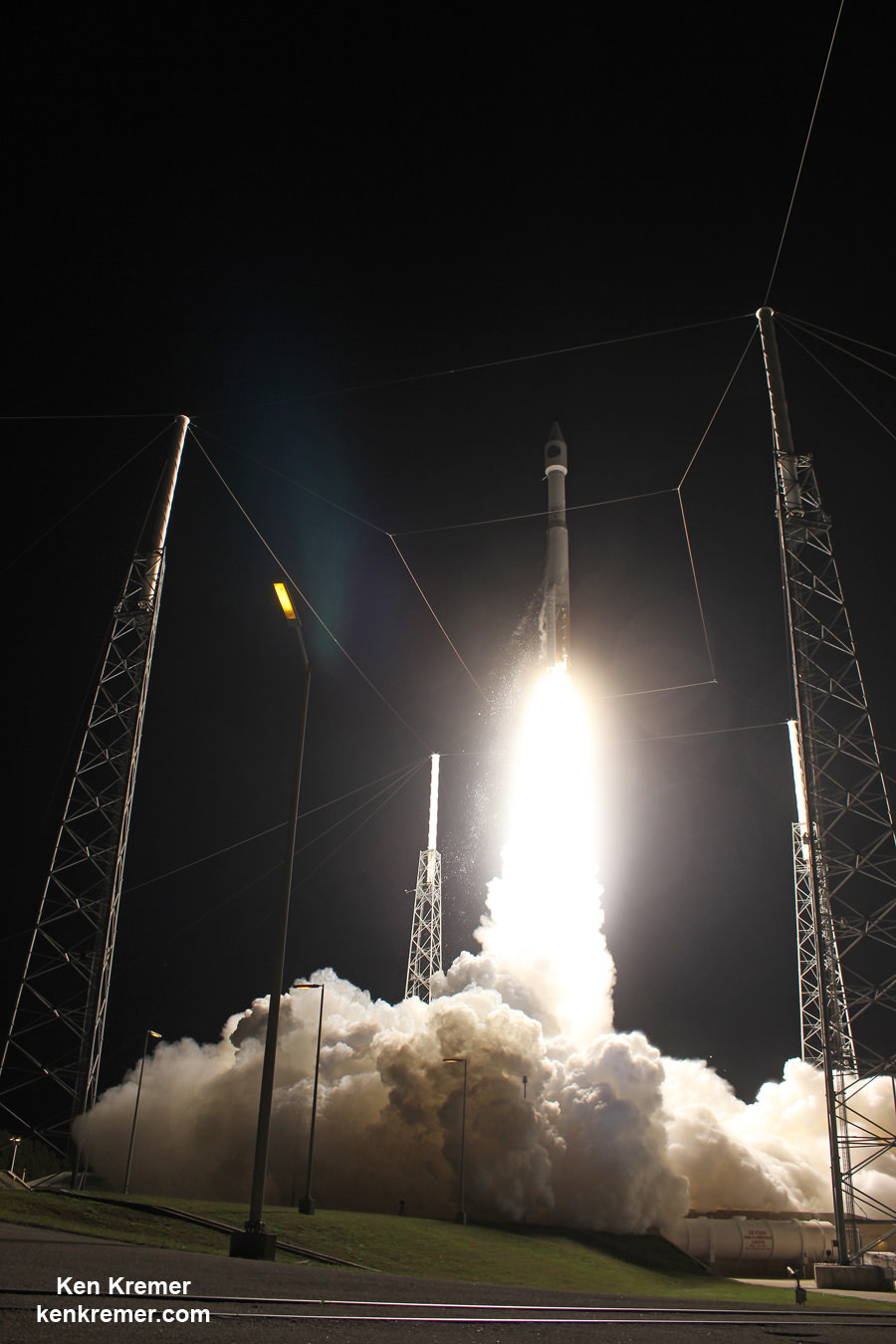
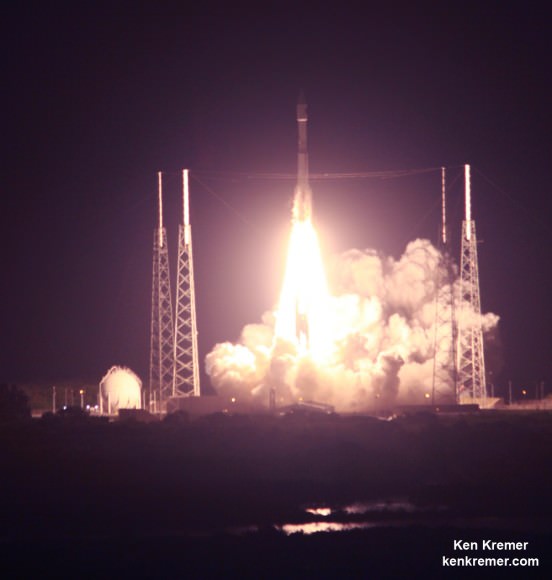
Video caption: High resolution and color corrected SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage landing video of CRS-6 first stage landing following launch on April 14, 2015. Credit: SpaceX
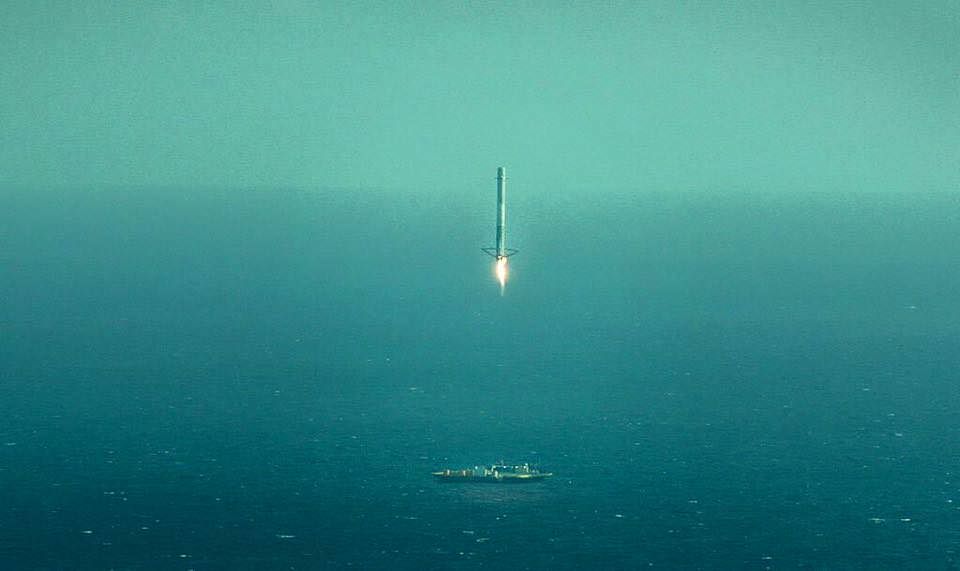
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – A new high resolution video from SpaceX shows just how close the landing attempt of their Falcon 9 first stage on an ocean floating barge came to succeeding following the rockets launch on Tuesday afternoon, April 14, from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on a resupply run for NASA to the International Space Station (ISS).
Newly added video shows video taken from the barge:
The SpaceX Falcon 9 carrying the Dragon cargo vessel blasted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on April 14, 2015 at 4:10 p.m. EDT (2010:41 GMT) on the CRS-6 mission bound for the space station.
The flawless Falcon 9 liftoff came a day late following a postponement from Monday, April 13, due to threatening clouds rolling towards the launch pad in the final minutes of the countdown. See an up close video view of the launch from a pad camera, below.
Video caption: SpaceX CRS-6 Falcon 9 Launch to the International Space Station on April 14, 2015. Credit: Alex Polimeni
The dramatic hi res landing video was released by SpaceX CEO Elon Musk. It clearly reveals the deployment of the four landing legs at the base of the booster as planned in the final moments of the landing attempt, aimed at recovering the first stage booster.
By about three minutes after launch, the spent fourteen story tall first stage had separated from the second stage and reached an altitude of some 125 kilometers (77 miles) following a northeastwards trajectory along the U.S. east coast.
SpaceX engineers relit a first stage Merlin 1D engine some 200 miles distant from the Cape Canaveral launch pad to start the process of a precision guided descent towards the barge, known as the ‘autonomous spaceport drone ship’ (ASDS).
It had been pre-positioned offshore of the Carolina coast in the Atlantic Ocean.
SpaceX initially released a lower resolution view taken from a chase plane captured dramatic footage of the landing.
“Looks like Falcon landed fine, but excess lateral velocity caused it to tip over post landing,” tweeted SpaceX CEO Elon Musk.
