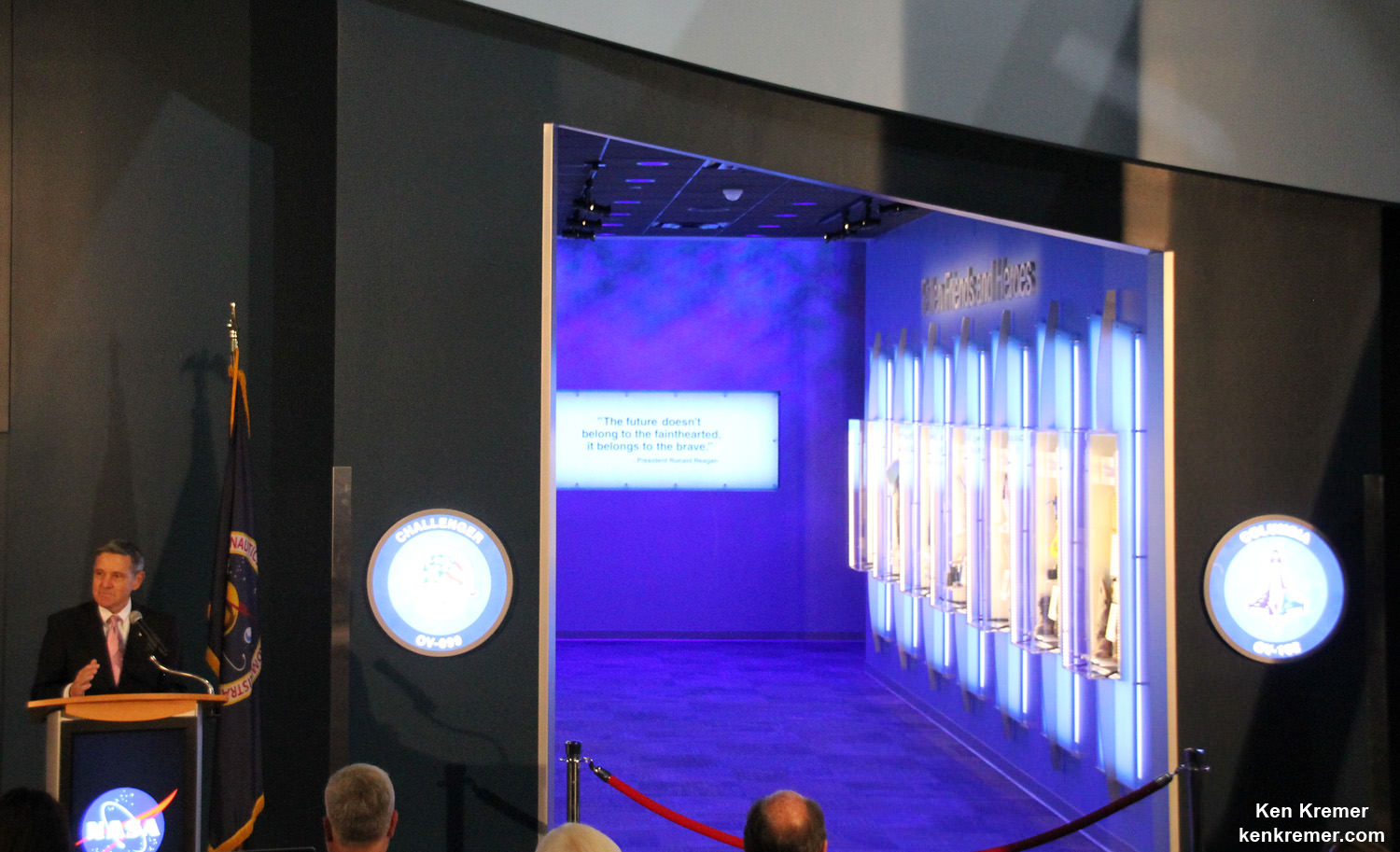
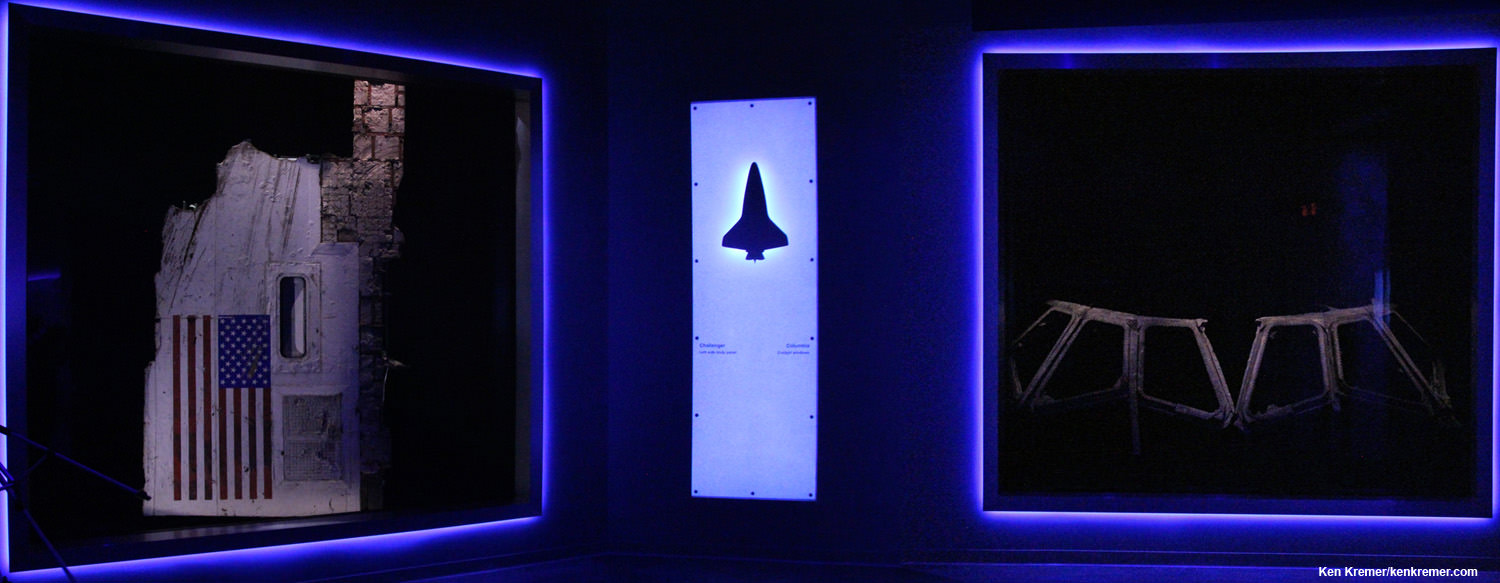
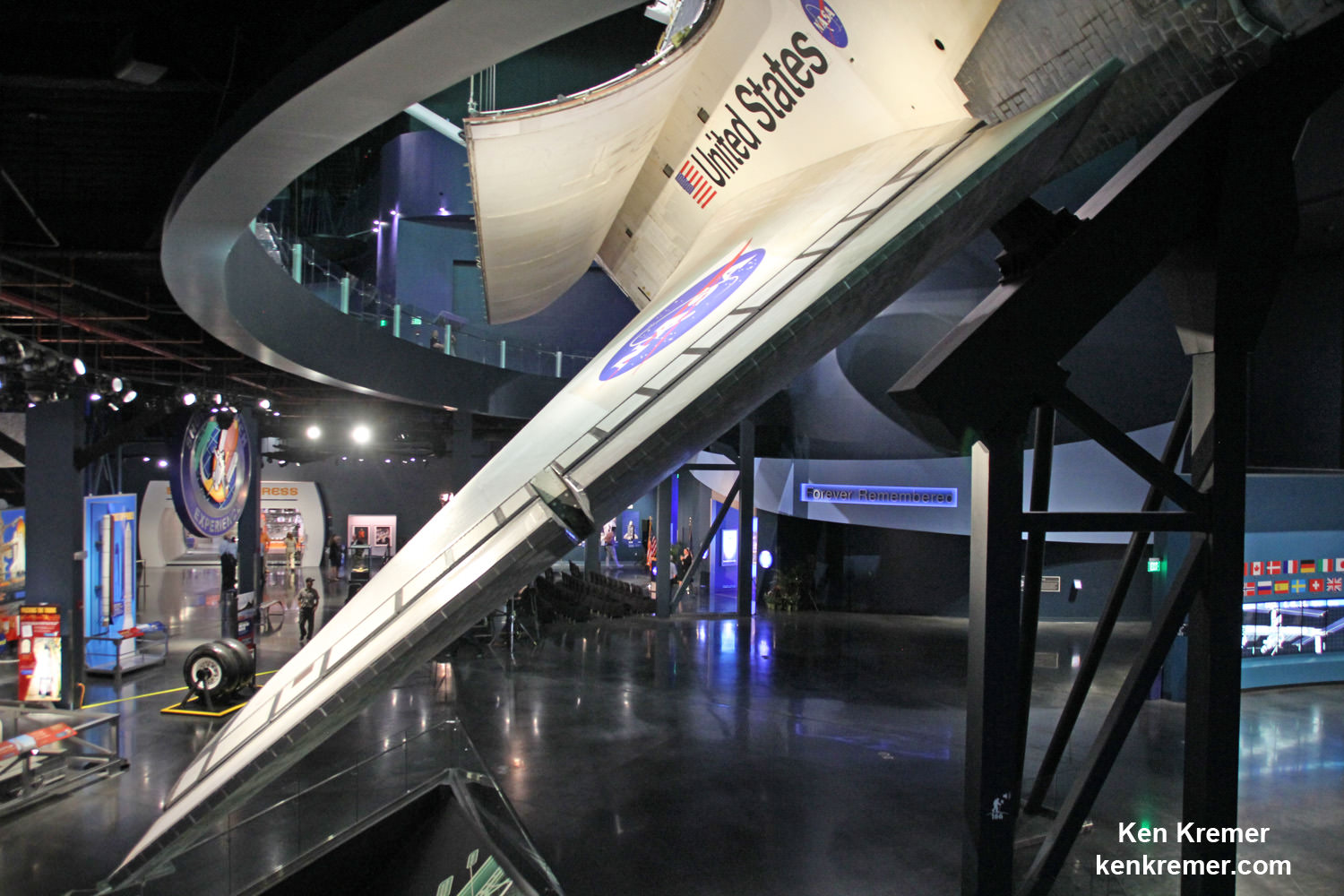
An iconic section of the fuselage recovered from space shuttle Challenger with the American flag (left) and the flight deck windows recovered from space shuttle Columbia (right) are part of a new, permanent memorial, “Forever Remembered,” that opened on June 27, 2015 in the Space Shuttle Atlantis exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida – featuring shuttle hardware and personal crew items never before on display for viewing by the public. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
Story/photos updated[/caption]
NASA’s two lost Shuttle crews from the searing Challenger and Columbia accidents are now memorialized in the newly opened, permanent and highly emotional “Forever Remembered” tribute display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida.
The “Forever Remembered” memorial tribute was officially opened by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden and Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, both veteran shuttle astronauts, at a very special and moving small private NASA ceremony attended by families of the 14 fallen crew members and invited members of the media including Universe Today on June 27, 2015.
“I believe that it’s important to share this story with everyone, and not just push it aside, or try to hide it,” Cabana said at the ceremony, as tears welled up in everyone present.
The shuttle tribute is located on the ground floor of the Space Shuttle Atlantis pavilion at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and features shuttle orbiter hardware recovered from both the Challenger STS-51L and Columbia STS-107 accidents, as well as personal crew items from all 14 courageous astronauts who lost their lives – items never before on display for viewing by the public.
