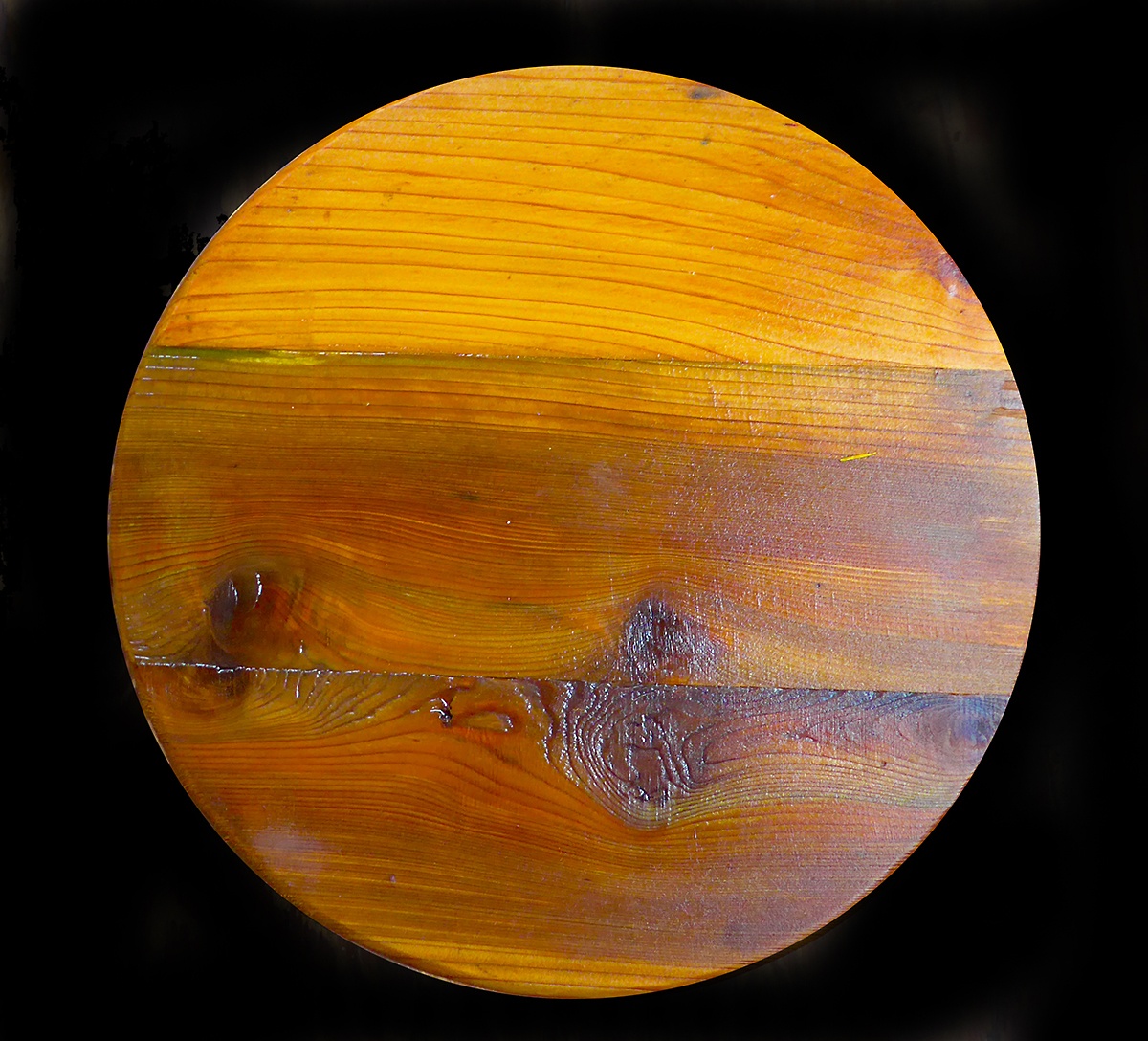
My Dad’s a pretty good woodworker, and recently completed a wooden table that looks surprisingly like Jupiter, Great Red Spot, atmospheric bands and all.
Continue reading “My Dad Made a Table That Looks Surprisingly Like Jupiter”Are the Clouds of Jupiter Haunted?
