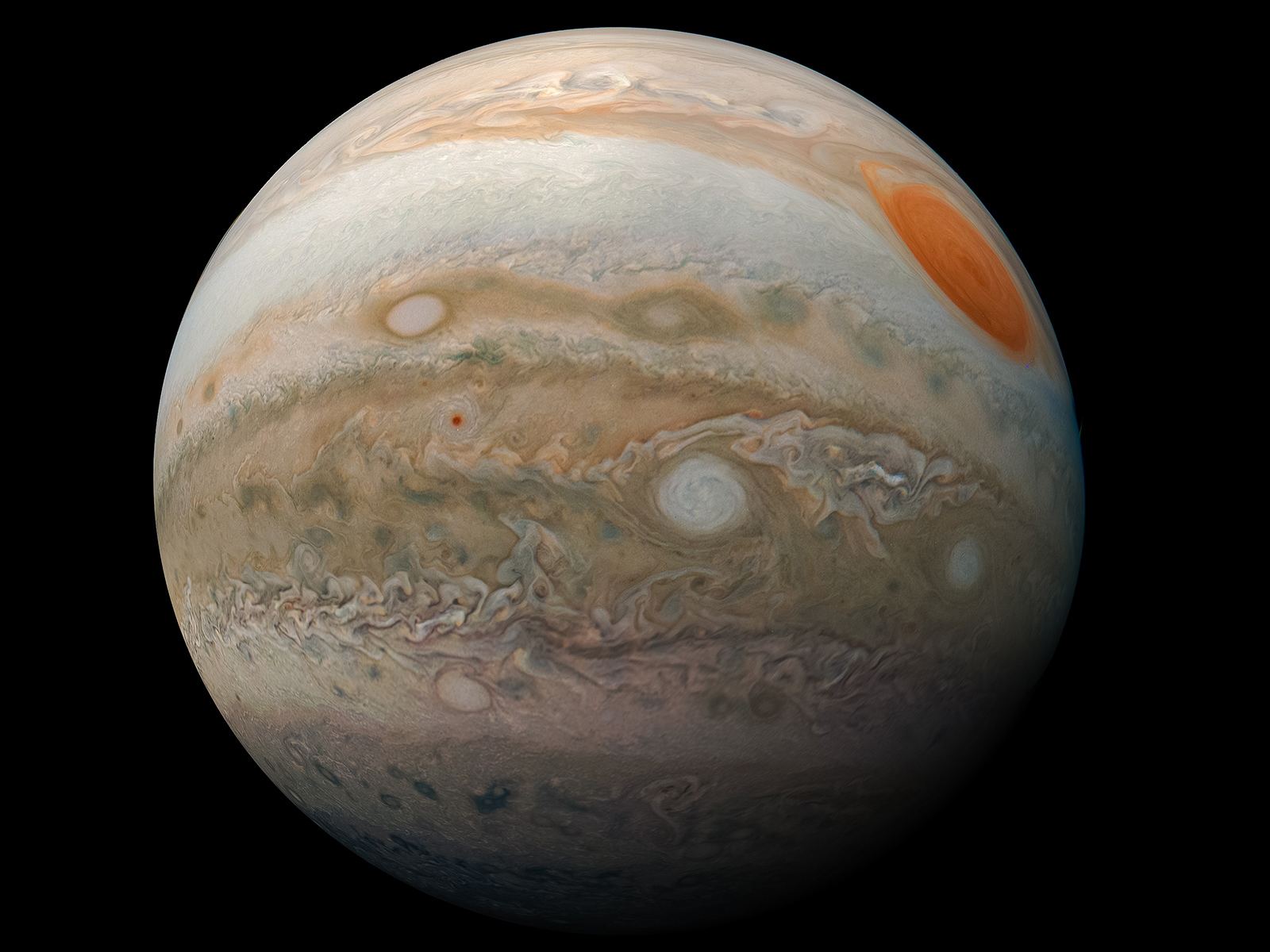
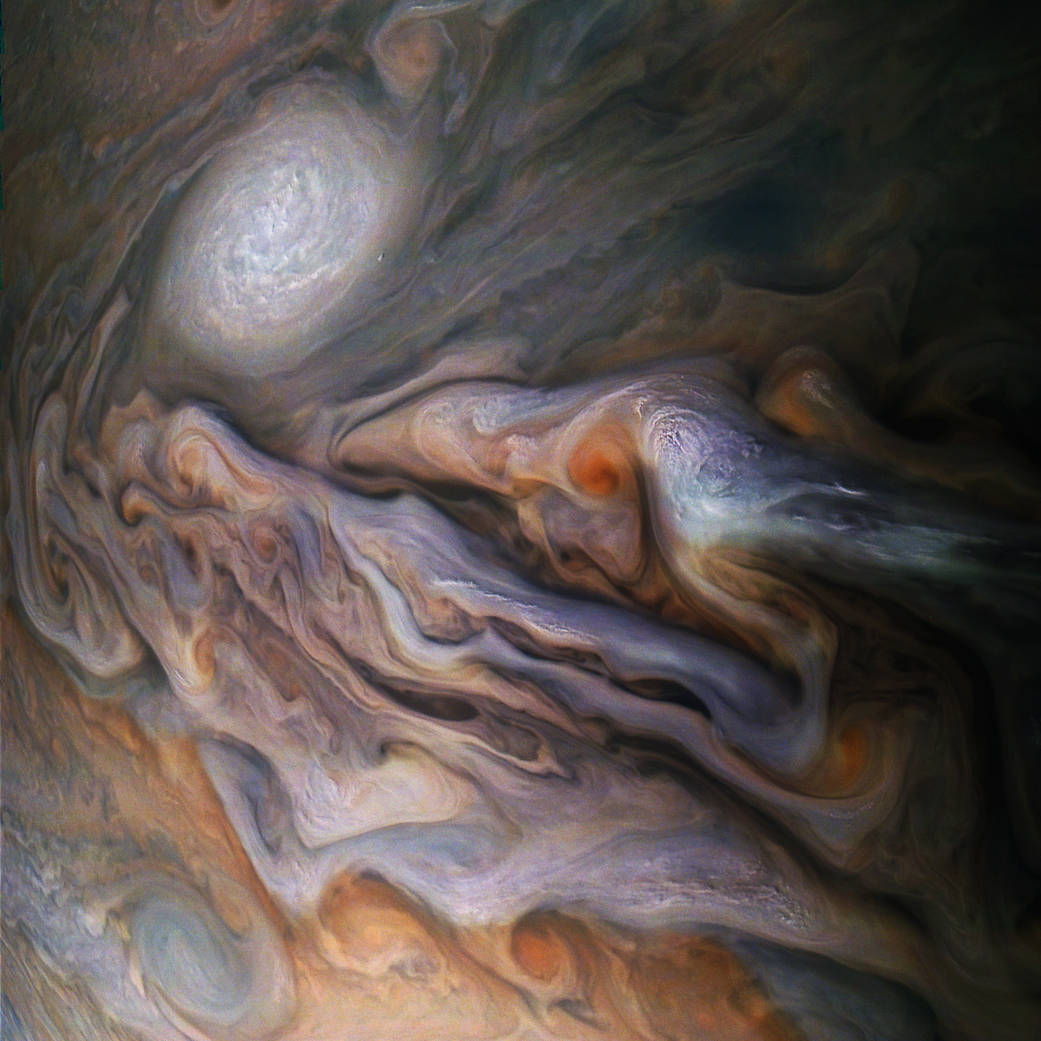
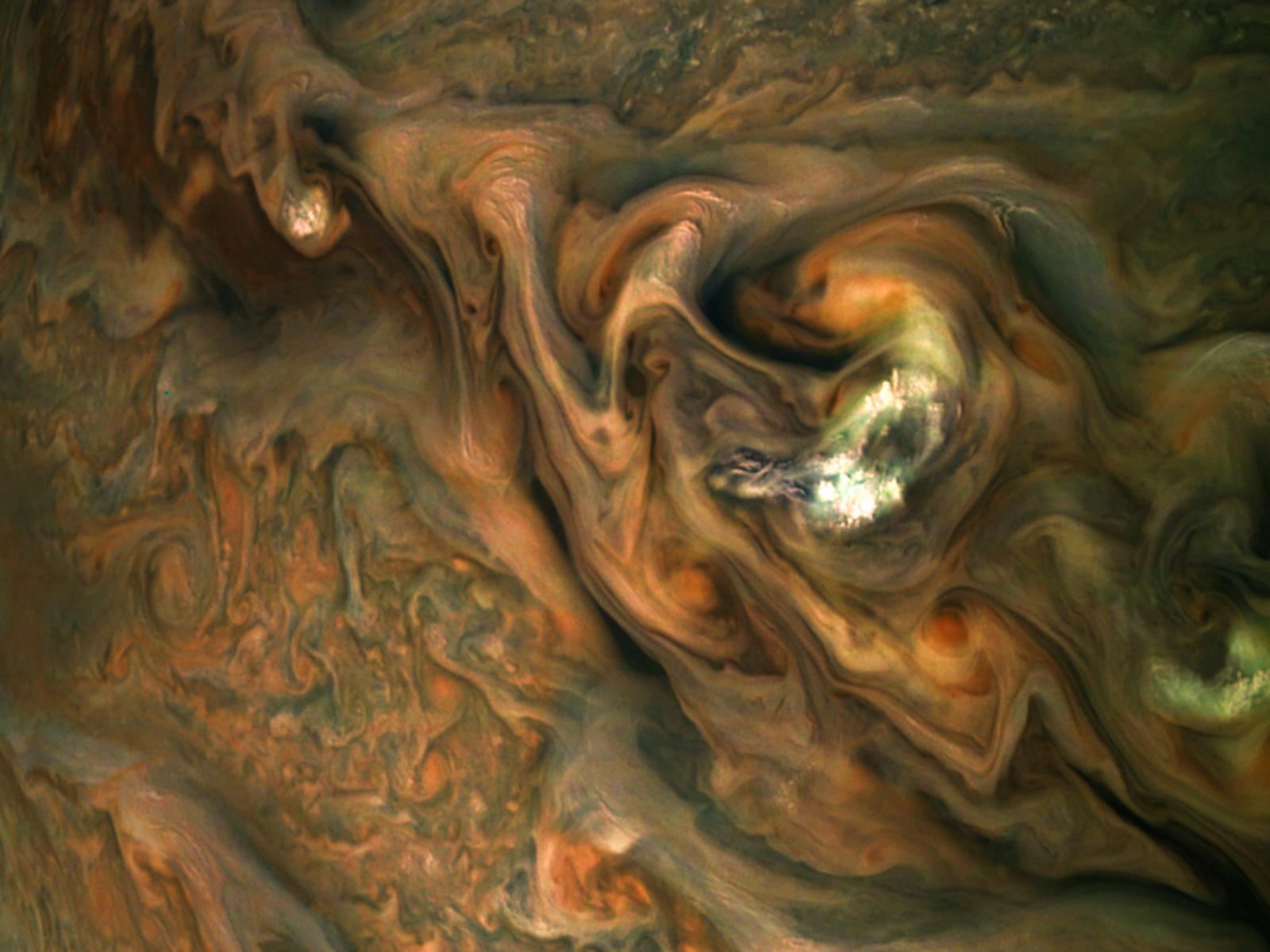
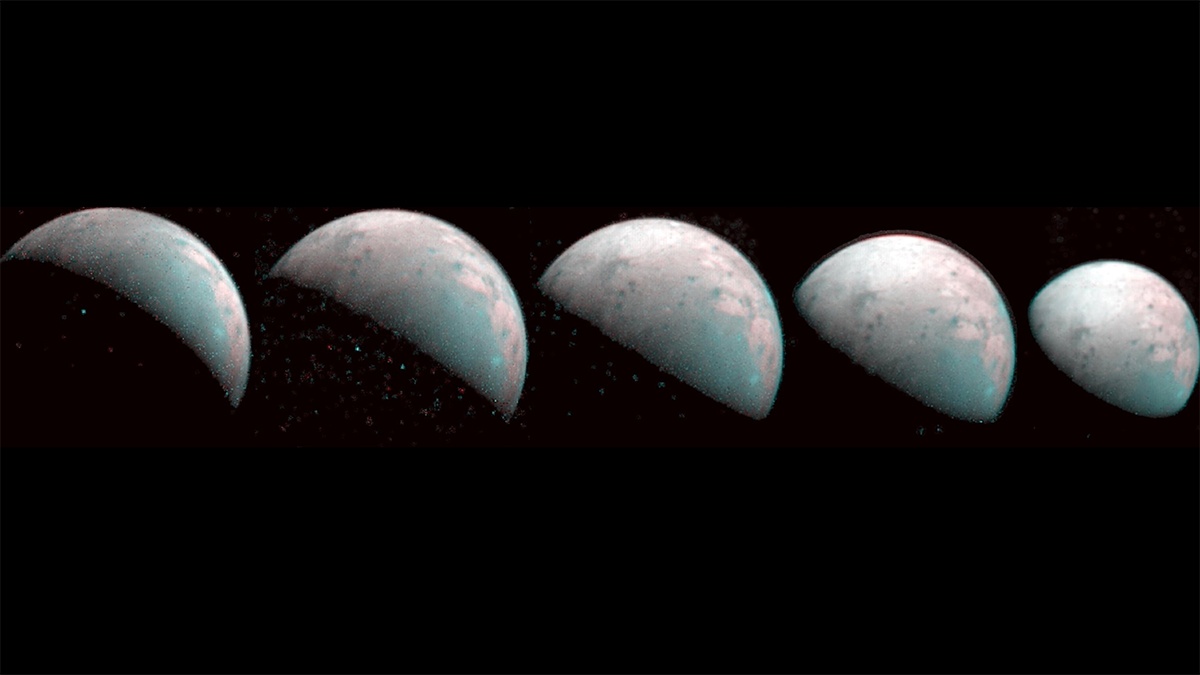
The Juno mission to Jupiter has been extended to September 2025 – or however long the spacecraft can keep operating around Jupiter.
While Juno has so far focused its attention on the giant planet alone, the mission extension will include observations of Jupiter’s rings and large moons, with targeted observations and close flybys planned of the moons Ganymede, Europa, and Io.
This will be the first close flybys of these moons since the Galileo mission in 1995-2003.
Continue reading “With its New Extension, Juno is Going to be Visiting Jupiter’s Moons”