The 2000 square foot exhibit features an iconic section of the fuselage recovered from space shuttle Challenger emblazoned with the American flag and the flight deck windows recovered from space shuttle Columbia, that are part of the permanent “Forever Remembered” memorial that opened on June 27, 2015 – see photo above.
It also holds the largest collection of personal items of both flight crews in individual displays about the 14 crew members in a hallway that leads to a plaque with a quote from U.S. President Ronald Reagan.
“The future doesn’t belong to the fainthearted, it belongs to the brave,” said President Ronald Reagan in remarks to the nation in mourning shortly after the explosion of Space Shuttle Challenger on Jan. 28, 1986.

The “Forever Remembered” display was conceived in private by a very small circle spearheaded by Cabana and unknown by outsiders until the day it was formally opened. It completes the display inside the Atlantis pavilion, which commemorates NASA’s three decade long Space Shuttle Program that flew 135 missions from 1981 to 2011 with the reusable delta-winged vehicles that “captivated a generation.”
It is intended to be an emotional experience and “designed to honor the crews, pay tribute to the spacecraft and emphasize the importance of learning from the past” and the tragic consequences. This will enable safer flights in the future and fortify the spirit of never giving up on the exploration of space.
“The tragedies galvanized the agency to learn from these painful events, not only to safely return the shuttle fleet to flight, but to help assure the safety of future explorers,” NASA said in a statement.
Several dozen family members attended the tearful, heartfelt opening ceremony of “Forever Remembered” with very emotional remarks from Cabana and Bolden.
“These crews and these vehicles are part of who we are as an agency, and a nation. They tell the story of our never ending quest to explore, and our undying spirit to never give up,” Cabana stated at the ceremony.
