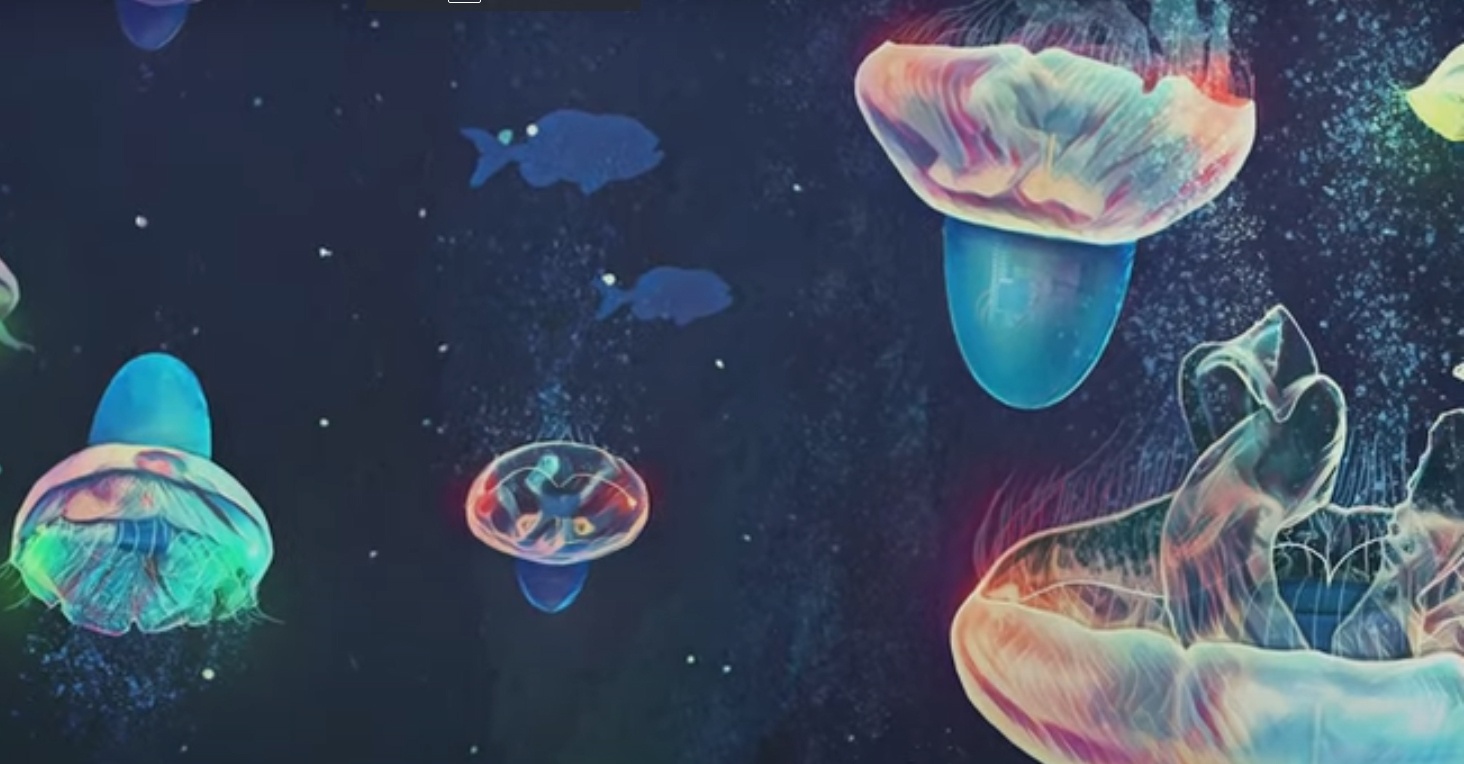
Earth’s oceans are—like space—a largely unexplored frontier. Relatively few humans have explored either place, using specialized life-support equipment. Unlike space, however, the oceans also have other beings that can explore them: jellyfish. They can head to places underwater that humans can never go. That makes them interesting candidates for autonomous ocean exploration.
