[/caption]
Greetings, fellow SkyWatchers! You can breathe now… the Venus Transit is over and we’re back to the mundane astronomical excitement like great globular clusters, an early morning conjunction and two meteor showers – the Ophiuchids and June Lyrids. If you’re up to the ordinary, then follow along as we capture some great galaxies and a very challenging study! Dust off your optics and meet me in the back yard…
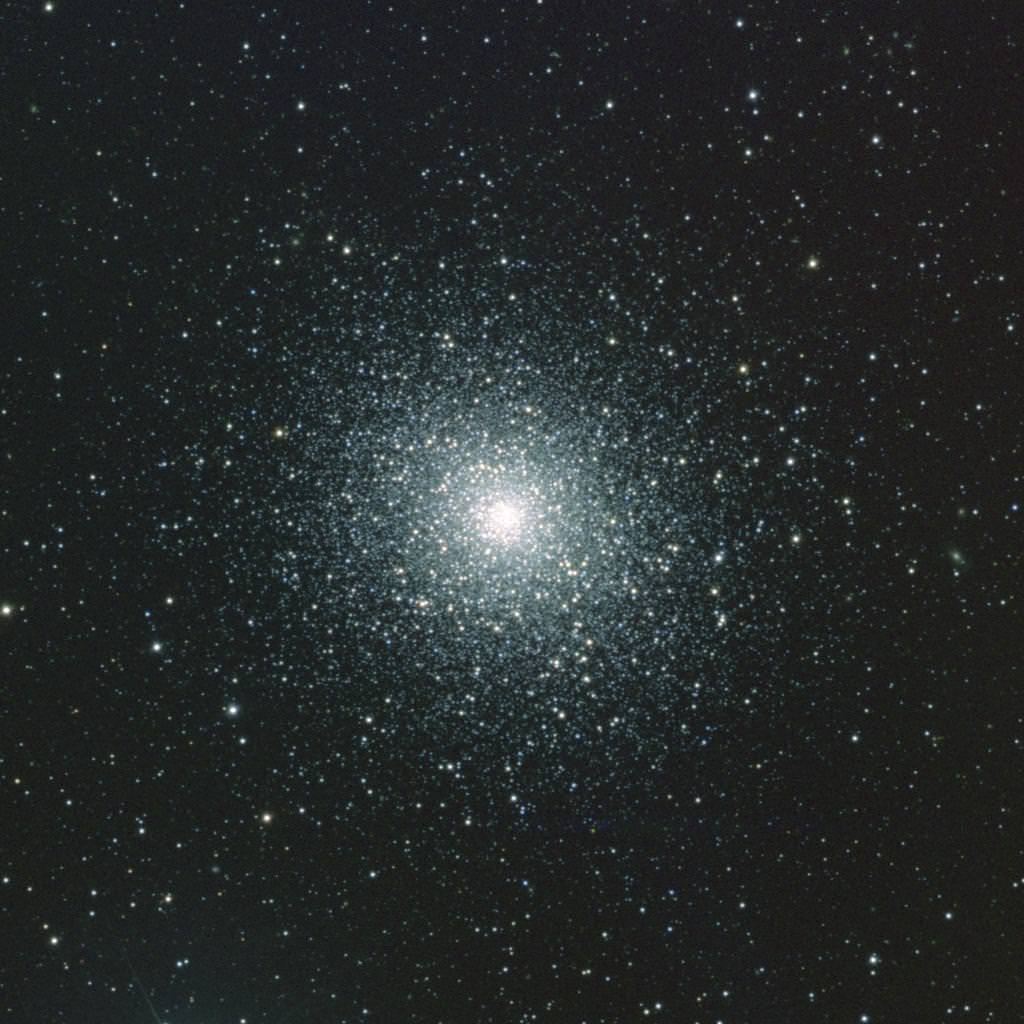
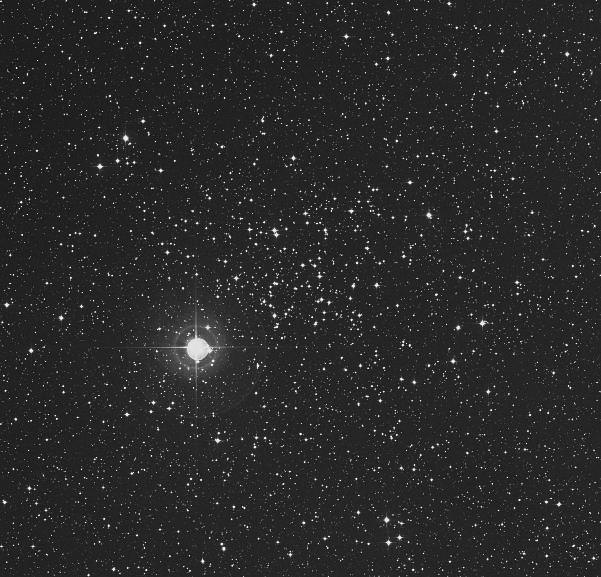
Monday, June 11 – Tonight we make the jump to Serpens Caput, which is in itself a challenge to recognize with the unaided eye. Using bright Spica as a guide, look about a handspan northeast for two of the brightest stars in the constellation – Alpha, and Lambda to its northeast. Using binoculars, locate a pairing with Delta to the north-northwest and Mu to the south. Now return to Alpha and hop a little less than a fistwidth to the southwest where you will encounter double star 5 Serpens and the mighty M5 (Right Ascension: 15 : 18.6 – Declination: +02 : 05).
While Gottfried Kirch and his wife Maria were watching a comet on May 5, 1702, they stumbled across a huge, bright object that they considered a “nebulous star.” Forty-two years later, it was found again by Messier who labeled it as M5 and described it as a round nebula which didn’t contain any stars. But, thank heaven for William Herschel! Some 27 years later he counted up to 200 resolvable stars in this globular cluster and reported “the middle is so compressed that it is impossible to distinguish the components.”
Even in today’s binoculars, M5 shows a grainy texture that begins resolution to even the smallest of telescopes and invites larger ones to an explosion of stellar population. Slightly elliptical in appearance, M5 is believed to be one of the oldest globular clusters with a calculated age of 13 billion years, and it contains 105 known variable stars – as well as a dwarf nova. At a distance of 24,500 light-years and stretching across 165 light-years of space, this magnificent object so dominates its territory that it would gather in any stars straying within 400 light-years of its tidal influence!
