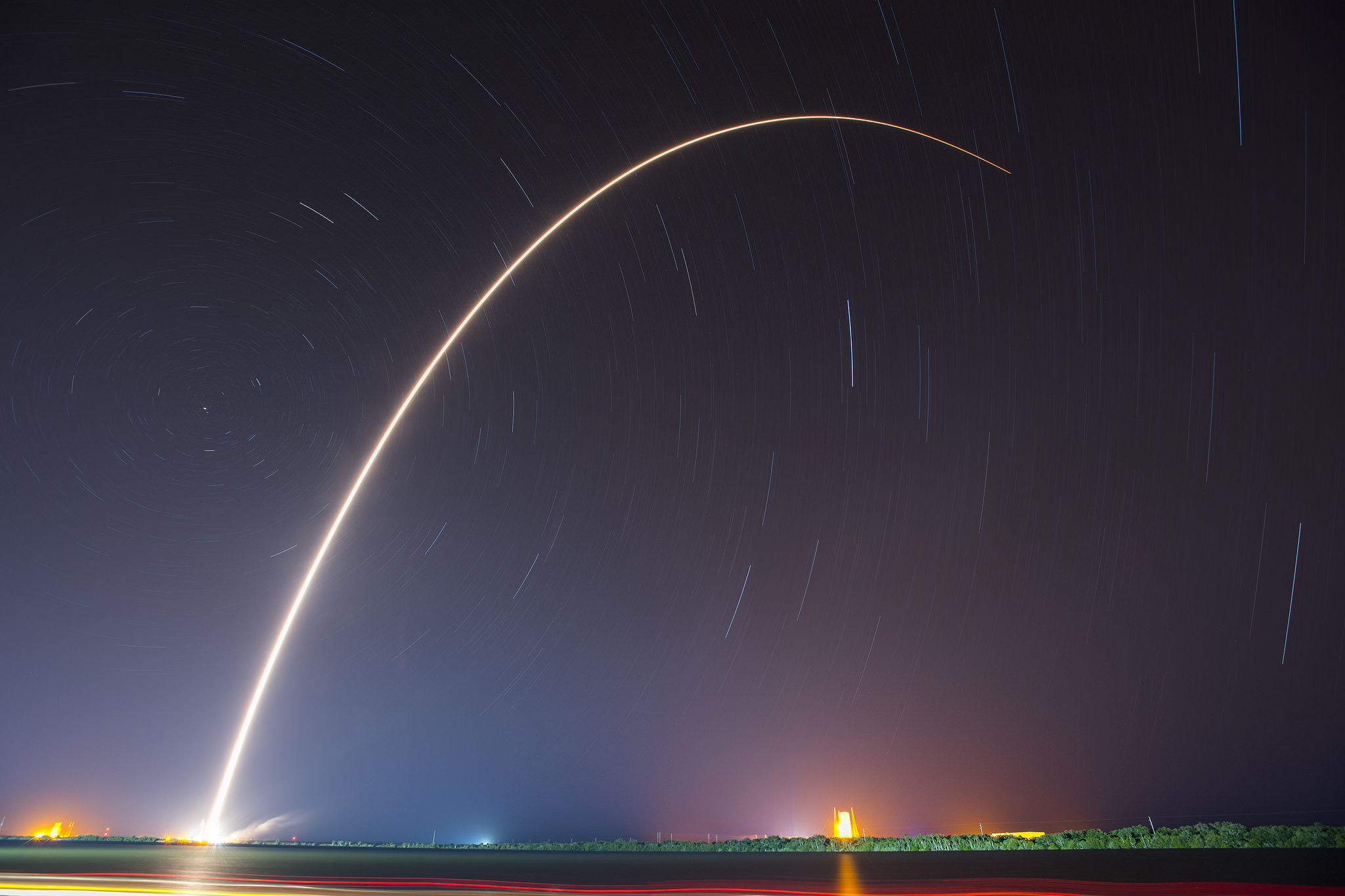
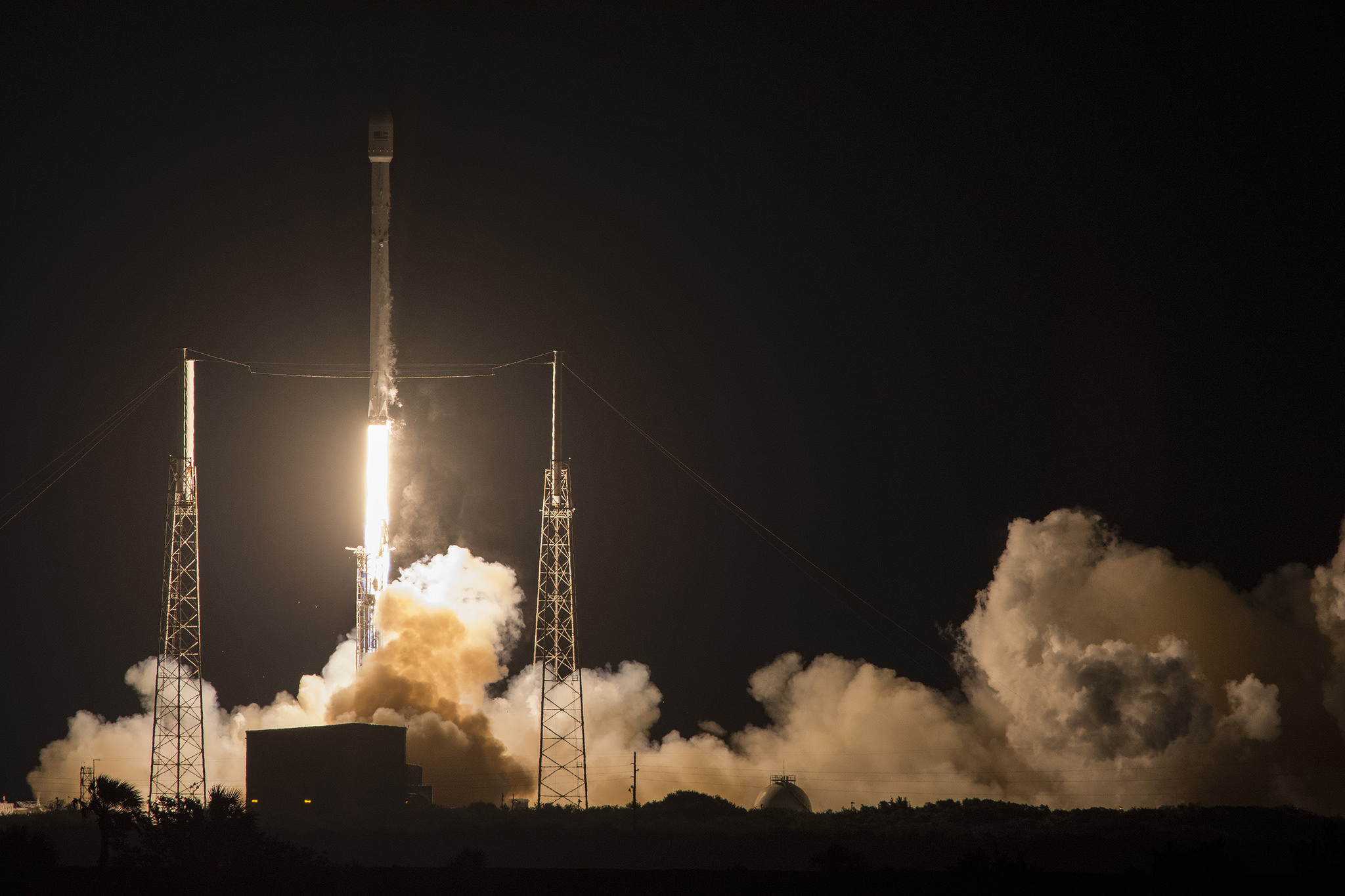
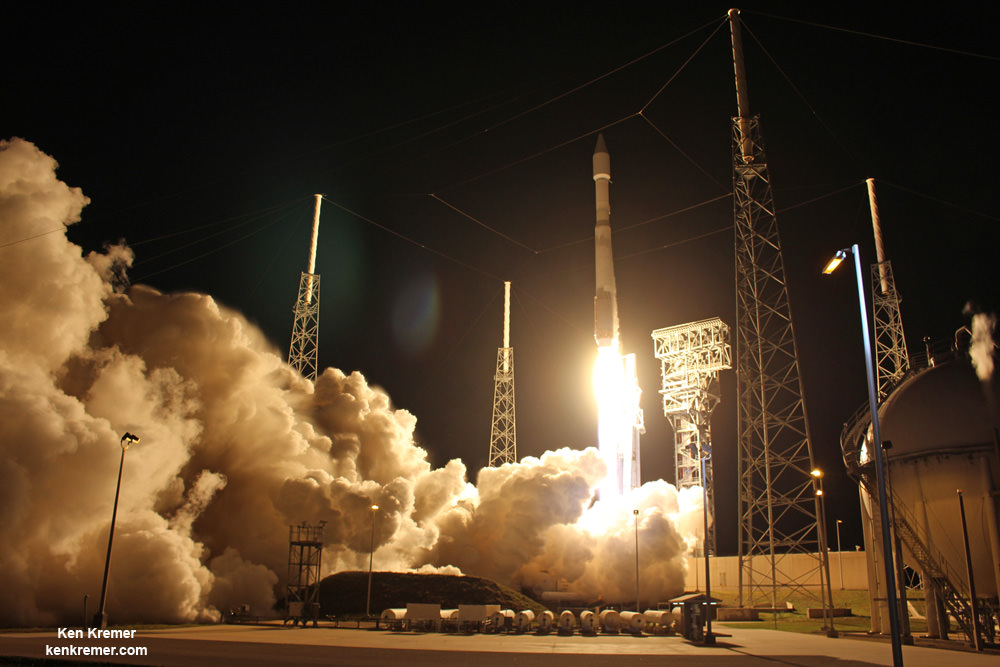
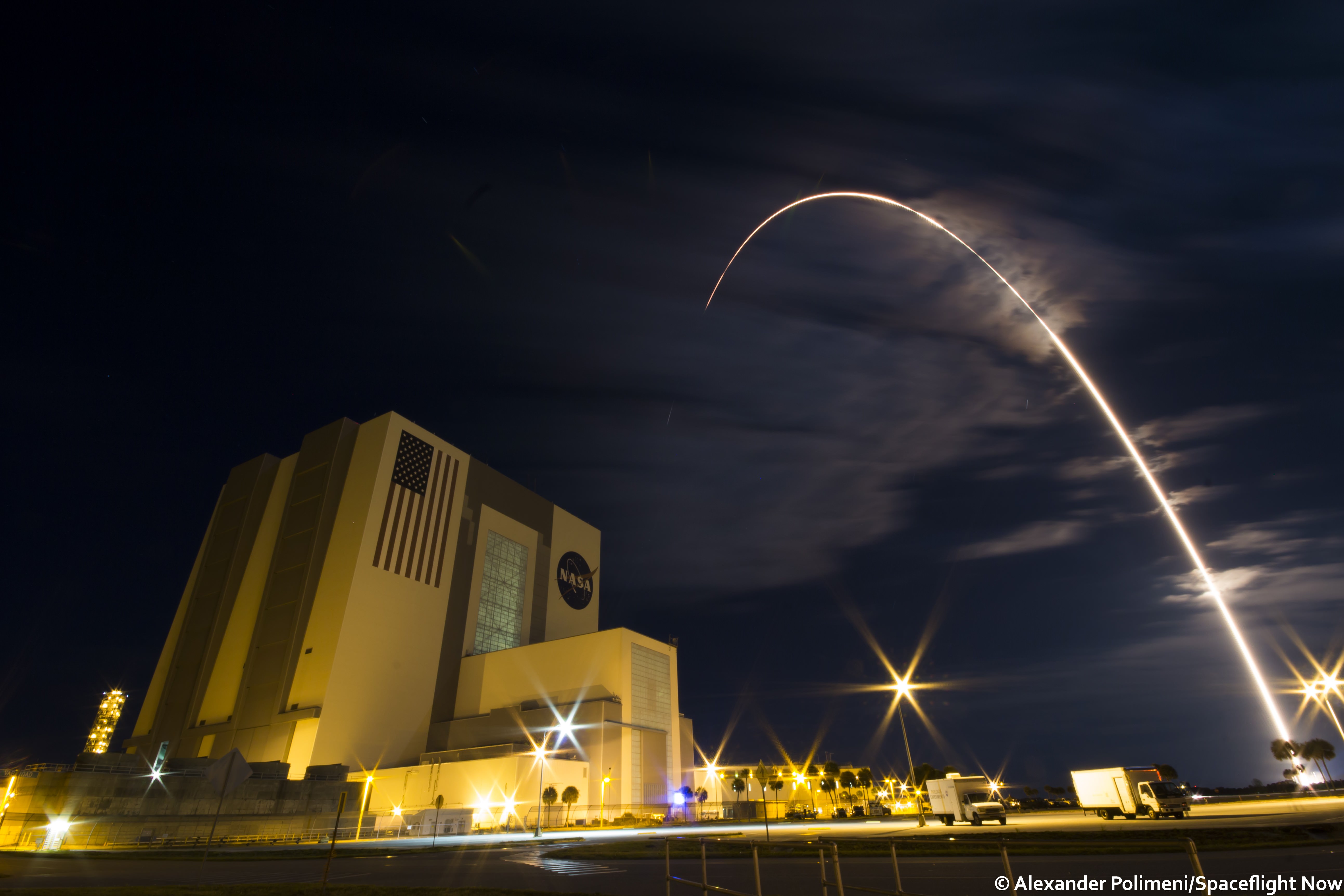
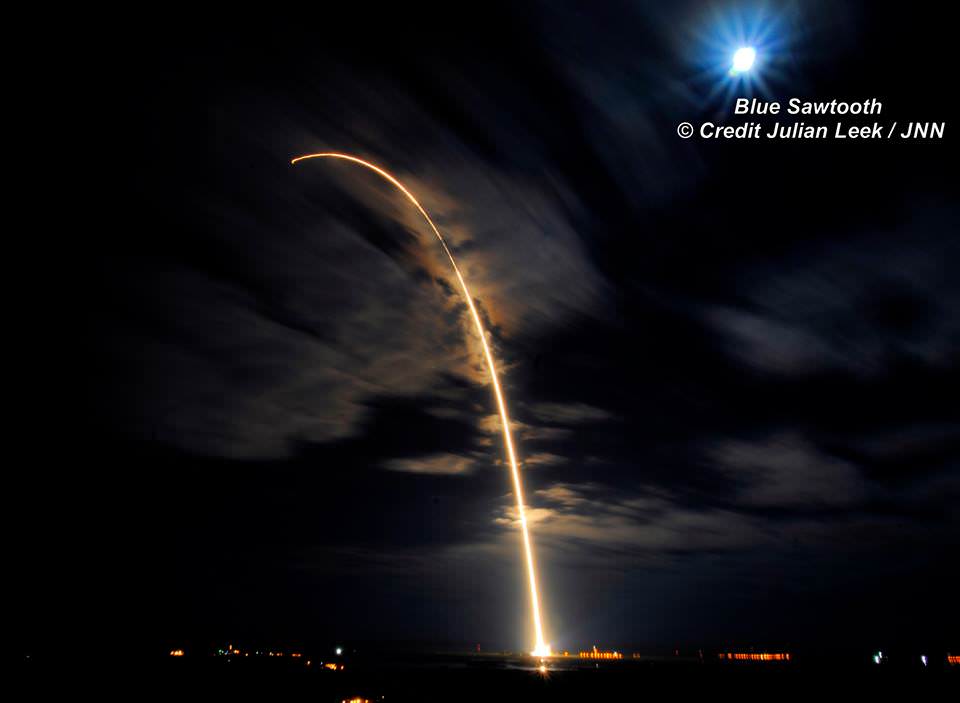
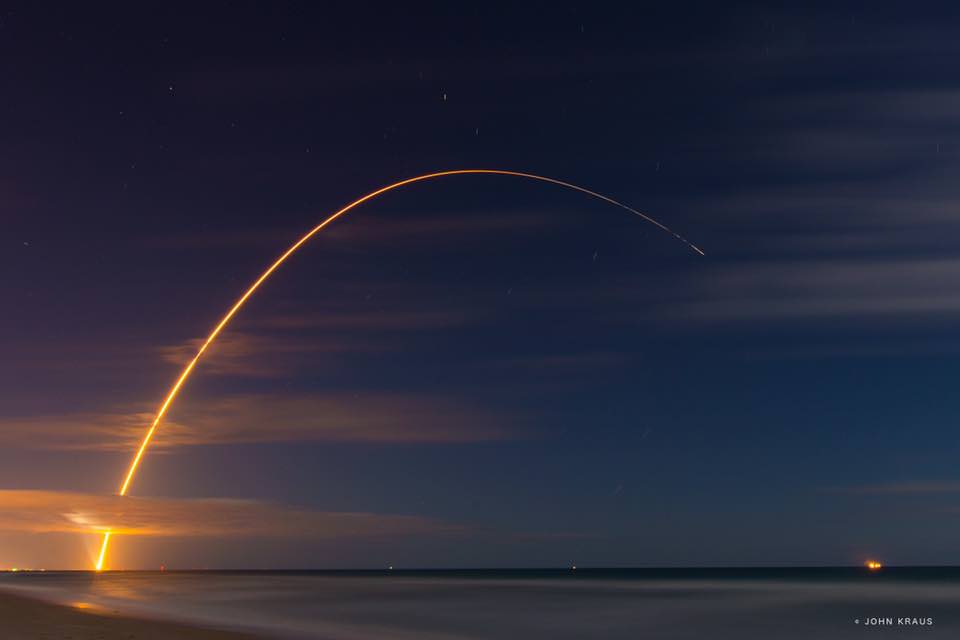
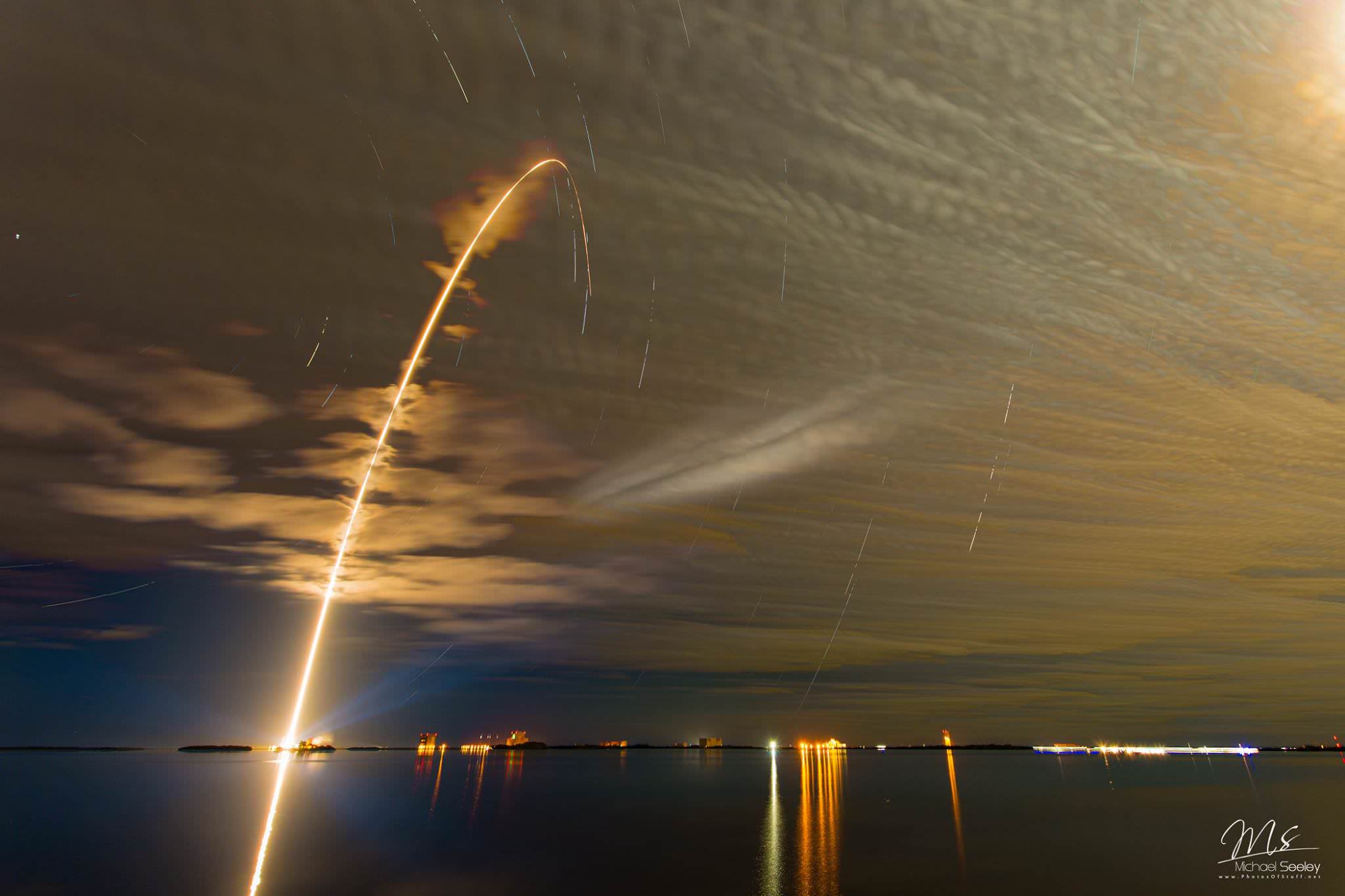
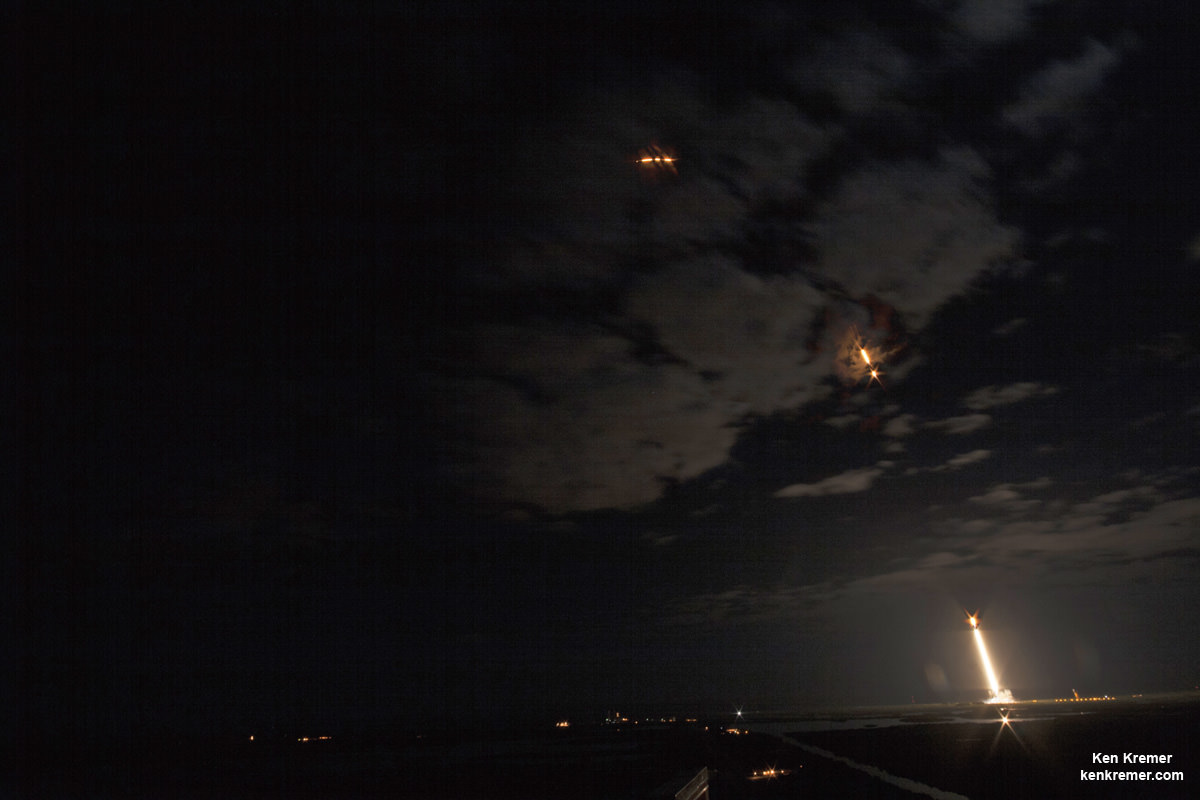
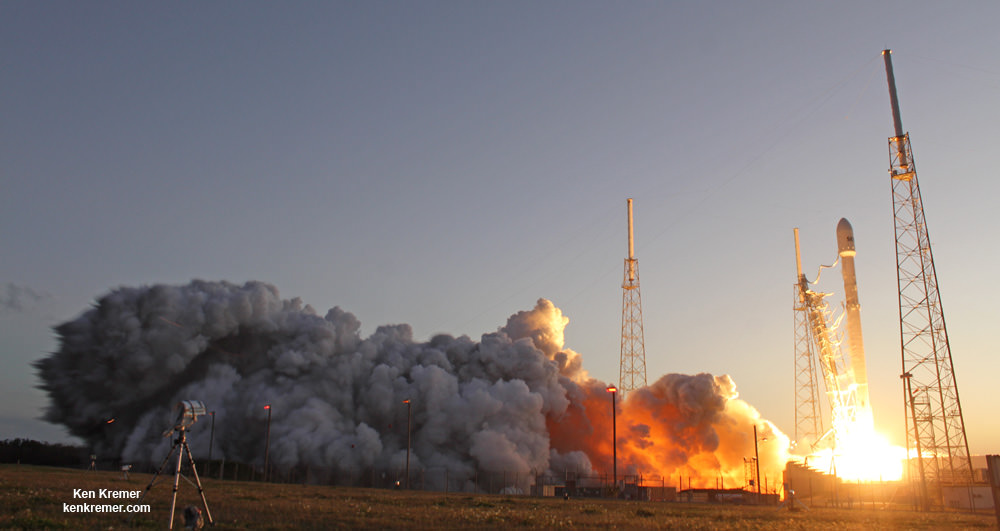
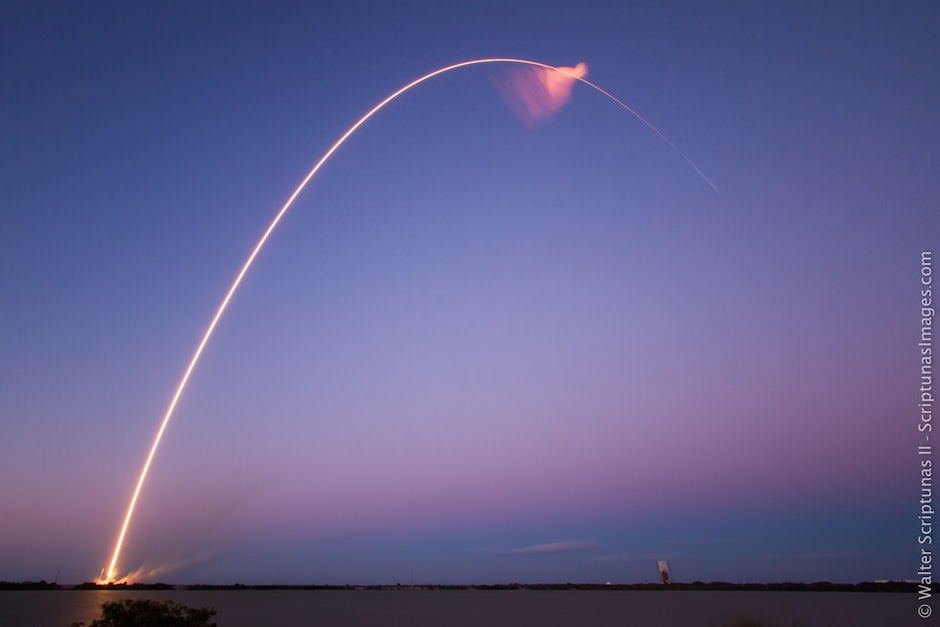
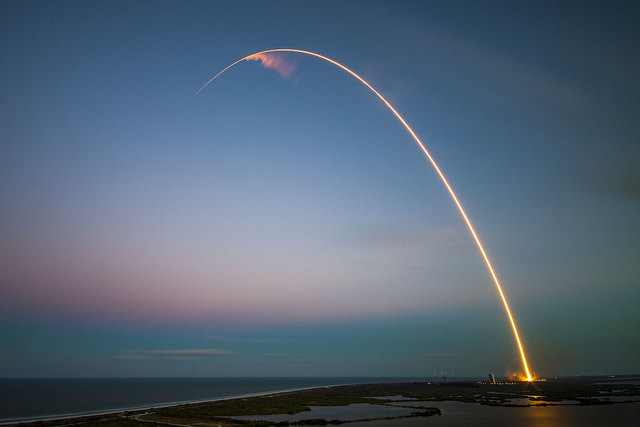
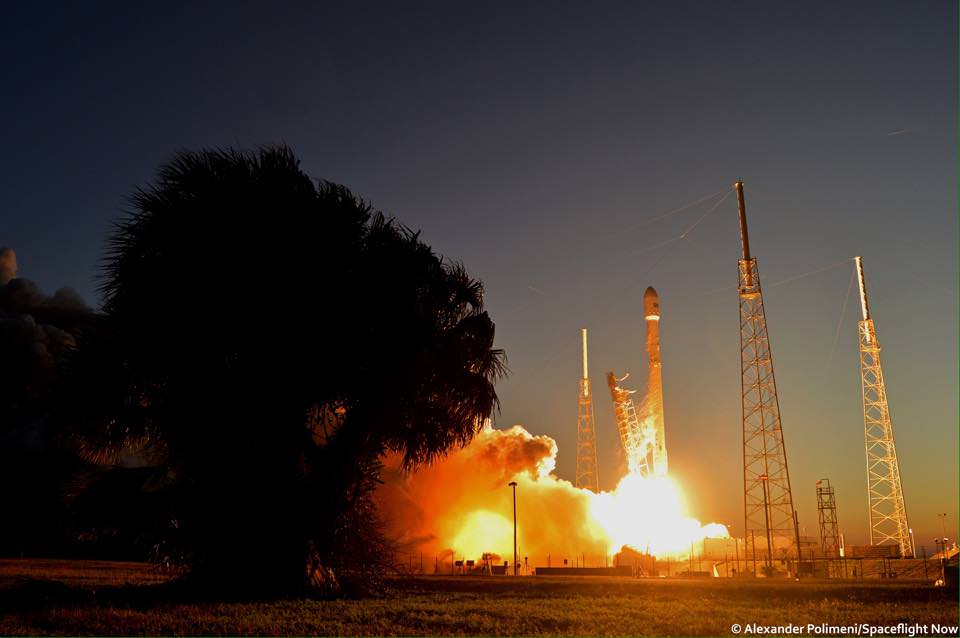
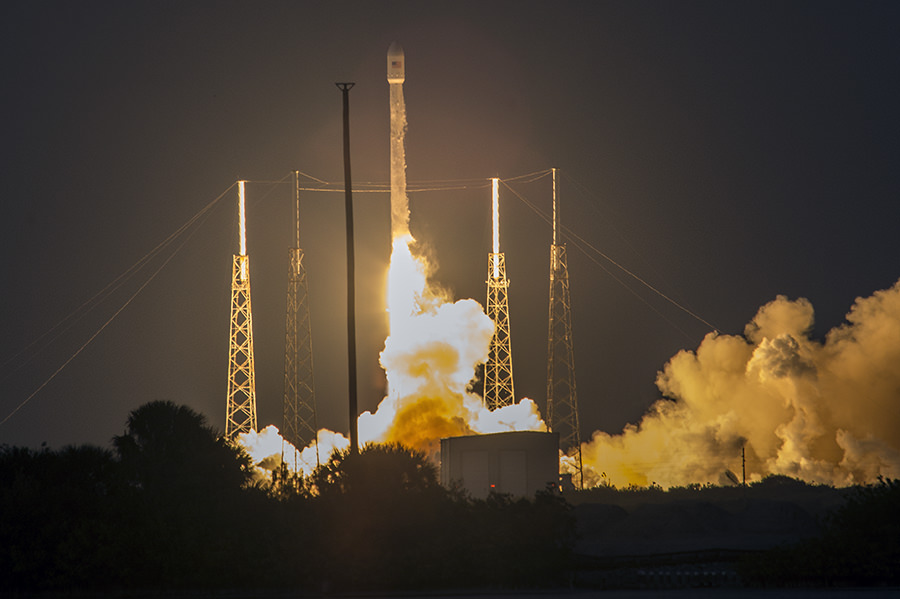