Columbia and Challenger were the nation’s first two orbiters to be built. Columbia launched on the maiden space shuttle flight on April 12, 1981 on what is revered by many as the “boldest test flight in history” with NASA astronauts John Young and Bob Crippen.
“When I look into those windows, I see John Young and Bob Crippen preparing to launch on the boldest test flight in history, the first flight of America’s space shuttle, Columbia,” Cabana added.
“I see a much younger Bob Cabana launching to space on his first command, and I see Rick and Willie and the rest of the 107 crew smiling and experiencing the wonders of space on the final flight of Columbia.”
The idea to create a permanent memorial originated with a team led by Bob Cabana, and approved by Charlie Bolden only after every one of the astronauts families were in complete and unqualified agreement that this tribute display was the right thing to do in memory of their loved ones, tragically lost during the in flight accidents in 1986 and 2003.
“The crews of Challenger and Columbia are forever a part of a story that is ongoing,” Bolden said at the ceremony.
“It is the story of humankind’s evolving journey into space, the unknown, and the outer-reaches of knowledge, discovery and possibility. It is a story of hope.”
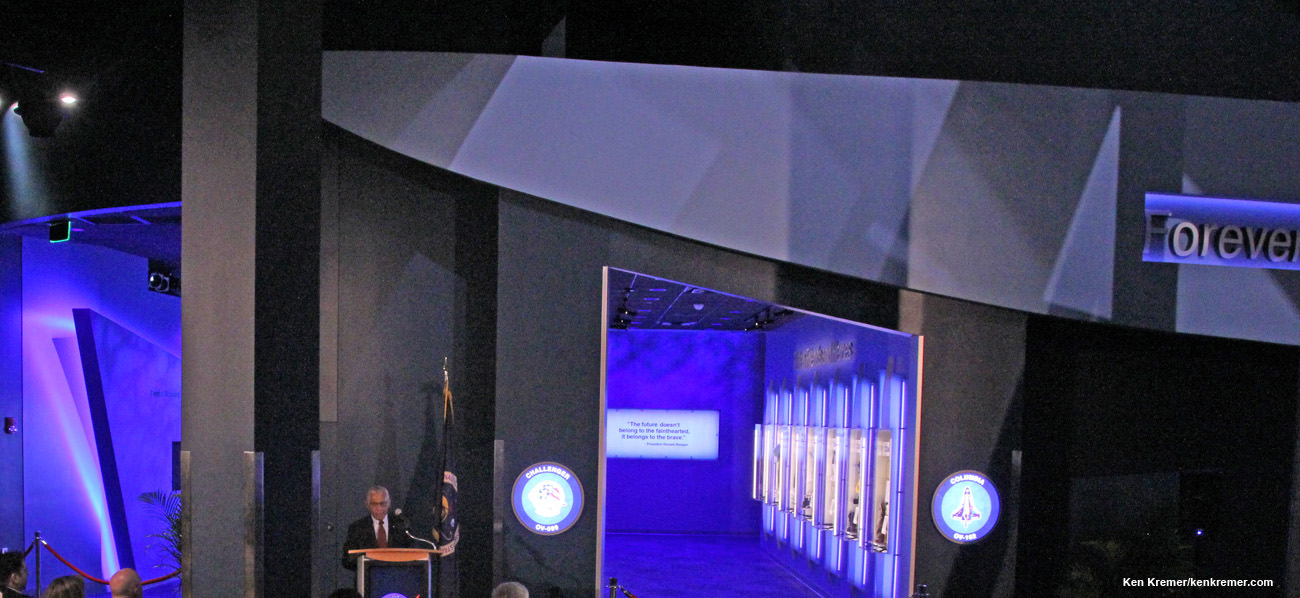

The wives of the two shuttle commanders, shared their thoughts on the new exhibit:
“It’s a beautiful remembrance of all the shuttles, with the marvelous display of Atlantis. Nothing compares to it in the world,” said June Scobee Rodgers, whose husband, Dick Scobee, commanded Challenger on STS-51L, in a statement.
“But Challenger and Columbia are not forgotten, and they’re well represented.”
“I knew it would be very emotional to see, but honestly, I didn’t expect to be so impacted by it. I just can’t stop thinking about it. As you walk in, you know you’re in a special place,” Evelyn Husband Thompson said of the memorial. Her husband, Rick, commanded Columbia on STS-107.

Here is a NASA description of both the Columbia and Challenger accidents and crews:
“Temperatures at Kennedy Space Center were just a few degrees above freezing on the morning of Jan. 28, 1986, as Challenger lifted off on its 10th mission, STS-51L. One minute and 13 seconds into the flight, a booster failure caused an explosion that destroyed the vehicle, resulting in the loss of the crew of seven astronauts: Commander Francis Scobee, Pilot Michael J. Smith, Mission Specialists Judith Resnik, Ellison Onizuka and Ronald McNair, and Payload Specialists Gregory Jarvis and Christa McAuliffe, a New Hampshire schoolteacher.”
“Seventeen years later, on Jan. 16, 2003, NASA’s flagship orbiter Columbia thundered into orbit on STS-107, a 16-day science mission. On board were Commander Rick Husband, Pilot Willie McCool, Payload Commander Michael Anderson, Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, David Brown and Laurel Clark, and Payload Specialist Ilan Ramon, Israel’s first astronaut. On Feb. 1, 2003, the orbiter broke apart in the skies above east Texas as it re-entered Earth’s atmosphere on the way to a planned landing at Kennedy. Seven more lives were lost.”

Today the fallen astronauts legacy of human spaceflight lives on at NASA with the International Space Station, the development of Commercial Crew manned capsules for low Earth orbit, and the development of the Orion deep space crew exploration vehicle and SLS rocket for NASA’s ambitious plans to send ‘Human to Mars’ in the 2030s.
Read more about both fallen shuttle crews and the Apollo 1 crew who perished in a launch pad accident in January 1967 in my tribute story posted here during NASA’s solemn week of remembrance in January.
