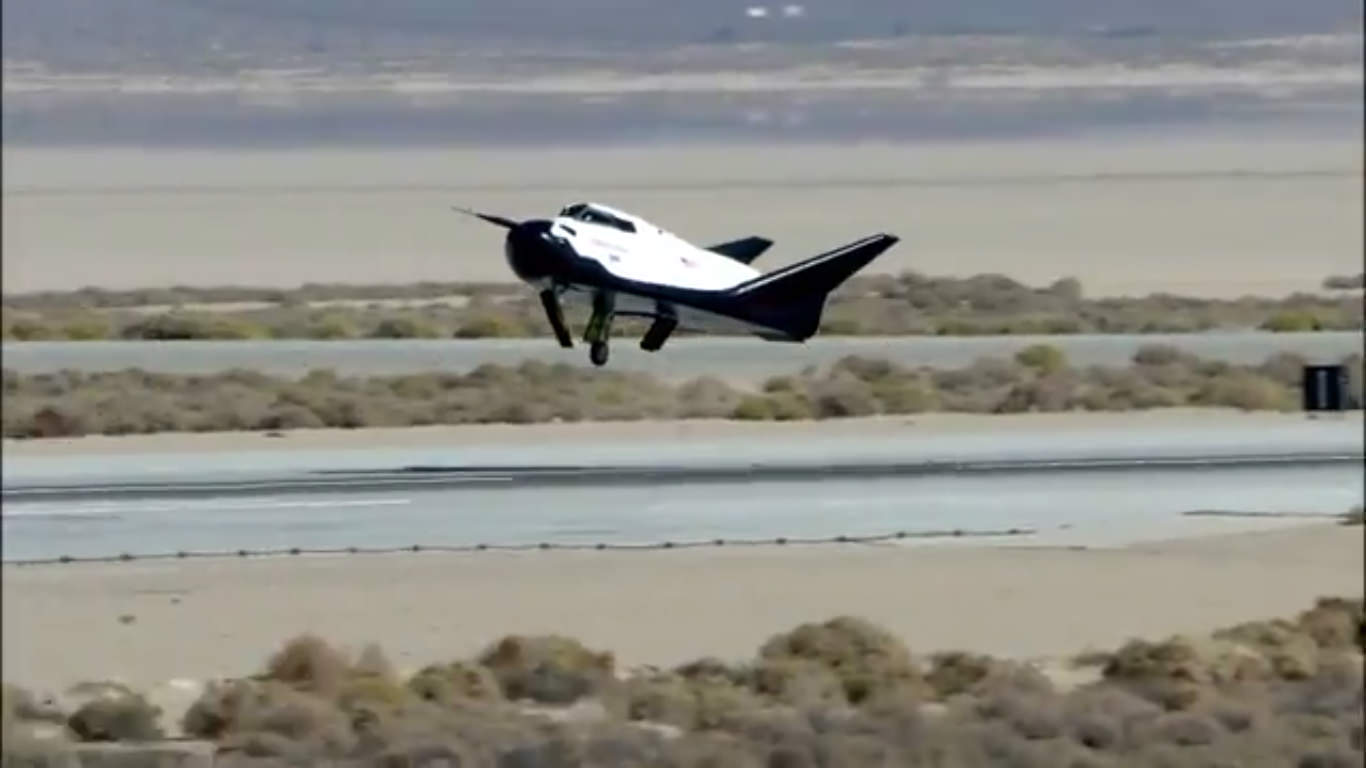
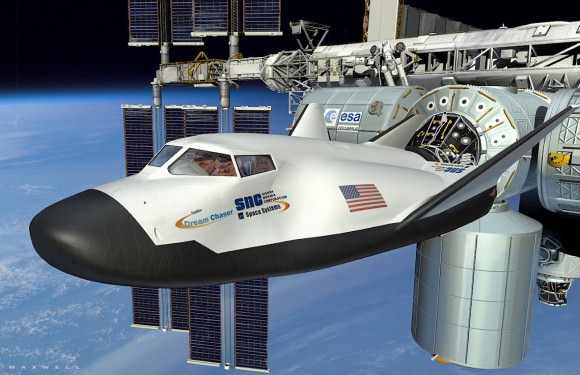
Left landing gear tire visibly failed to deploy as private Dream Chaser spaceplane approaches runway at Edwards Air Force Base, Ca. during first free flight landing test on Oct. 26, 2013 – in this screenshot. Credit: Sierra Nevada Corp.
Watch approach and landing test video below[/caption]
The privately built Dream Chaser ‘space taxi’ that was damaged after landing during its otherwise successful first ever free-flight glide test on Saturday, Oct 26, is repairable and the program will live on to see another day, says the developer Sierra Nevada Corp., (SNC).
The Dream Chaser engineering test vehicle skidded off the runway and landed sideways when its left landing gear failed to deploy at the last second during touchdown on runway 22L at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., said Mark Sirangelo, corporate vice president for SNC Space Systems, at a media teleconference.
The primary goal of the Oct. 26 drop test was to see whether the Dream Chaser mini-shuttle would successfully fly free after being released by an Erickson Air-Crane from an altitude of over 12,000 feet and glide autonomously for about a minute to a touchdown on the Mojave desert landing strip.
“We had a very successful day with an unfortunate anomaly at the end of the day on one of the landing gears,” said Sirangelo.
Dream Chaser is one of three private sector manned spaceships being developed with funding from NASA’s commercial crew program known as Commercial Crew Integrated Capability (CCiCap) initiative to develop a next-generation crew transportation vehicle to ferry astronauts to and from the International Space Station – totally lost following the space shuttle retirement.