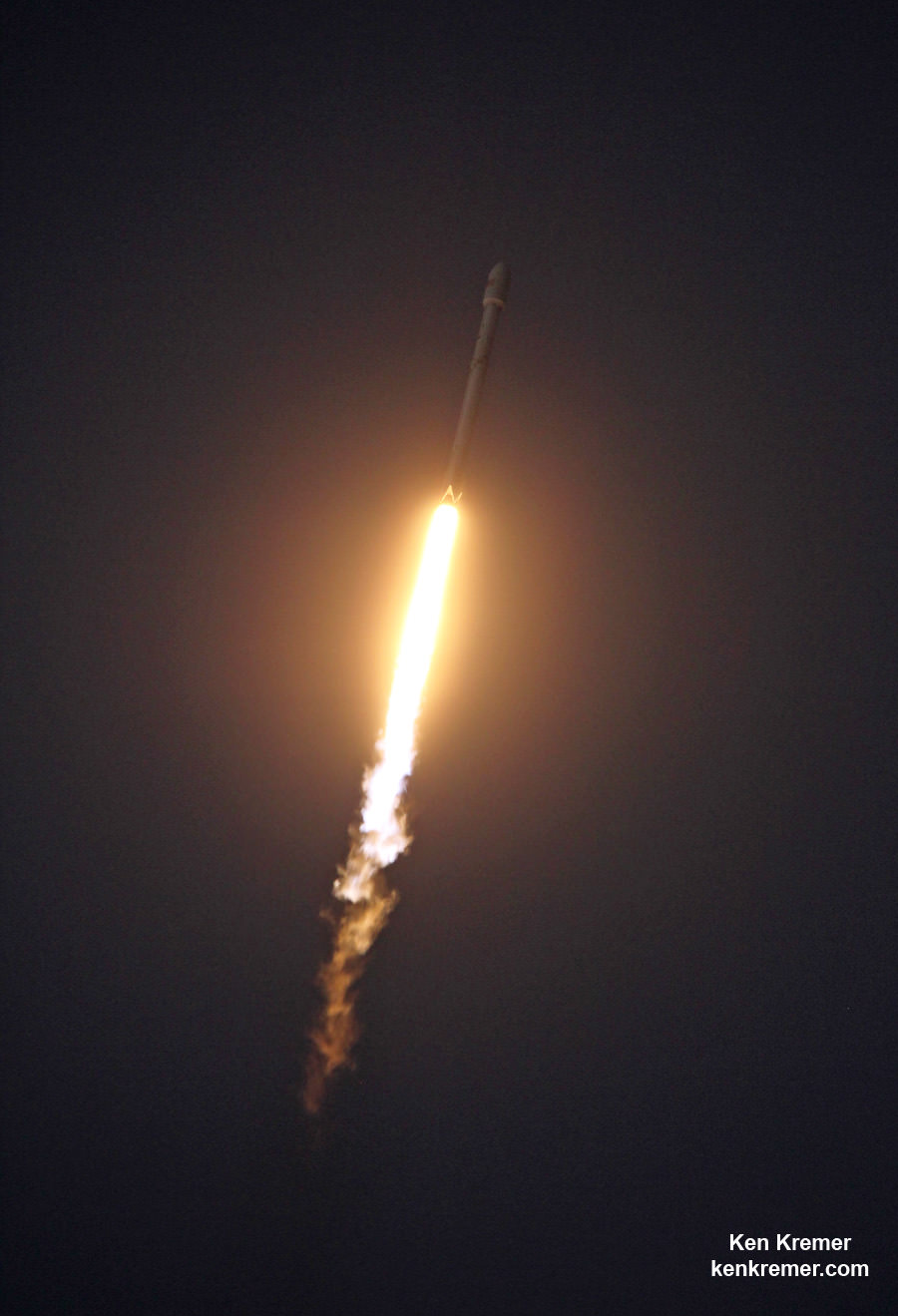
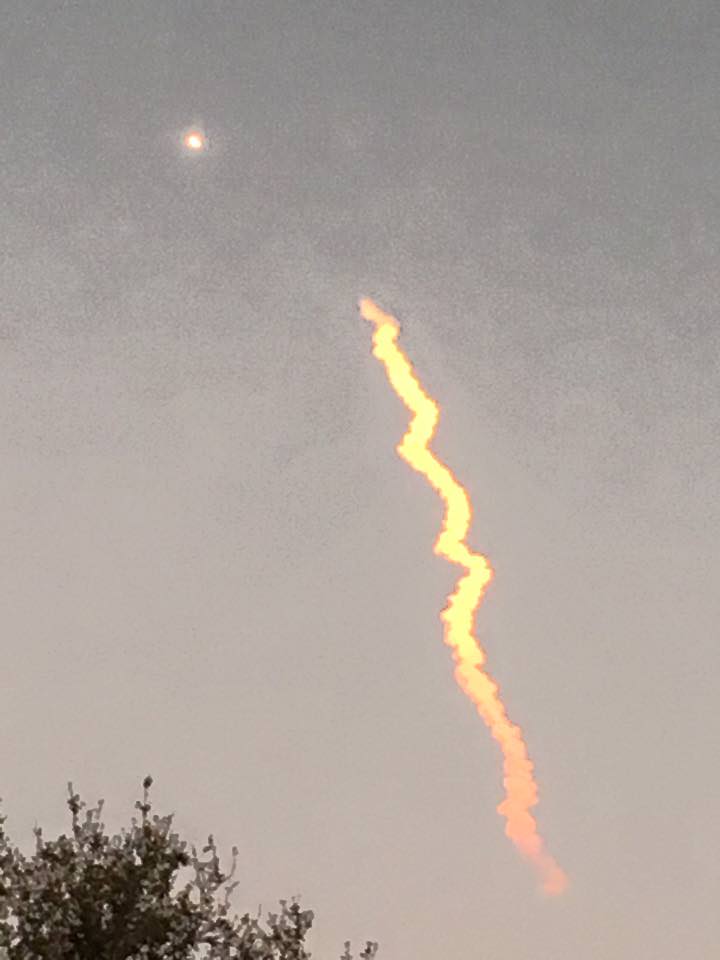
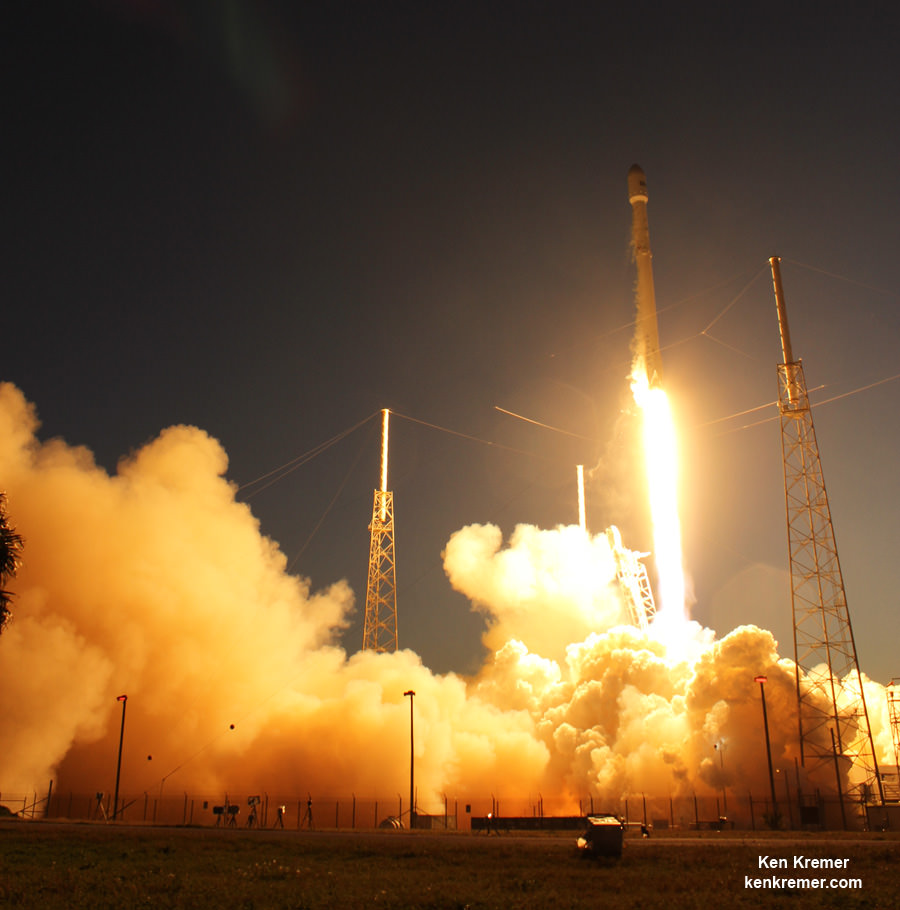
SpaceX scored a double whammy of successes this morning, May 6, following the stunning nighttime launch of a Japanese comsat streaking to orbit on the firm’s Falcon 9 rocket and nailing the breathtaking touchdown of the spent first stage just minutes later – furthering the goal of rocket reusability
Under clear Florida starlight, the upgraded SpaceX Falcon 9 soared to orbit on 1.5 million pounds of thrust on a mission carrying the JCSAT-14 