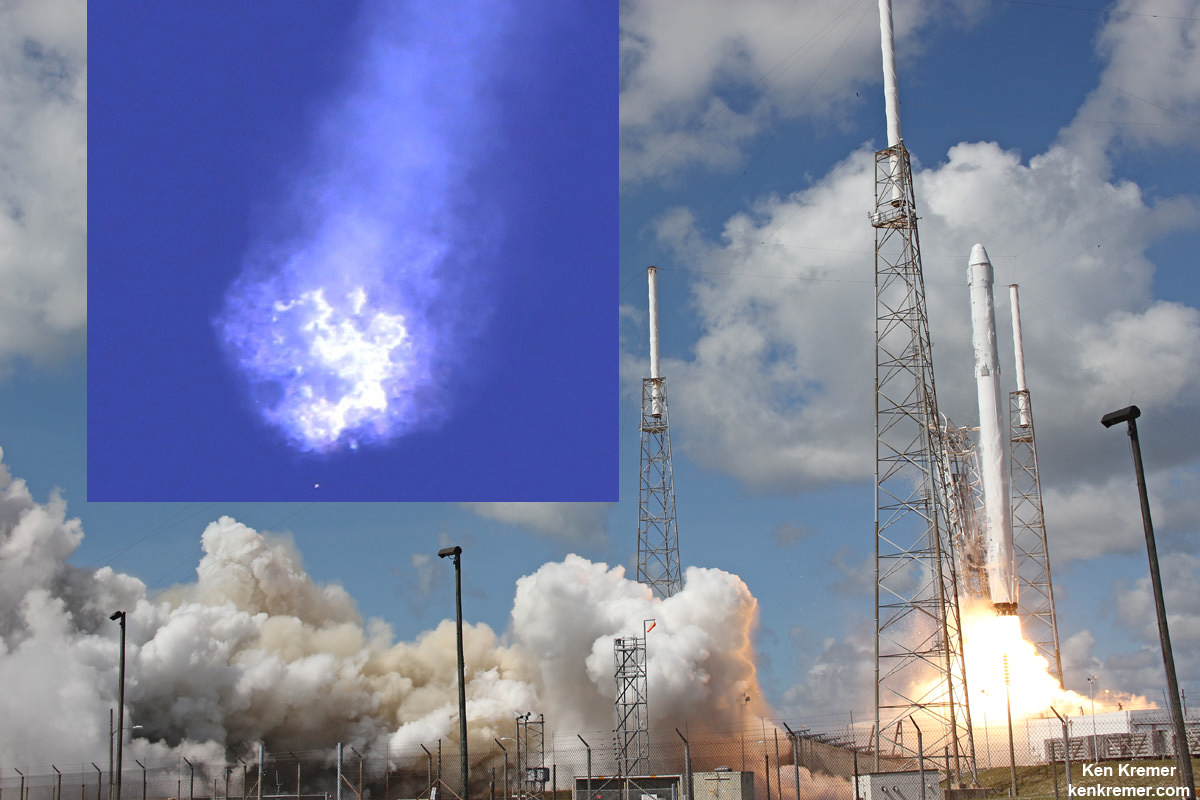
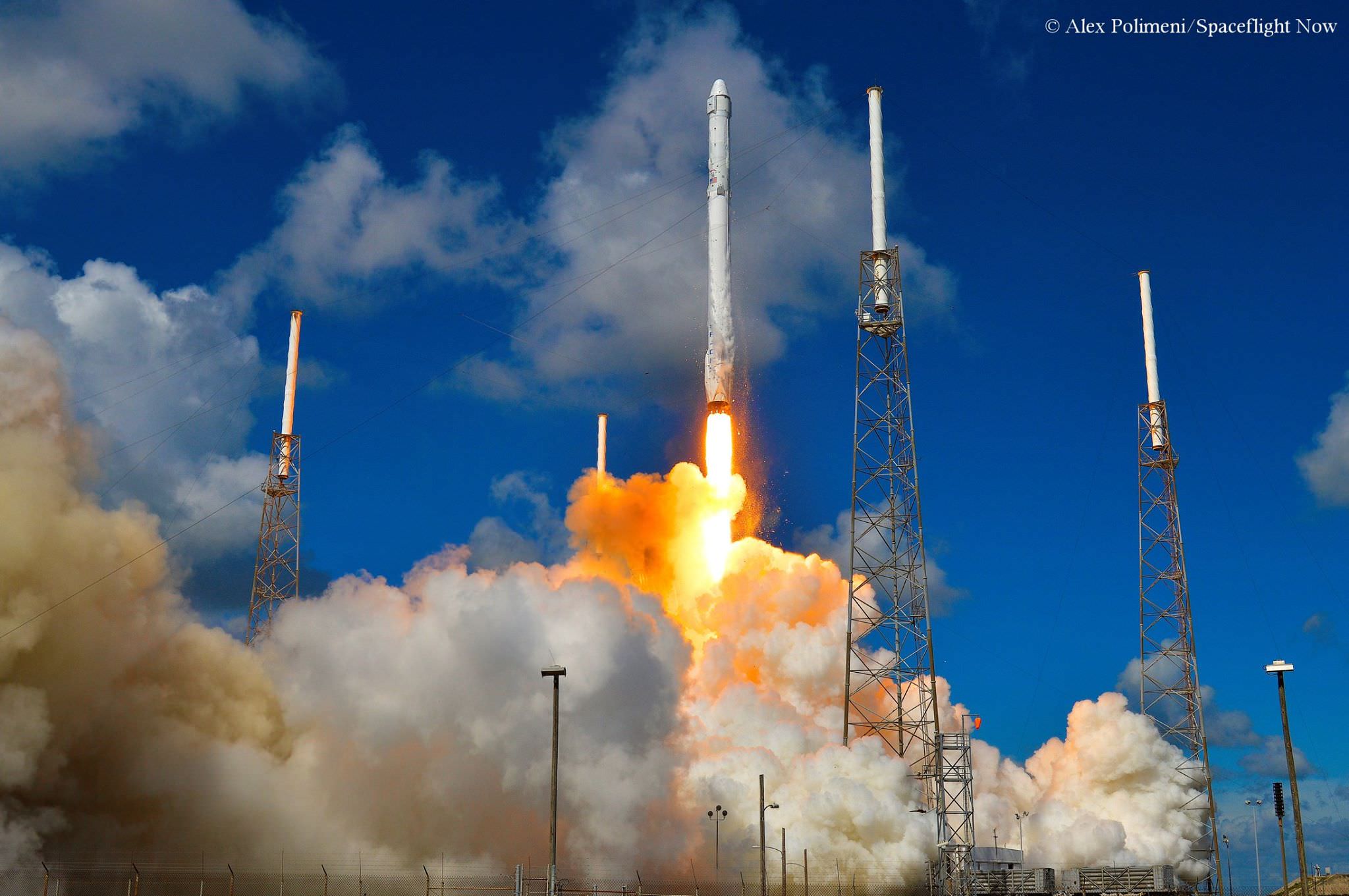
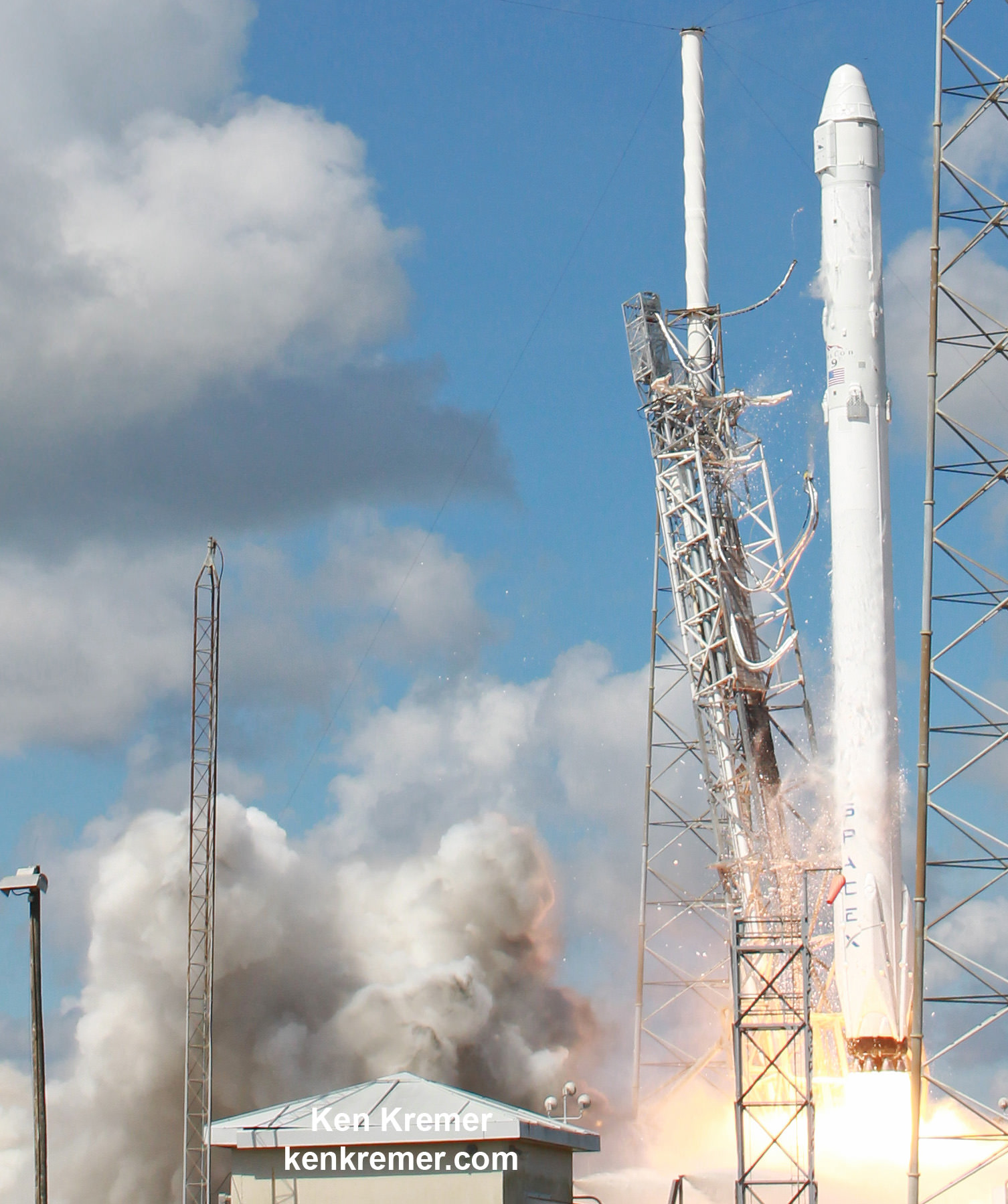
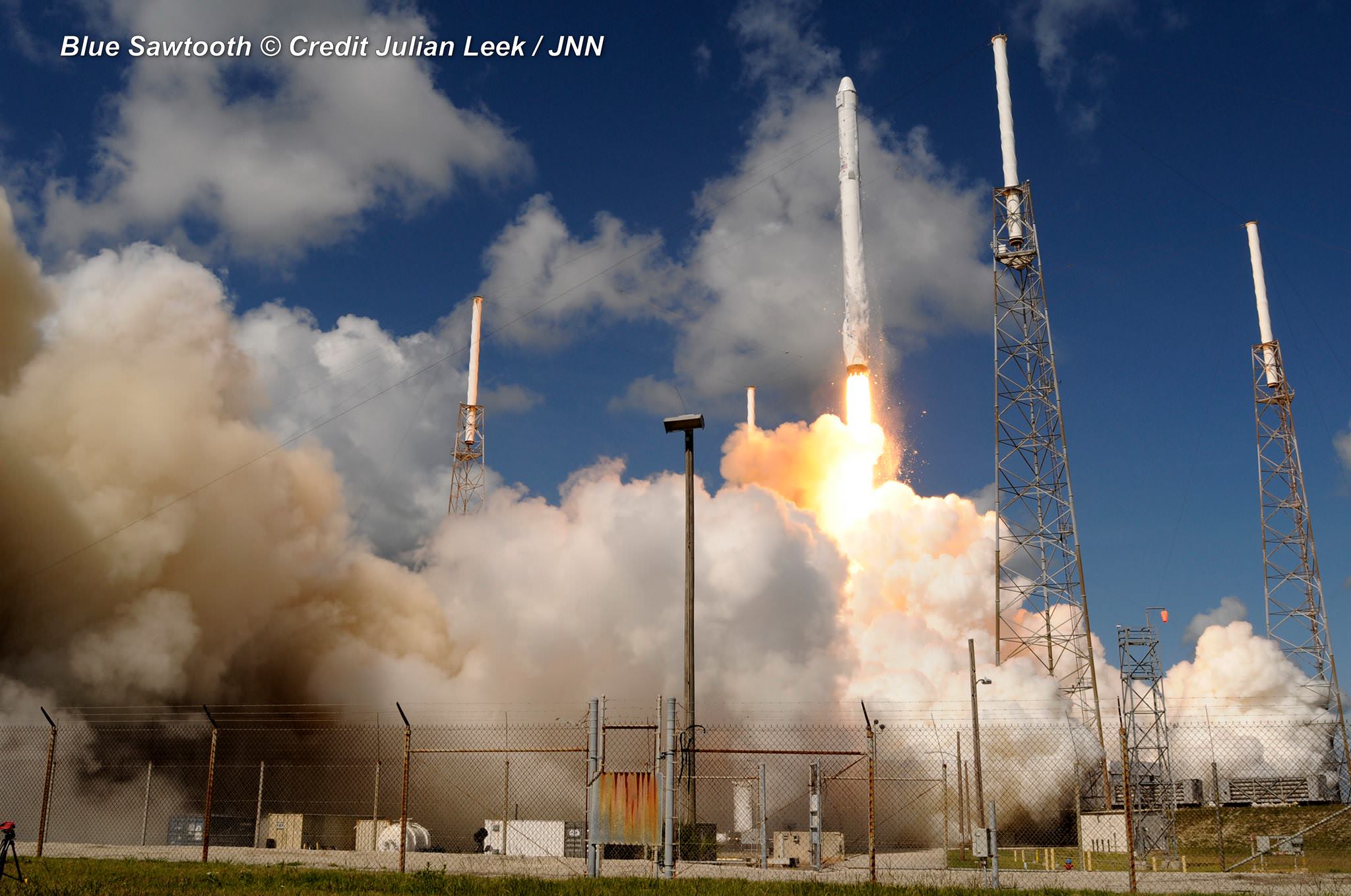
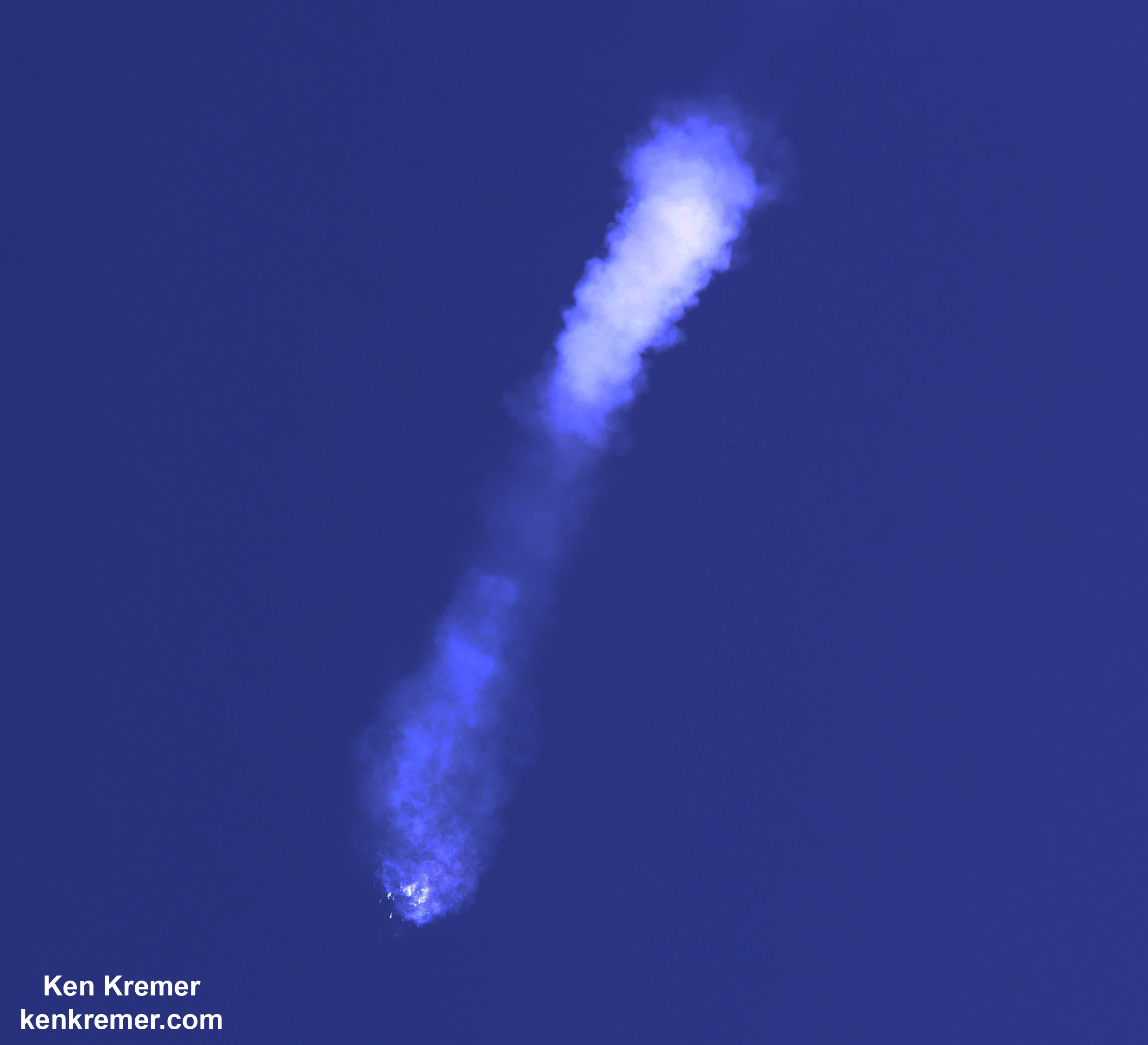
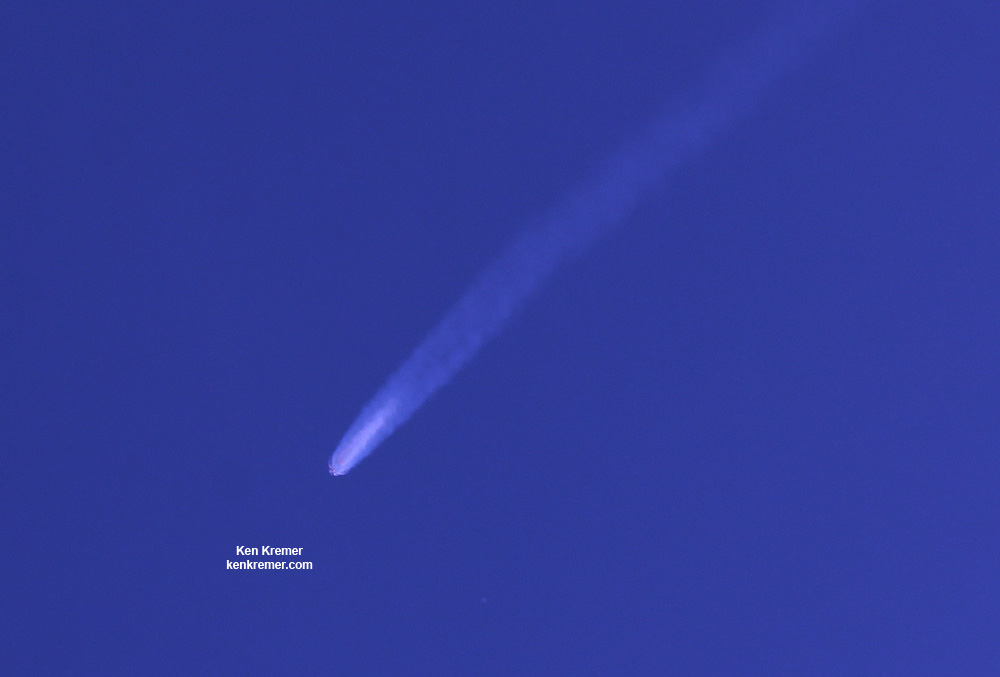
