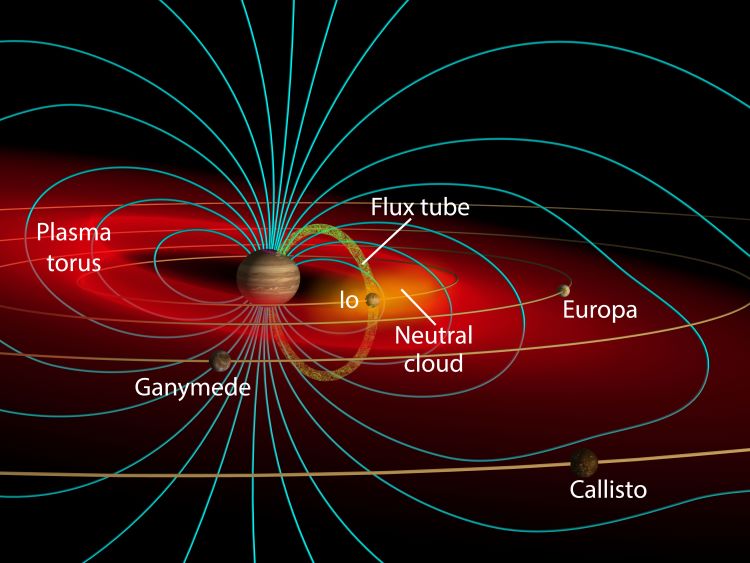
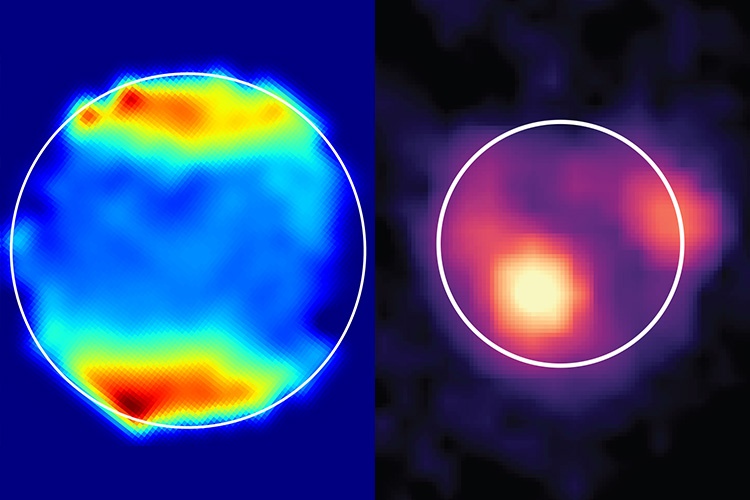
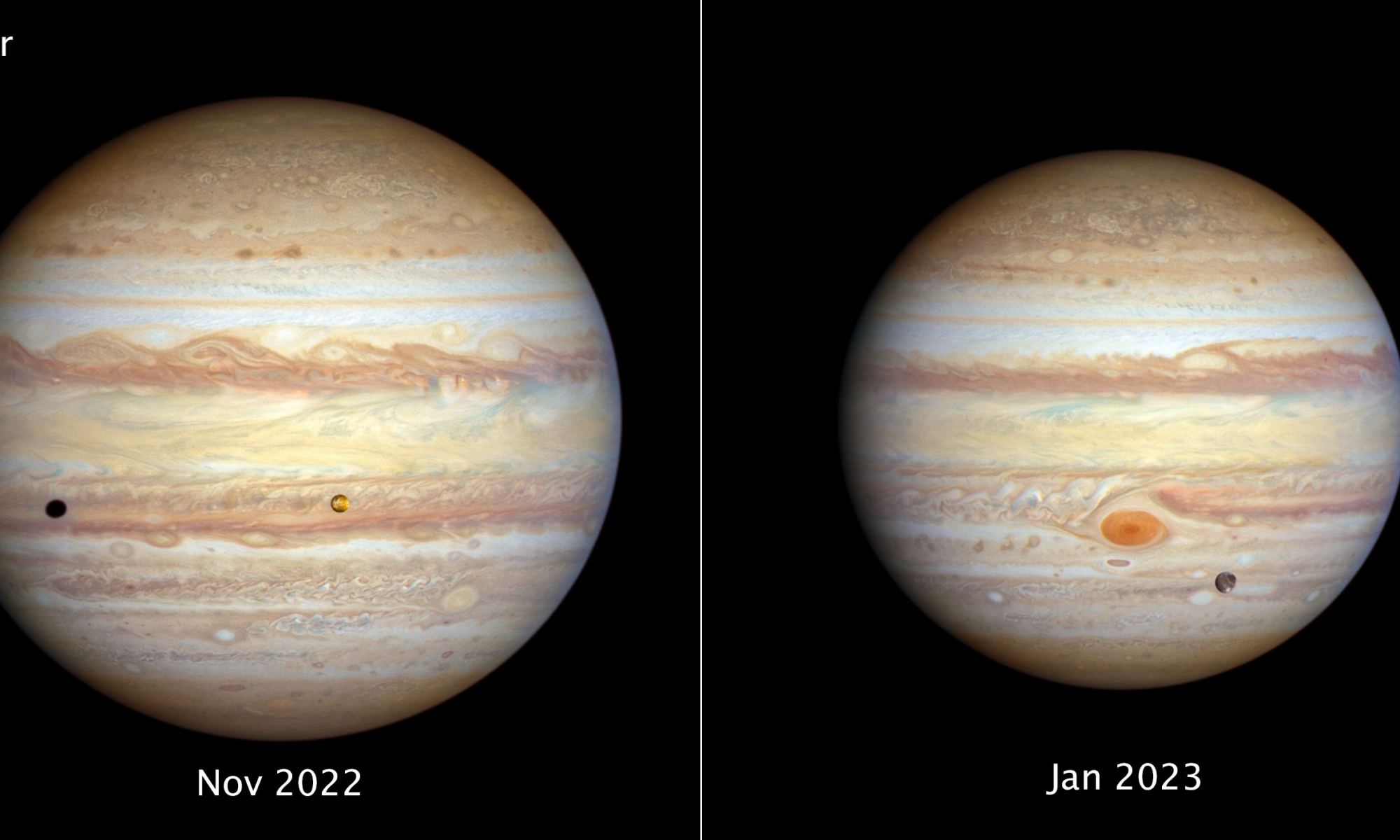
The two most powerful space telescopes ever built, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and Hubble Space Telescope, are about to gather data about the most volcanically body in the entire solar system, Jupiter’s first Galilean Moon, Io. This data will be used in combination with upcoming flybys of Io by NASA’s Juno spacecraft, which is currently surveying the Jupiter system and is slated to conduct these flybys later this year and early 2024. The purpose of examining this small, volcanic moon with these two powerful telescopes and one orbiting spacecraft is for scientists to gain a better understanding of how Io’s escaping atmosphere interacts with Jupiter’s surrounding magnetic and plasma environment.
Continue reading “Exploring Io’s Volcanic Activity via Hubble and Webb Telescopes”Exploring Io’s Volcanic Activity via Hubble and Webb Telescopes