commercial communications satellite, following an on time liftoff at 1:21 a.m. EDT this morning from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fl.
The spectacular launch and dramatic landing were both broadcast in real time on a live launch webcast from SpaceX.

Today’s Falcon launch was the 4th this year for SpaceX and took place less than 4 weeks after the last launch (on an ISS cargo mission for NASA) and sea based barge landing.
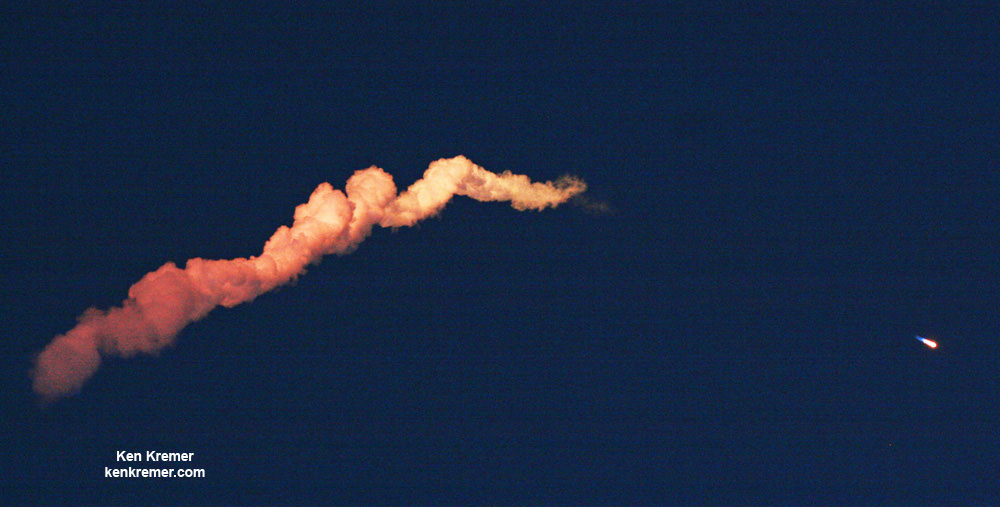
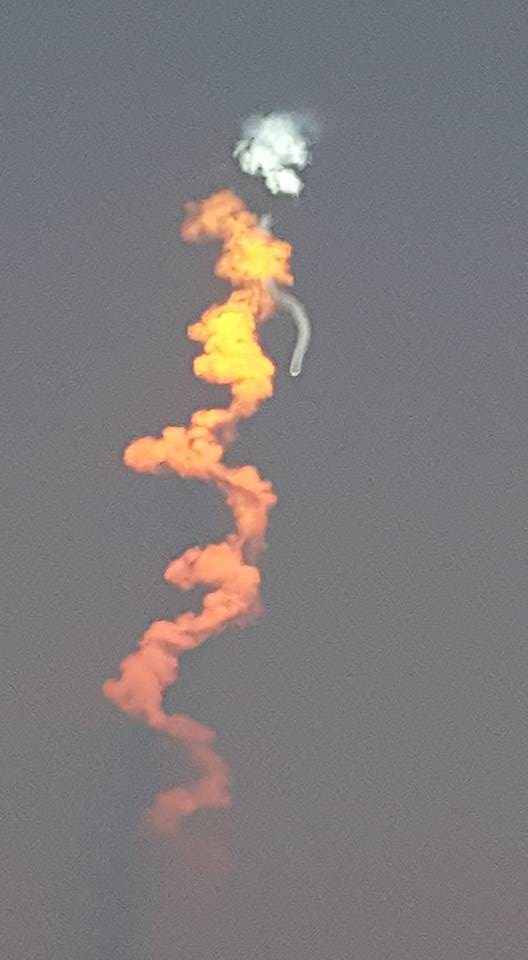