Mid-to-larger telescopes will begin such awesome resolution on M5?s many chains and its bright core region that it will be a cluster you will visit again and again over the years. No matter what size binoculars or telescope you use, this 5.6 magnitude class V globular cluster is one of the five brightest of all!
Tuesday, June 12 – As with all astronomical projects, there are sometimes difficult ones needed to complete certain study fields – such as challenging globular clusters. Tonight we’ll take a look at one such cluster needed to complete your list and you’ll find it by using M5 as a guide.
Palomar 5 is by no stretch of the imagination easy. For those using GoTo systems and large telescopes, aiming is easy… But for star hoppers a bit of instruction goes a long way. Starting at M5 drop south for the double 5 Serpens and again south and slightly west for another, fainter double. Don’t confuse it with 6 Serpens to the east. About half a degree west you’ll encounter an 8th magnitude star with 7th magnitude 4 Serpens a half degree south. Continue south another half degree where you will discover a triangle of 9th magnitude stars with a southern one at the apex. This is home to Palomar 5 (RA 15 16 05.30 Dec -00 06 41.0).
Discovered by Walter Baade in 1950, this 11.7 magnitude, Class XII globular is anything but easy. At first it was believed to be a dwarf elliptical and possibly a member of our own Local Group of galaxies due to some resolution. Later studies showed that Palomar 5 was indeed a globular cluster – but one that was being ripped apart by the tidal forces of the Milky Way.
75,000 light-years away from us and 60,000 light-years from the galactic center, Palomar 5?s members are escaping and leaving trails that span 13,000 light-years…a process which may have been happening for several billion years. Although it is of low surface brightness, even telescopes as small as 6? can distinguish just a few individual members northwest of the 9th magnitude marker star – but even telescopes as large as 31? fail to show much more than a faint sheen (under excellent conditions) with a handful of resolvable stars. Even though it may be one of the toughest you’ll ever tackle, be sure to take the time to make a quick sketch of the region to complete your studies. Good luck!
