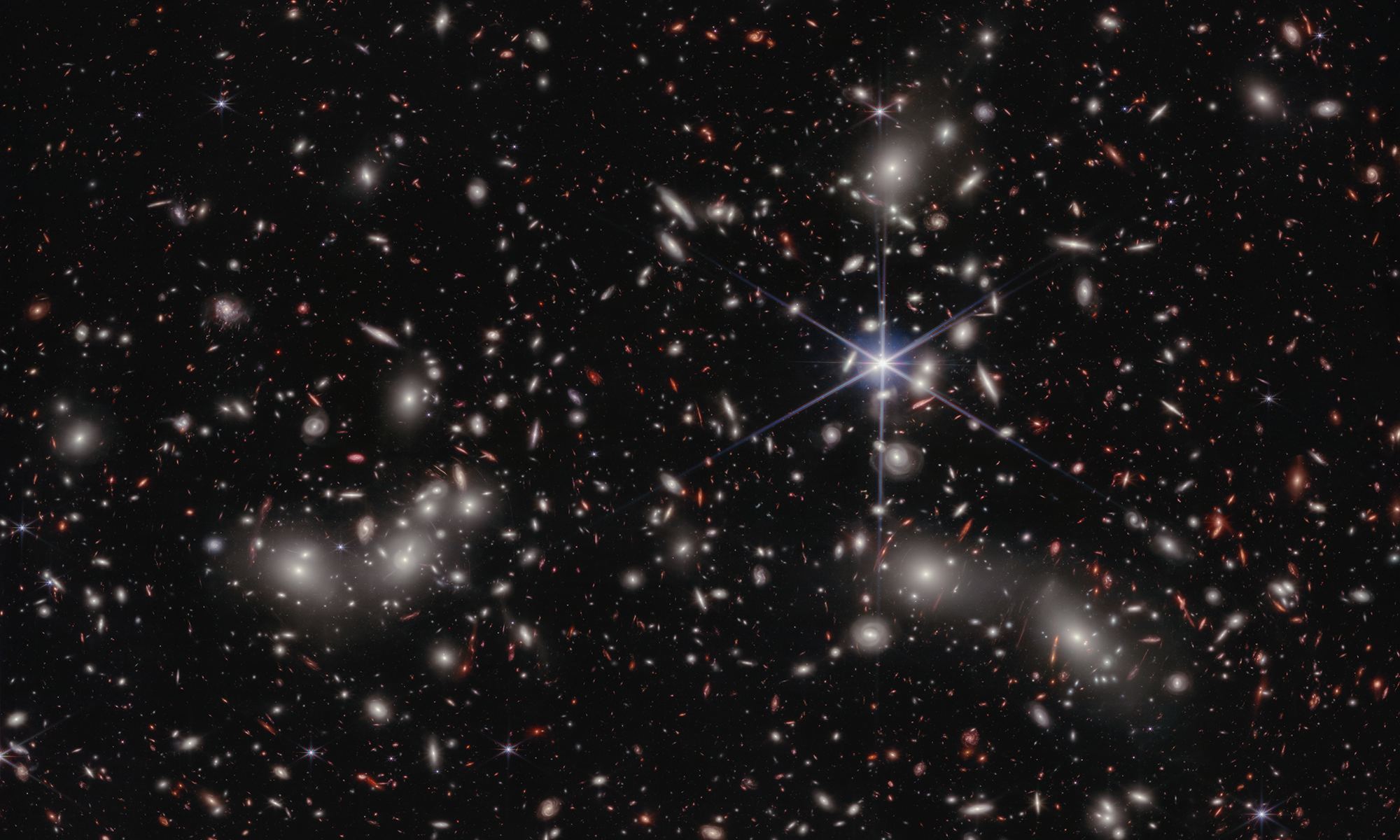
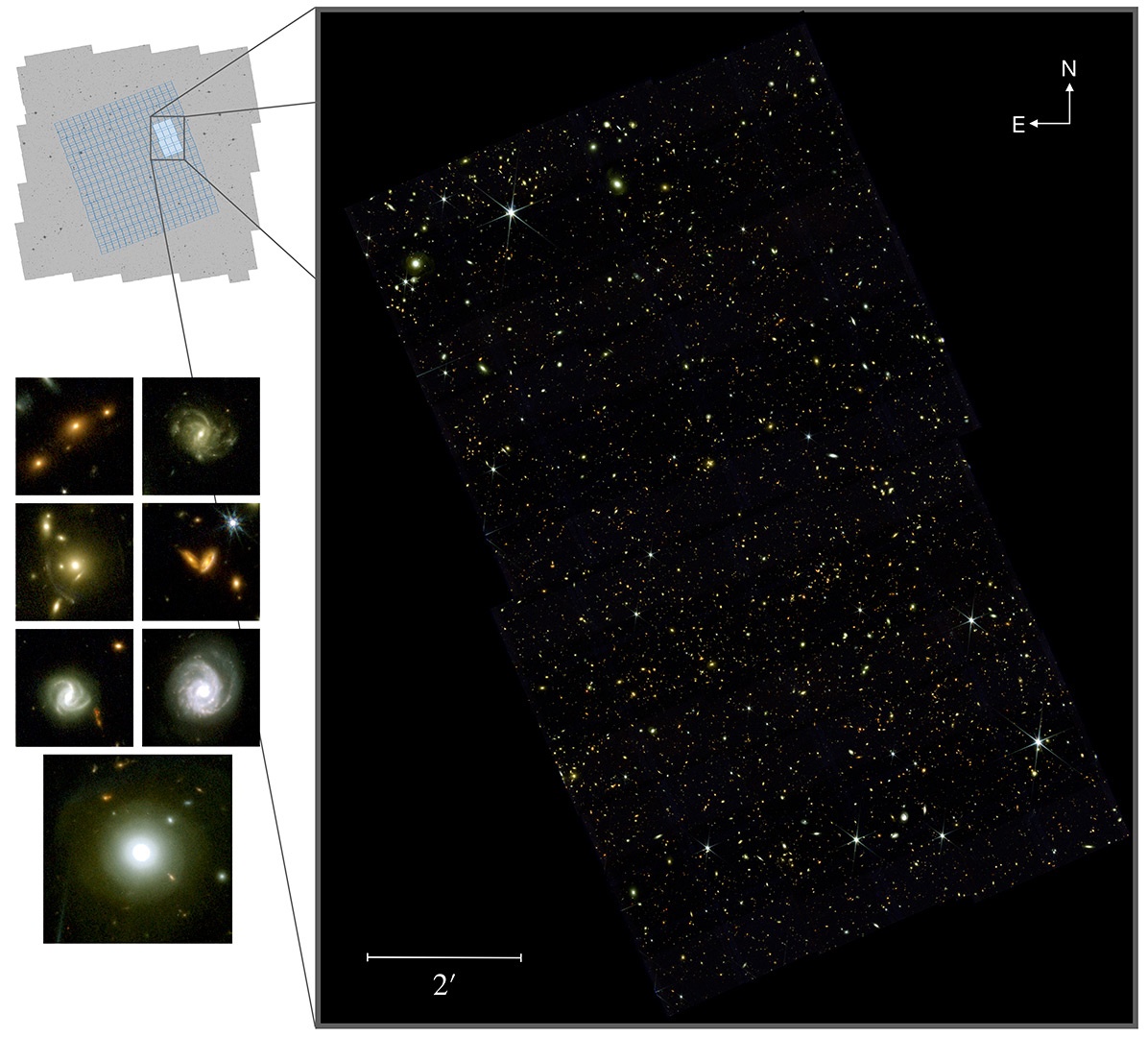
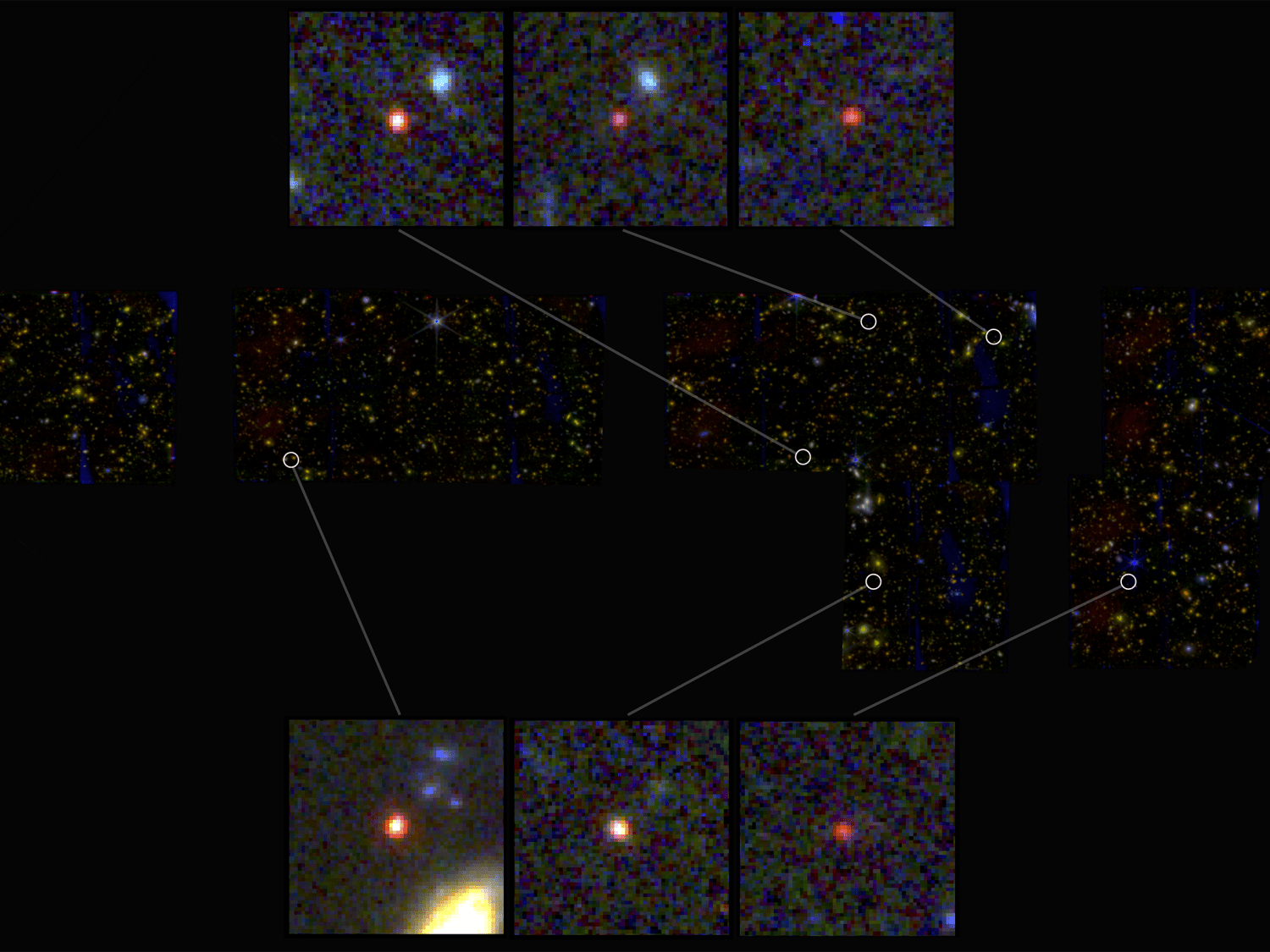
Hubble Space Telescope’s Deep Field revealed thousands of galaxies in a seemingly empty spot in the sky. Now, the James Webb Space Telescope has taken deep field observations to the next level with its COSMOS-Web survey, revealing 25,000 galaxies in just six pictures, the first from this new survey.
“It’s incredibly exciting to get the first data from the telescope for COSMOS-Web,” said principal investigator Jeyhan Kartaltepe, from the Rochester Institute of Technology’s School of Physics and Astronomy, in press release. “Everything worked beautifully and the data are even better than we expected. We’ve been working really hard to produce science quality images to use for our analysis and this is just a drop in the bucket of what’s to come.”
Continue reading “JWST Sees So Many Galaxies, and It's Just Getting Started”