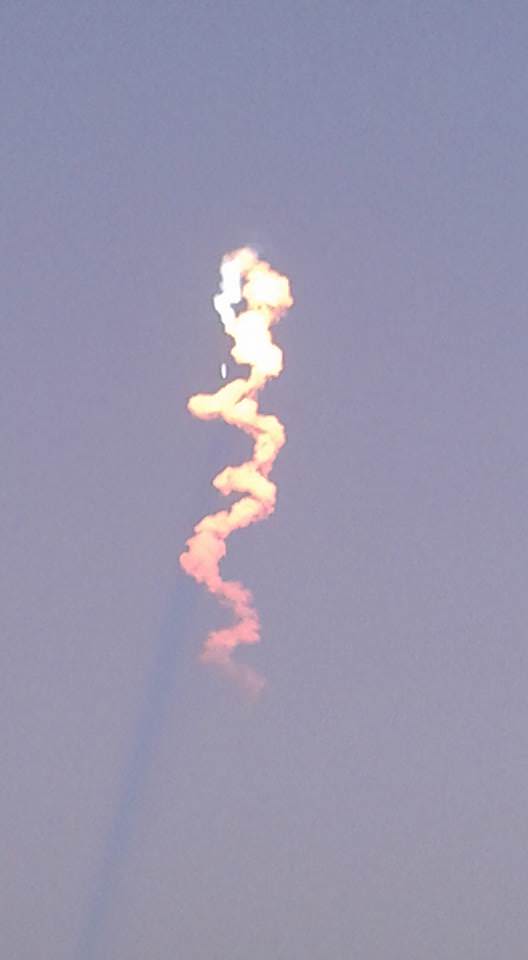
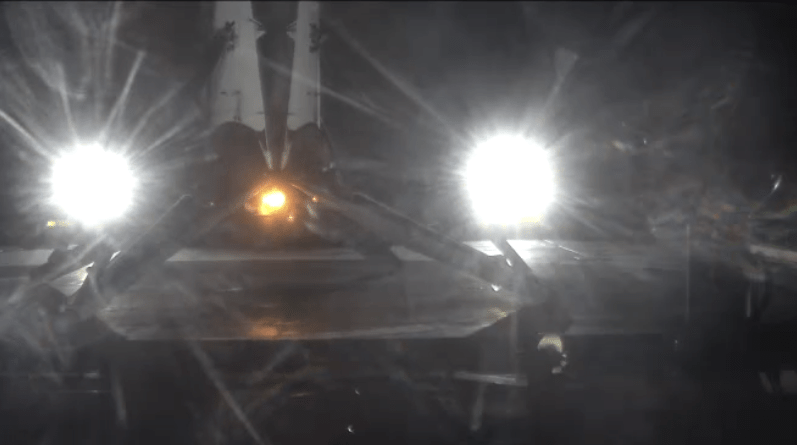
Barely nine minutes after liftoff the 156 foot tall Falcon 9 first stage carried out a propulsive soft landing on an ocean going platform located some 400 miles off the east coast of Florida.
“First stage landing on drone ship in Atlantic confirmed,” said a SpaceX official during the webcast, which showed a glowing body approaching the horizon.
“Woohoo!!” tweeted SpaceX CEO and billionaire founder Elon Musk.
This marked the second successful landing at sea for SpaceX following the prior history making touchdown success last month.