The unmanned approach and landing test (ALT) accomplished 99% of its objectives and was only marred by the mechanical failure of the left tire to drop down and deploy for a safe and smooth rollout.
SNC released a short 1 minute video of the test flight – see below – showing the helicopter drop, dive, glide and flare to touchdown. The failure of the landing gear to drop is clearly seen. But the video cuts away just prior to touchdown and does not show the aftermath of the skid or damage to the vehicle.
“The Dream Chaser spacecraft automated flight control system gently steered the vehicle to its intended glide slope. The vehicle adhered to the design flight trajectory throughout the flight profile. Less than a minute later, Dream Chaser smoothly flared and touched down on Edwards Air Force Base’s Runway 22L right on centerline,” said SNC in a statement with the video.
The vehicle is “repairable and flyable again,” Sirangelo noted.
More good news is that the ships interior was not damaged and the exterior can be fixed.
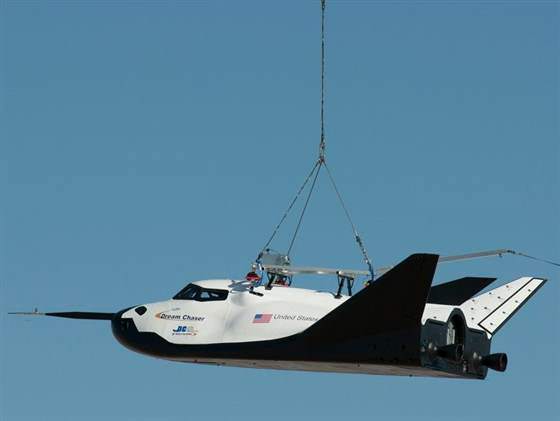
Dream Chaser measures about 29 feet long with a 23 foot wide wing span and is about one third the size of NASA’s space shuttle orbiters.

Since there was no pilot in the cockpit no one was injured. That also meant that no evasive action could be taken to drop the gear.
“We don’t think it’s actually going to set us back,” Sirangelo noted. “In some interesting way, it might actually accelerate it.
NASA’s commercial crew initiative aims at restoring America’s manned spaceflight access to low Earth orbit and the International Space Station (ISS) – perhaps by 2017 – following the forced shutdown of the Space Shuttle program in 2011.
Until an American commercial space taxi is ready for liftoff, NASA is completely dependent on the Russian Soyuz capsule for astronaut rides to the ISS at a cost of roughly $70 million per seat.
Because Congress continues to significantly cut NASA’s budget further delays can be expected – inevitably meaning more payments to Russia and no savings for the American tax payer.
SNC was awarded $227.5 million in the current round of NASA funding and must successfully complete specified milestones, including up to five ALT drop tests to check the aerodynamic handling in order to receive payment.

This particular vehicle had been intended to fly two test flights. Further drop tests were planned with a new test vehicle to be constructed.
The way forward is being evaluated.
“We don’t think there is going to be any significant delay to the program as a result of this. This was meant to be a test vehicle with a limited number of flights,” Sirangelo said.
SNC and NASA have assembled a team to investigate the cause of the anomaly.
“SNC cannot release any further video at this time,” said SNC.
Dream Chaser is a reusable mini shuttle that launches from the Florida Space Coast atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket and lands on the shuttle landing facility (SLF) runway at the Kennedy Space Center, like the space shuttle.