Wednesday, June 13 –Today in 1983, Pioneer 10 becomes the first manmade object to leave the solar system. What wonders would it see? Are there other galaxies out there like our own? Will there be life like ours? While we can’t see through Pioneer’s “eyes,” tonight let’s use our own as we quest for a look in the mirror…
Our object will be Herschel II.76 – also known as NGC 5970. Begin by identifying Beta and Delta Serpens Caput and look for finderscope Chi between them. Less than a degree southwest you will see a similar magnitude double star. Hop about 1/3 degree northwest and you will find your galaxy mark just a fraction southwest of a 7th magnitude star (RA 15 38 30.12 Dec -12 11 10.9).
NGC 5970 is not particularly easy for smaller scopes even near 11th magnitude because of low surface brightness, but it could be a distant twin of our own galaxy, so similar is it to the Milky Way in structure. At 105 million light-years away, it is no great surprise that we see it as faint – for its light left around the time the dinosaurs ruled the Earth. Stretching across 85,000 light-years of space, this grand spiral has been extensively studied in its nucleus region, obscuring dust regions, and stellar population. And – like us – it is also part of its own local group.
While smaller telescopes will make out a slight elongated mist, in mid-to-large aperture NGC 5970 will appear oval shaped with a bright core and evidence of a central bar. While the edges of the galaxy seem well defined, look closely at the narrower ends where material seems more wispy. While averted in this fashion, the nucleus will sometimes take on a stellar appearance – yet lose this property with direct vision. Be sure to mark your Herschel notes on this one!
Thursday, June 14 – As the new hours of the day begin and you wait on dawn, keep watch for the peak of the Ophiuchids meteor shower with the radiant near Scorpius. The fall rate is poor with only 3 per hour, but fast moving bolides are common. This meteor stream will last for 25 days.
Tonight, while we have plenty of dark skies to go around, let’s go south in Libra and have a look at the galaxy pairing NGC 5903 (Right Ascension: 15 : 18.6 – Declination: -24 : 04) and NGC 5898 (Right Ascension: 15 : 18.2 – Declination: -24 : 06). You’ll find them about three degrees northeast of Sigma, and just north of a pair of 7th magnitude stars.
While northernmost NGC 5903 seems to be nothing more than a faint elliptical with a brighter concentration towards the center and an almost identical elliptical – NGC 5898 – to the southwest, you’re probably asking yourself… Why the big deal over two small ellipticals? First off, NGC 5903 is Herschel III.139 and NGC 5898 is Herschel III.138… two more to add to your studies. And second? The Very Large Array has studied this galaxy pair in the spectral lines of neutral hydrogen. The brighter of the pair, NGC 5898, shows evidence of ionized gas which has been collected from outside its galactic realm – while NGC 5903 seems to be running streamers of material towards it. A double-galaxy, double-accretion event!
But there’s more…
Look to the southeast and you’ll double your pleasure and double your fun as you discover two double stars instead of just one! Sometimes we overlook field stars for reasons of study – but don’t do it tonight. Even mid-sized telescopes can easily reveal this twin pair of galaxies sharing “their stuff,” as well as a pair of double stars in the same low power field of view. (Psst… slim and dim MCG 043607 and quasar 1514-241 are also here!) Ain’t it grand?
Friday, June 15 – Tonight, before you hunt down the faint fuzzies and spend the rest of the night drooling on the Milky Way, let’s go globular and hunt up two very nice studies worthy of your time. Starting at Alpha Librae, head five degrees southeast for Tau and yet another degree southeast for the splendid field of NGC 5897 (RA 15 17 24.40 Dec -21 00 36.4).
This class XI globular might appear very faint to binoculars, but it definitely makes up for it in size and beauty of field. It was first viewed by William Herschel on April 25, 1784 and logged as H VI.8 – but with a less than perfect notation of position. When he reviewed it again on March 10, 1785 he logged it correctly and relabeled it as H VI.19. At a distance of a little more than 40,000 light-years away, this 8.5 magnitude globular will show some details to the larger telescope, but remain unresolved to smaller ones. As a halo globular cluster, NGC 5897 certainly shows signs of being disrupted and has a number of blue stragglers as well as four newly discovered variables of the RR Lyrae type.