“May need to increase size of rocket storage hangar,” tweeted Musk.
“Yeah, this was a three engine landing burn, so triple deceleration of last flight. That’s important to minimize gravity losses.”
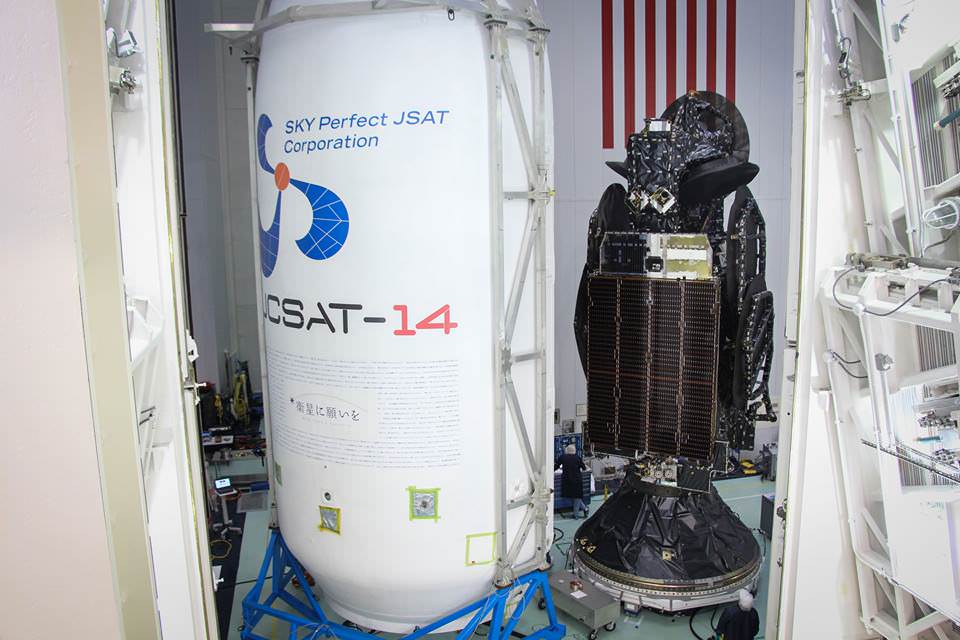
The commercial SpaceX launch lofted the JCSAT-14 Japanese communications satellite to a Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) for SKY Perfect JSAT – a leading satellite operator in the Asia – Pacific region.