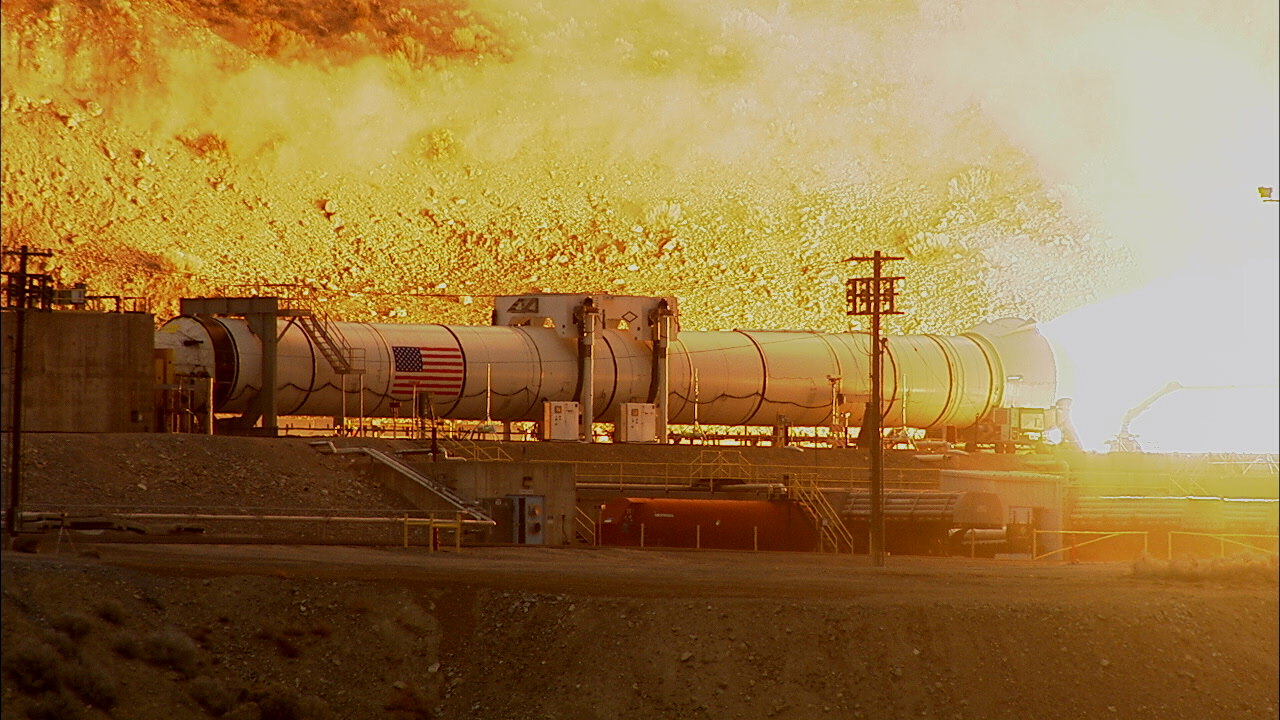
The Falcon successfully reached the tiny ocean floating barge in the Atlantic Ocean, but tilted over somewhat over in the final moments of the approach, and tipped over after landing and exploded in a fireball.
“Either not enough thrust to stabilize or a leg was damaged. Data review needed.”
“Looks like the issue was stiction in the biprop throttle valve, resulting in control system phase lag,” Musk elaborated. “Should be easy to fix.”
The next landing attempt is set for the SpaceX CRS-7 launch, currently slated for mid- June, said Hans Koenigsmann, SpaceX Director of Mission assurance, at a media briefing at KSC.

Overall CRS-6 is the sixth SpaceX commercial resupply services mission and the seventh trip by a Dragon spacecraft to the station since 2012.
The 20 story tall Falcon 9 hurled Dragon on a three day chase of the ISS where it will rendezvous with the orbiting outpost on Friday, April 17. Astronauts will grapple and berth Dragon at the station using the robotic arm.

Read Ken’s earlier onsite coverage of the CRS-6 launch from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Ken Kremer
………….
Learn more about SpaceX, Mars rovers, Orion, Antares, MMS, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Apr 18/19: “Curiosity explores Mars” and “NASA Human Spaceflight programs” – NEAF (NorthEast Astronomy Forum), 9 AM to 5 PM, Suffern, NY, Rockland Community College and Rockland Astronomy Club