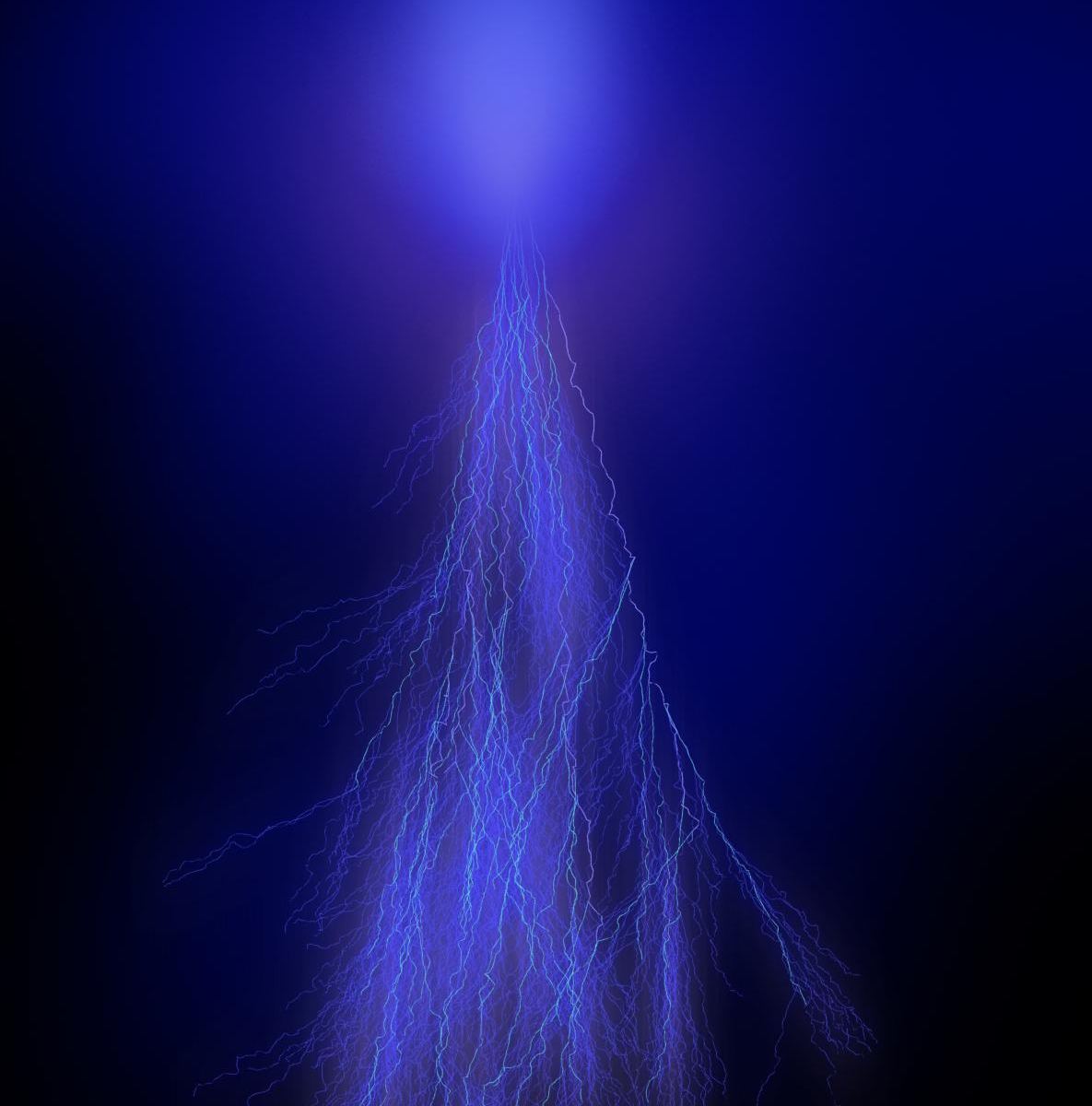

Are spirits amongst the clouds of Jupiter? The answer might be yes! A recent publication in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets has identified what appear to be “Sprites” in the Jovian Atmosphere.
In European Folklore, ‘Sprites’ (derived from Latin ‘spiritus’ or spirit) were elemental and ethereal beings visiting Earth. The term is fitting for “lightning sprites”, a natural meteorological phenomenon with many eye-witness testimonies but not captured on camera until 1989. Created by lightning discharges in Earth’s atmosphere, sprites are part of larger family of phenomena called TLE’s, or “Transient Luminous Events”, that last for only fractions of a second.