After a brief reignition of the second stage, the spacecraft successfully separated from the upper stage and was deployed some 32 minutes after liftoff – as seen via the live SpaceX webcast.
“The Falcon 9 second stage delivered JCSAT-14 to a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit,” said SpaceX.
Via a fleet of 15 satellites, Tokyo, Japan based SKY Perfect JSAT provides high quality satellite communications to its customers.
The JCSAT-14 communications satellite was designed and manufactured by Space Systems/Loral for SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation.
It will succeed and replace the JCSAT-2A satellite currently providing coverage to Asia, Russia, Oceania and the Pacific Islands.
JCSAT-14 is equipped with C-band and Ku-Band transponders that will extend JCSAT-2A’s geographical footprint across the Asia-Pacific region.

The Falcon 9 soft landed on the “Of Course I Still Love You” drone ship positioned some 400 miles (650 kilometers) off shore in the Atlantic Ocean.
Prior to the launch, SpaceX officials had rated the chances of a successful landing as “unlikely” due to “this launch mission’s GTO destination, the first stage will be subject to extreme velocities and re-entry heating.”
“Rocket reentry is a lot faster and hotter than last time, so odds of making it are maybe even, but we should learn a lot either way,” said Musk.
Nevertheless, despite those difficulties, the landing turned out to be another stunning success for SpaceX CEO Elon Musk’s vision of radically slashing the cost of sending rocket to space by recovering the boosters and eventually reusing them.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.