Now let’s return to Alpha Librae and head about a fistwidth south across the border into Hydra and two degrees east of star 57 for NGC 5694 – also in an attractive field (RA 14 39 36.52 Dec -26 32 18.0).
Also discovered by Herschel, and cataloged as H II.196, this class VII cluster is far too faint for binoculars at magnitude 10, and barely within reach of smaller scopes. As one of the most remote globular clusters in our galaxy, few telescopes can hope to resolve this more than 113,000 light-year distant ball of stars whose brightest is magnitude 16.5 – and it also possesses no variables. Traveling at 190 kilometers per second, metal-poor NGC 5694 will not have the same fate as NGC 5897… For this is a globular cluster that is not being pulled apart by our galaxy – but escaping it!
Saturday, June 16 – No matter if you stayed up late chasing deep sky, or got up early, right now is the time to catch the peak of the June Lyrids meteor shower. Although it’s not the most outstanding of displays, no Moon will make it one of the best prospects of the year for those wishing to log their meteor observations. Look for the radiant near bright Vega – you may see up to 15 faint blue meteors per hour from this branch of the May Lyrid meteor stream.
Today in 1963, Valentina Tereshkova, aboard the Soviet Vostok 6, became the first woman ever to go into space. Her solo flight is still unique. Twenty years later, on the 18th, Sally Ride became the first American woman in orbit, aboard the Space Shuttle.
For observers of all skill levels and equipment, it’s simply time to stop and have a look at a seasonal favorite which is now nearly overhead – M13 (Right Ascension: 16 : 41.7 – Declination: +36 : 28). You’ll find this massive globular cluster quite easy to locate on the western side of the Hercules “keystone” about 1/3 the way between the northern and southern stars – Eta and Zeta.
At a little brighter than magnitude 6, this 25,100 light-year distant globular cluster can be seen unaided from a dark sky location. First noted by Edmond Halley in 1714, the “Great Hercules Cluster” was cataloged by Messier on June 1, 1764. Filled with hundreds of thousands of stars, yet only one young blue star, M13 could be as much as 14 billion years old.
Thirty-three years ago, the Great Hercules Cluster was chosen by the Arecibo Observatory as the target for the first radio message delivered into space, yet it will be a message that won’t be received for over 25 centuries. Look at it with wonder tonight… For the light that left as you are viewing it tonight did so at a time when the Earth was coming out of the Ice Age. Our early ancestors were living in caves and learning to use rudimentary tools. How evolved would our civilization be if we ever received an answer to our call?!
Sunday, June 17 – Celestial scenery alert! If you’re up before the Sun rises, be sure to check out the eastern skyline for the very close apparition of the Moon and Jupiter. The two will only be separated by about a half a degree. What a great way to wake up!
As the sky darkens tonight, let’s discover the wonderful world of low power. Start your journey by re-locating magnificent M13 and move about 3 degrees northwest. What you will find is a splendid loose open cluster of stars known as Dolidze/Dzimselejsvili (DoDz) 5 – and it looks much like a miniature of the constellation of Hercules. Just slightly more than 4 degrees to its east and just about a degree south of Eta Hercules is DoDz 6, which contains a perfect diamond pattern and an asterism of brighter stars which resembles the constellation of Sagitta.
Now we’re going to move across the constellation of Hercules towards Lyra. East of the “keystone” you will see a tight configuration of three stars – Omicron, Nu and Xi. About the same distance that separates these stars to the northeast you will find DoDz 9. Using minimal magnification, you’ll see a pretty open cluster of around two dozen mixed magnitude stars that are quite attractive. Now look again at the “keystone” and identify Lambda and Delta to its south. About midway between them and slightly to the southeast you will discover the stellar field of DoDz 8. The last is easy – all you need to do is know the beautiful red/green double, Ras Algethi (Alpha). Move about 1 degree to the northwest to discover the star-studded open cluster DoDz 7. These great open clusters are very much off the beaten path and will add a new dimension to your large binocular or low power telescoping experiences.
Until next week, keep your eyes on the skies!