Continue reading “Are the Clouds of Jupiter Haunted?”The Newest Picture of Jupiter and Europa Captured by Hubble
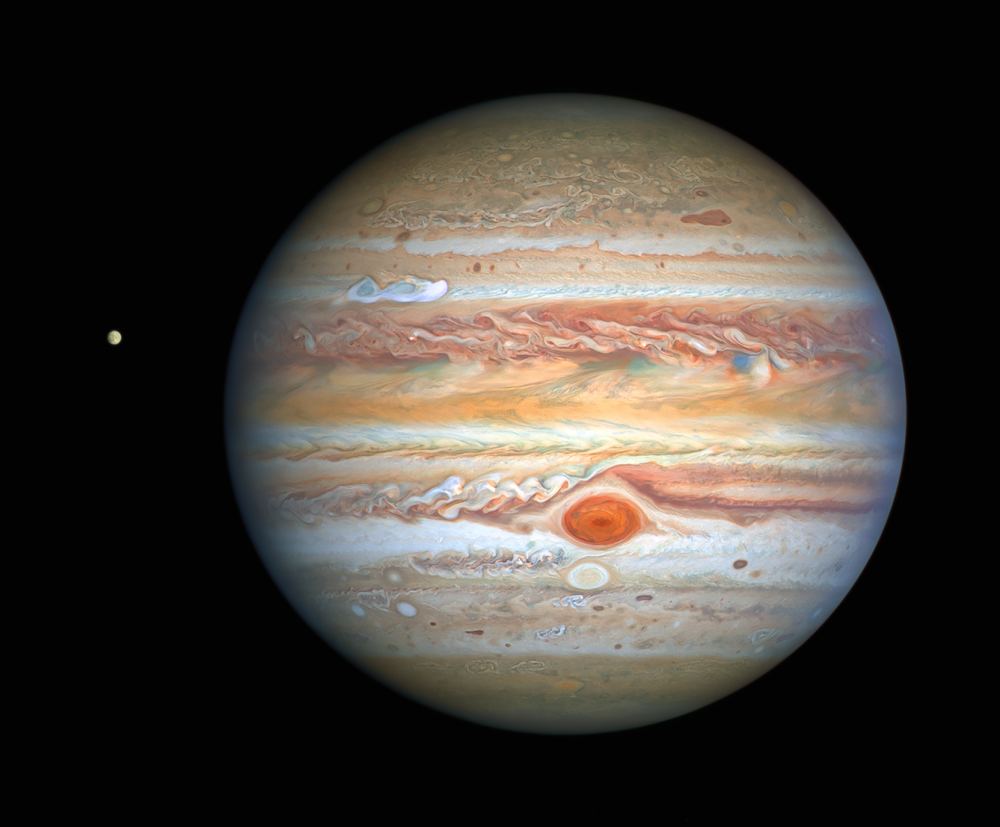
The venerable Hubble Space Telescope has given us another gorgeous picture of Jupiter and its moon Europa. The incredibly sharp image was captured on August 25th, and shows some of the stunning detail in Jupiter’s stormy atmosphere. Hidden in all that stormy activity is something new: a bright white storm plume travelling at about 560 km/h (350 mp/h).
Continue reading “The Newest Picture of Jupiter and Europa Captured by Hubble”See a 360 Degree Juno-Eye View of Jupiter During an Io Eclipse
Yesterday, we posted some incredible photos from the Juno Probe’s 29th flyby of Jupiter. Juno is in a highly elliptical orbit. It buzzes the planet at an altitude of 4,200km and then sweeps out to 8.1 million. Completing this circuit every 53 days, Juno only spends 2 hours within close proximity to Jupiter reducing the probe’s exposure to harmful radiation of high energy particles accelerated by Jupiter’s magnetic field.

Here’s Jupiter from Juno’s Latest Flyby
Jupiter.