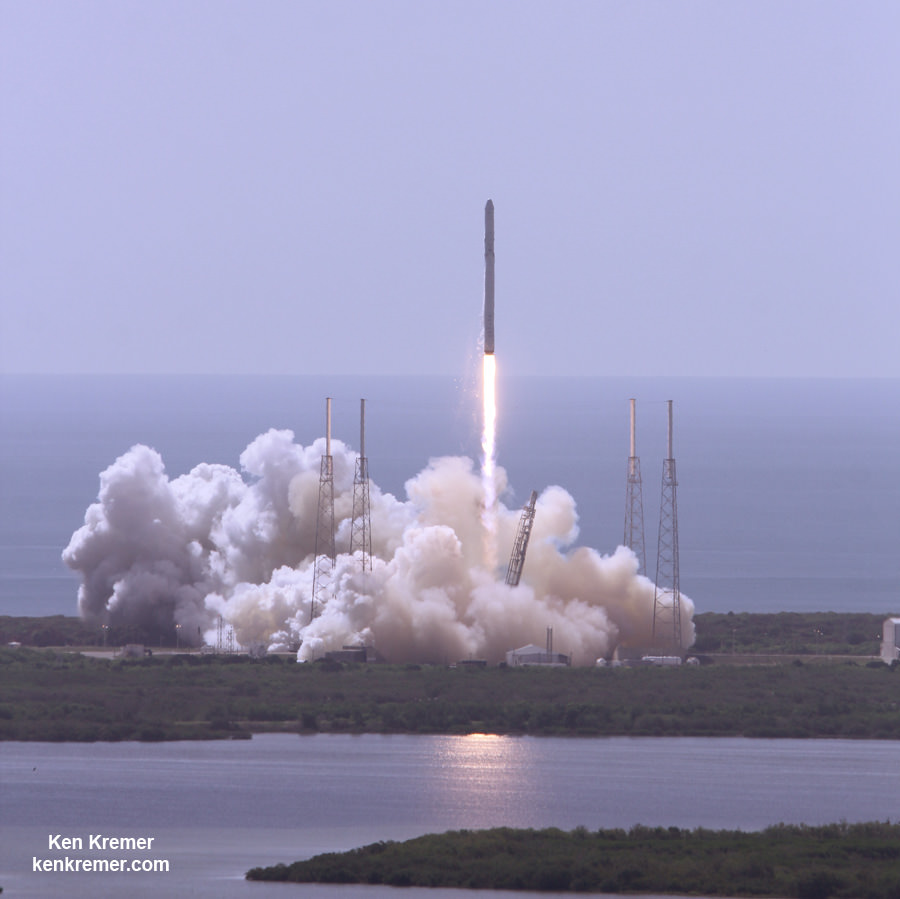
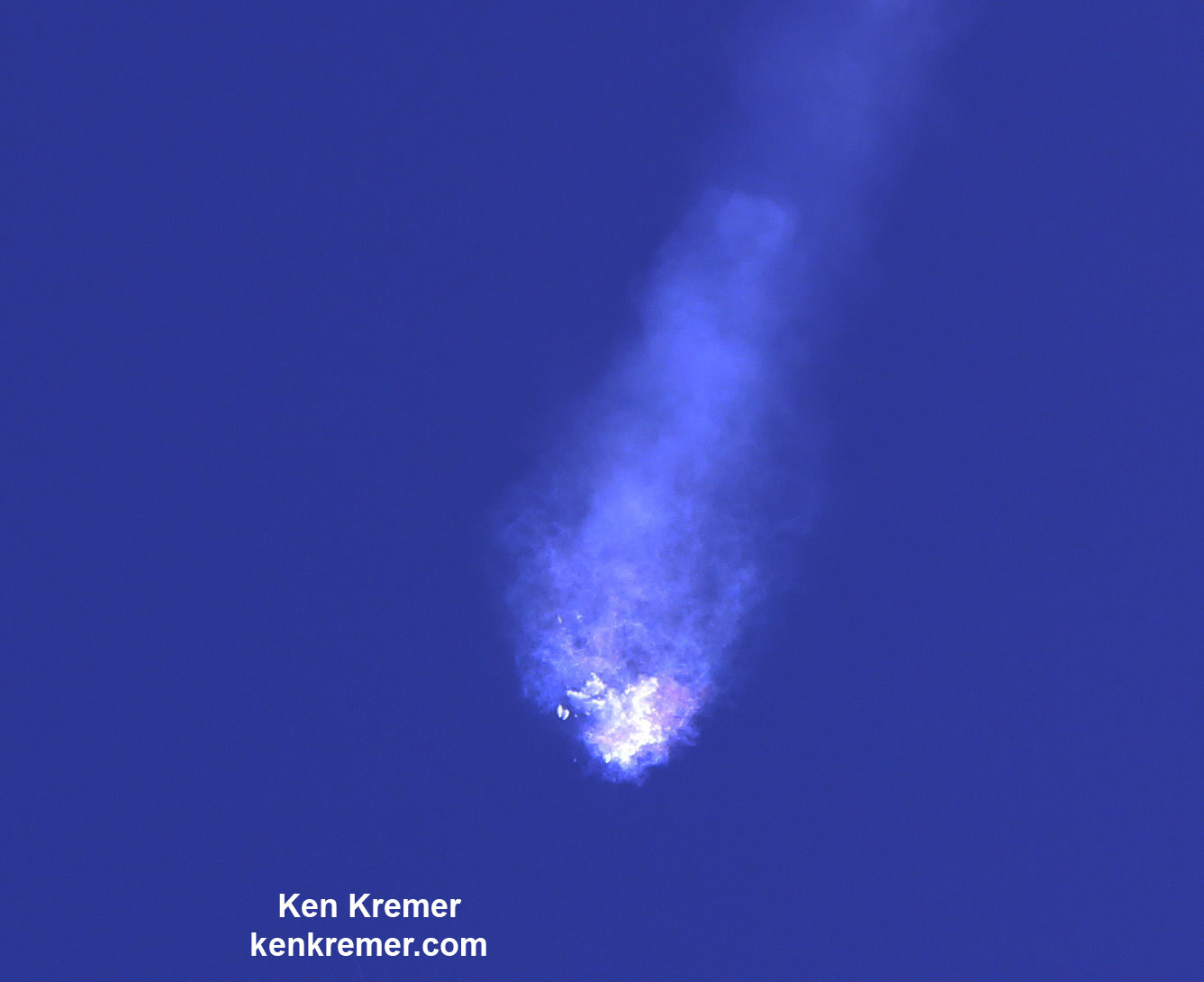
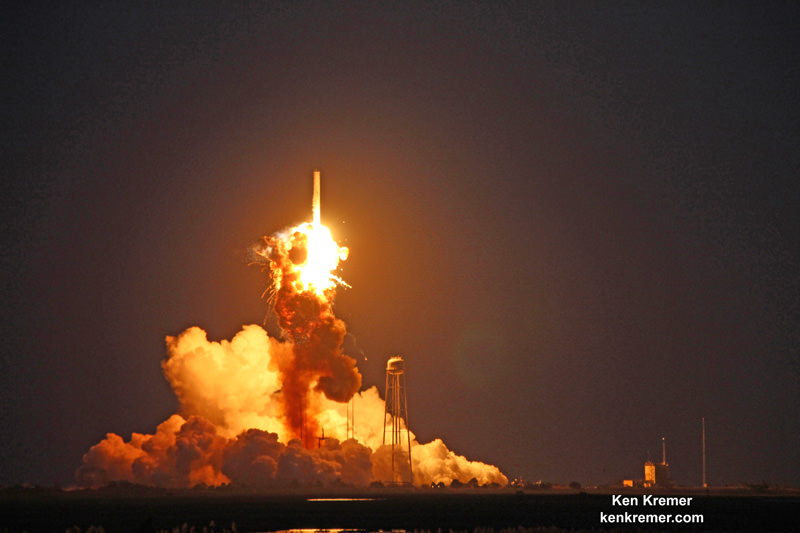
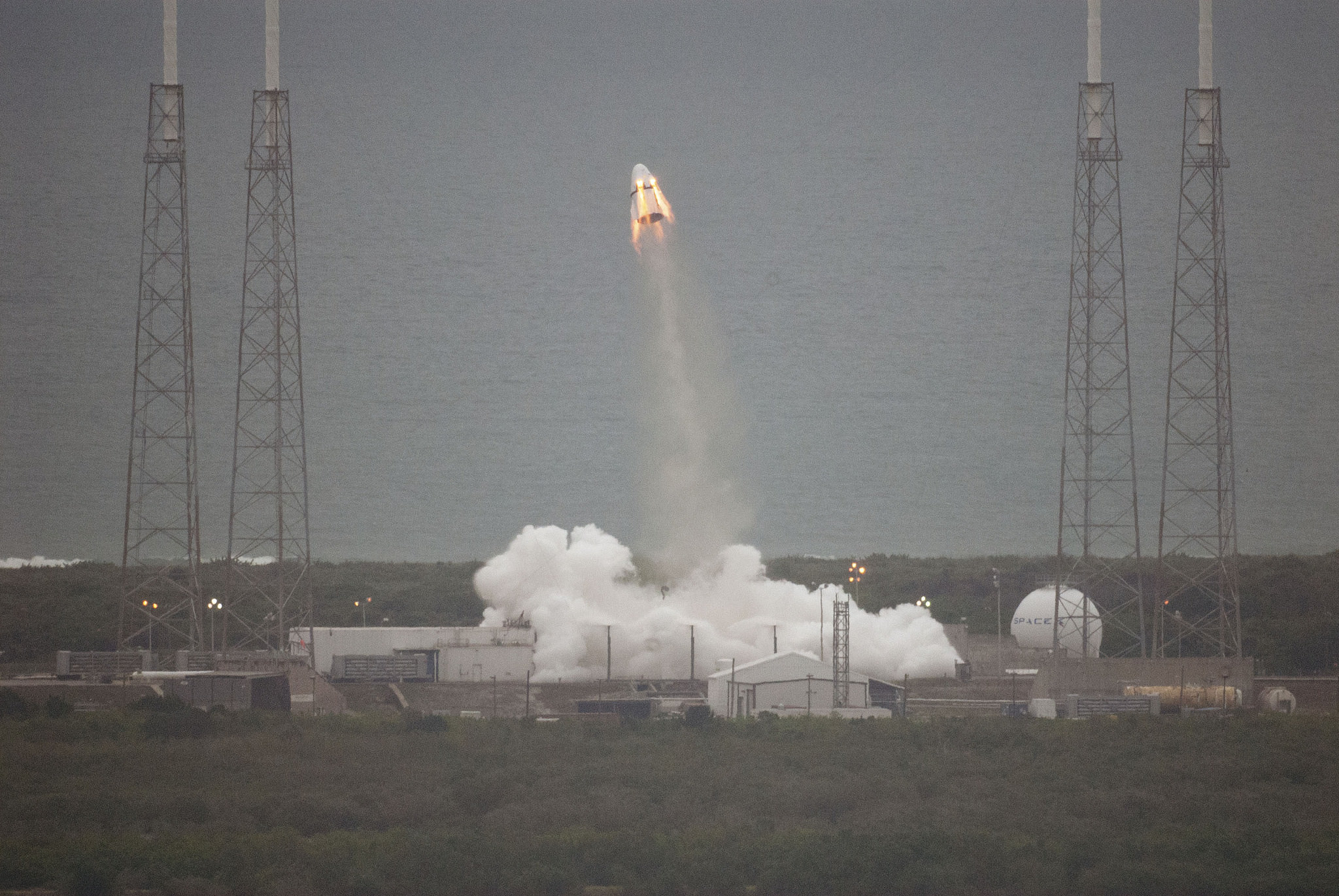
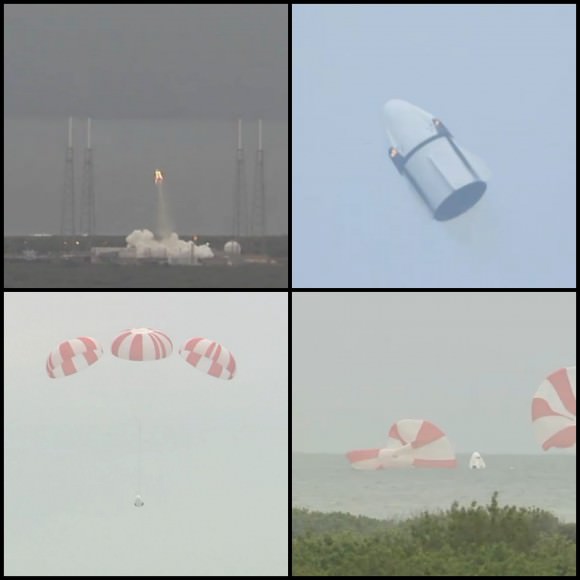
The explosion of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket some two minutes after launch on June 28, 2015 is a reminder that space flight is never easy or routine. Starting sometime in 2017, astronauts will launch to the ISS in a crew Dragon atop the Falcon 9. It will be equipped with a launch abort system that the shuttles never had, in case of a launch emergency.
I urge everyone to visit this hallowed “Forever Remembered” memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and remember those who made the ultimate sacrifice to benefit all of us in the quest for new knowledge of the boundless expanse of space leading to new discoveries we cannot fathom today.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.