Most massive planet in the solar system – twice that of all the other planets combined. This giant world formed from the same cloud of dust and gas that became our Sun and the rest of the planets. But Jupiter was the first-born of our planetary family. As the first planet, Jupiter’s massive gravitational field likely shaped the rest of the entire solar system. Jupiter could’ve played a role in where all the planets aligned in their orbits around the Sun…or didn’t as the asteroid belt is a vast region which could’ve been occupied by another planet were it not for Jupiter’s gravity. Gas giants like Jupiter can also hurl entire planets out of their solar systems, or themselves spiral into their stars. Saturn’s formation several million years later probably spared Jupiter this fate. Jupiter may also act as a “comet catcher.” Comets and asteroids which could otherwise fall toward the inner solar system and strike the rocky worlds like Earth are captured by Jupiter’s gravitational field instead and ultimately plunge into Jupiter’s clouds. But at other times in Earth’s history, Jupiter may have had the opposite effect, hurling asteroids in our direction – typically a bad thing but may have also resulted in water-rich rocks coming to Earth that led to the blue planet we know of today.

Jupiter Probably Has 600 Small, Irregular Moons
The better our technologies get, the better we get at finding objects in space. That’s certainly true of Jupiter and its moons. Prior to Galileo, nobody knew the other planets had moons. Then in 1609/10, as he made improvements to his telescope, he aimed it at the gas giant and eventually found four moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Now those four natural satellites also bear his name: the Galilean moons.
Over the centuries since then, and especially in our digital age, astronomical tools and methods kept improving. In particular, wide-field CCD (Charge Coupled Devices) have led to an explosion of astronomical discoveries. In recent years, the confirmed number of Jovian moons has risen to 79. Now, a new study says that there may be 600 small irregular moons orbiting Jupiter.
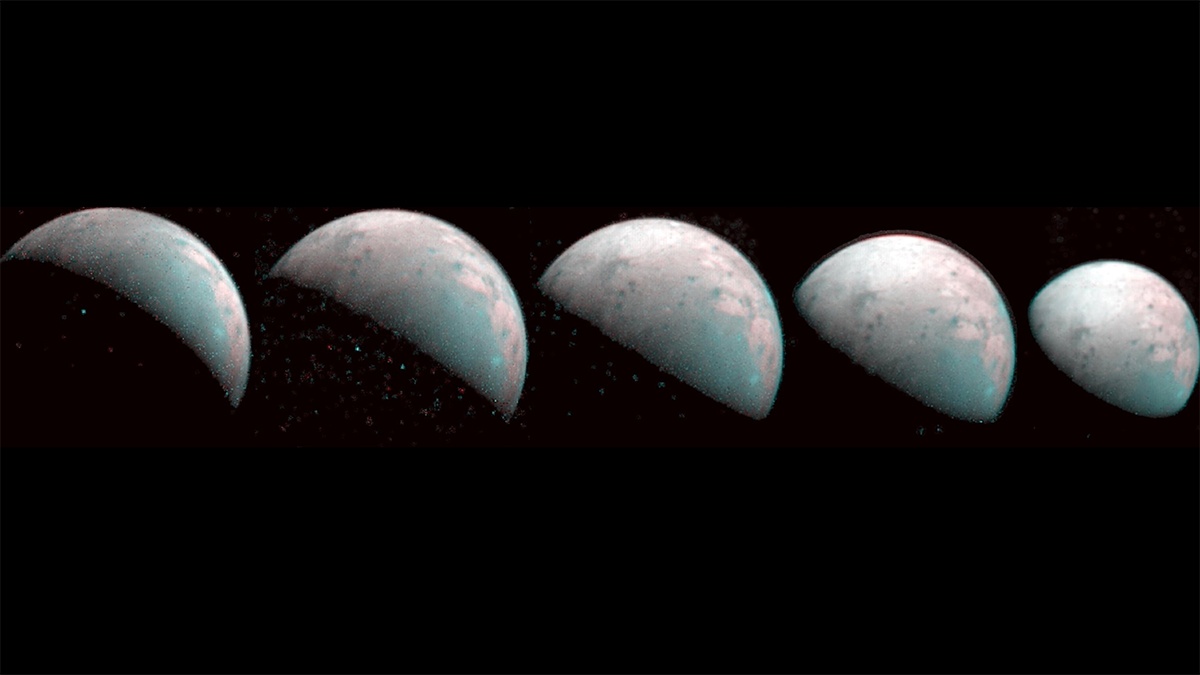
Continue reading “Jupiter Probably Has 600 Small, Irregular Moons”Juno Captures Pictures of Ganymede for the First Time
On July 5, 2016, NASA’s Juno spacecraft arrived around Jupiter, becoming the second mission in history to study the gas giant from orbit – the last being the Galileo spacecraft, which orbited Jupiter from 1995 to 2003. Since then, the spacecraft has gathered data on Jupiter’s atmosphere, composition, gravity field, and magnetic field in the hopes of learning more about how the planet formed and evolved.
In addition, the spacecraft has gathered some of the most breathtaking images ever taken of Jupiter and its system of moons. In fact, as the spacecraft was making another approach towards Jupiter on December 26th, 2019, it managed to capture the first infrared images of the moon Ganymede’s northern polar region. These images will inform future missions to this satellite, which could host life beneath its icy mantle.
Continue reading “Juno Captures Pictures of Ganymede for the First Time”Amateur Astronomers Find a Brand New Storm on Jupiter

There’s a new storm brewing on Jupiter. The most famous storm on Jupiter is the Great Red Spot, which has been active since at least the time of Galileo. Most of Jupiter’s storms don’t last for hundreds of years. They grow and fade just as they do on Earth. This latest storm was discovered by amateur astronomer Clyde Foster.
Continue reading “Amateur Astronomers Find a Brand New Storm on Jupiter”Spacecraft and Ground Telescopes Work Together to Give us Stunning New Pictures of Jupiter
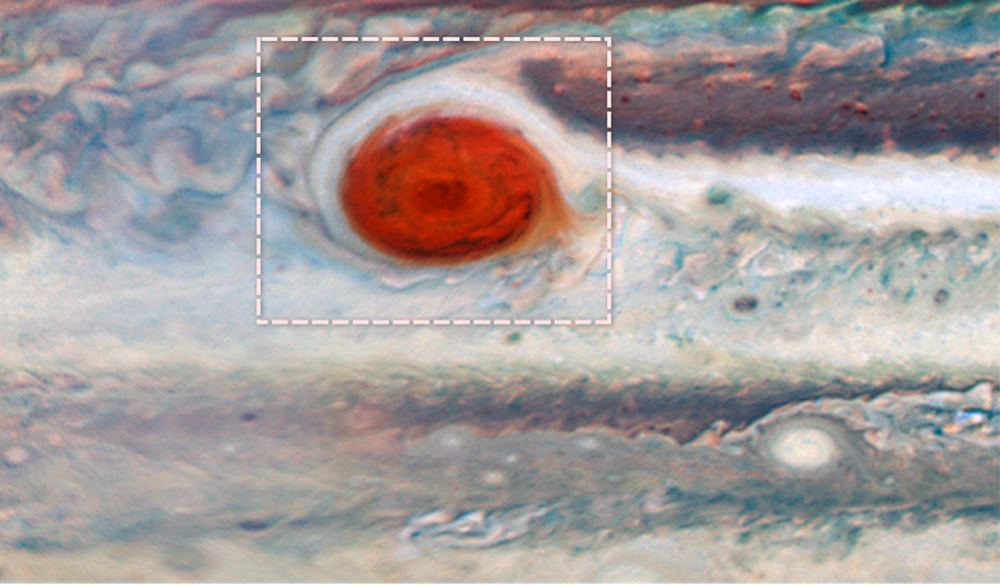
It’s difficult to imagine the magnitude of storms on Jupiter. The gas giant’s most visible atmospheric feature, the Great Red Spot, may be getting smaller, but one hundred years ago, it was about 40,000 km (25,000 miles) in diameter, or three times Earth’s diameter.
Jupiter’s atmosphere also features thunderheads that are five times taller than Earth’s: a whopping 64 km (40 miles) from bottom to top. Its atmosphere is not entirely understood, though NASA’s Juno spacecraft is advancing our understanding. The planet may contain strange things like a layer of liquid metallic hydrogen.
Now a group of scientists are combining the power of the Hubble Space Telescope, the Gemini Observatory and the Juno spacecraft to probe Jupiter’s atmosphere, and the awe-inspiring storms that spawn there.
Continue reading “Spacecraft and Ground Telescopes Work Together to Give us Stunning New Pictures of Jupiter”Artwork Inspired by Jupiter’s Great Red Spot

Artist Mik Petter has created a vibrant new piece of art based on JunoCam images of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS). The piece makes use of fractals, which are recursive mathematical creations; increasingly complex patterns that are similar to each other, yet never exactly the same.
Continue reading “Artwork Inspired by Jupiter’s Great Red Spot”