Continue reading “Cyborg Jellyfish Could Help Explore Oceans Autonomously”Juno Measures How Much Oxygen is Being Produced by Europa
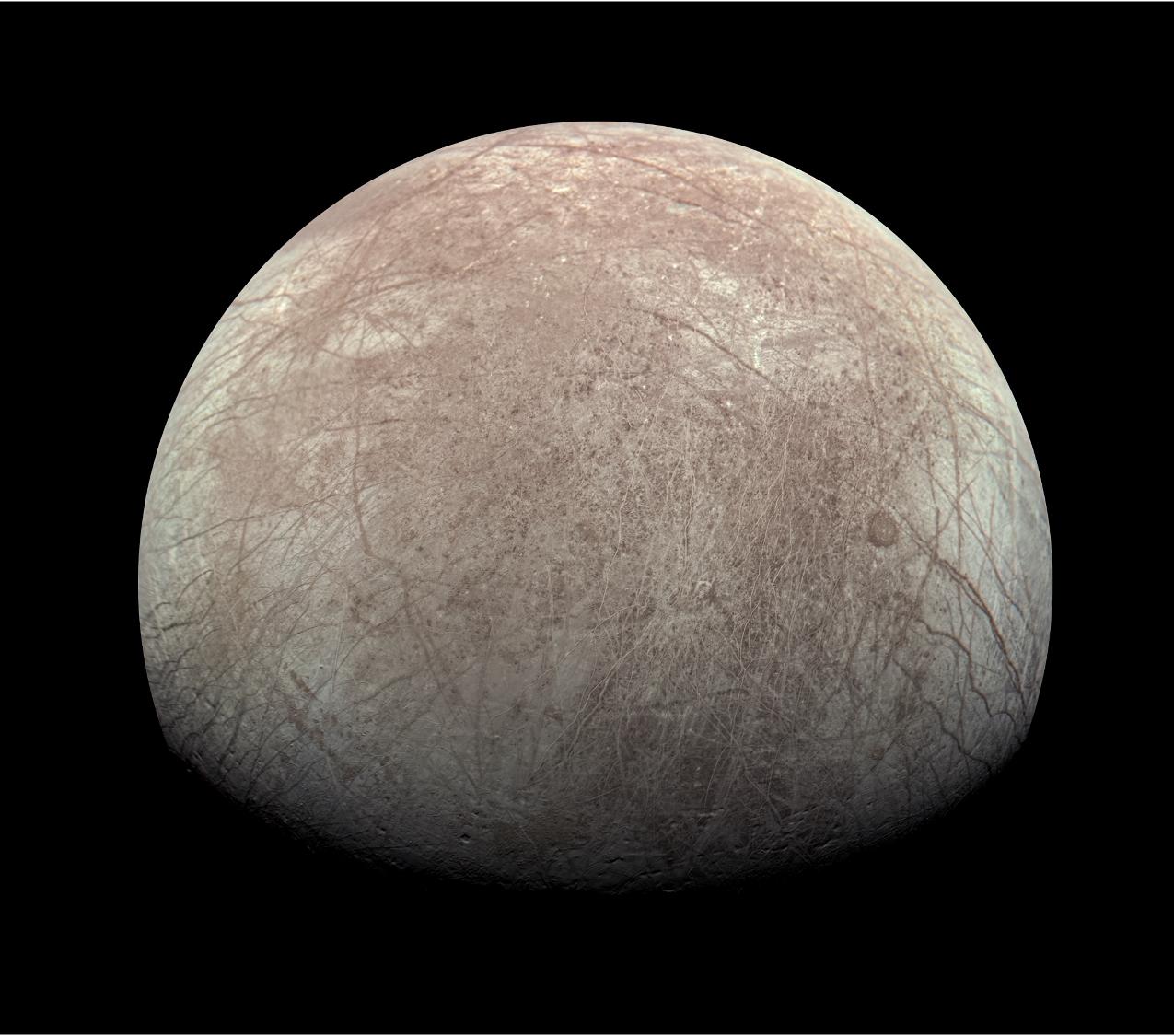

If the periodic table listed the elements in order of their importance to life, then oxygen might bully its way to the top. Without oxygen, Earth’s complex life likely would not exist. So when scientists detect oxygen on another world, they turn their attention to it.
Continue reading “Juno Measures How Much Oxygen is Being Produced by Europa”Cosmic Dust Could Have Helped Get Life Going on Earth
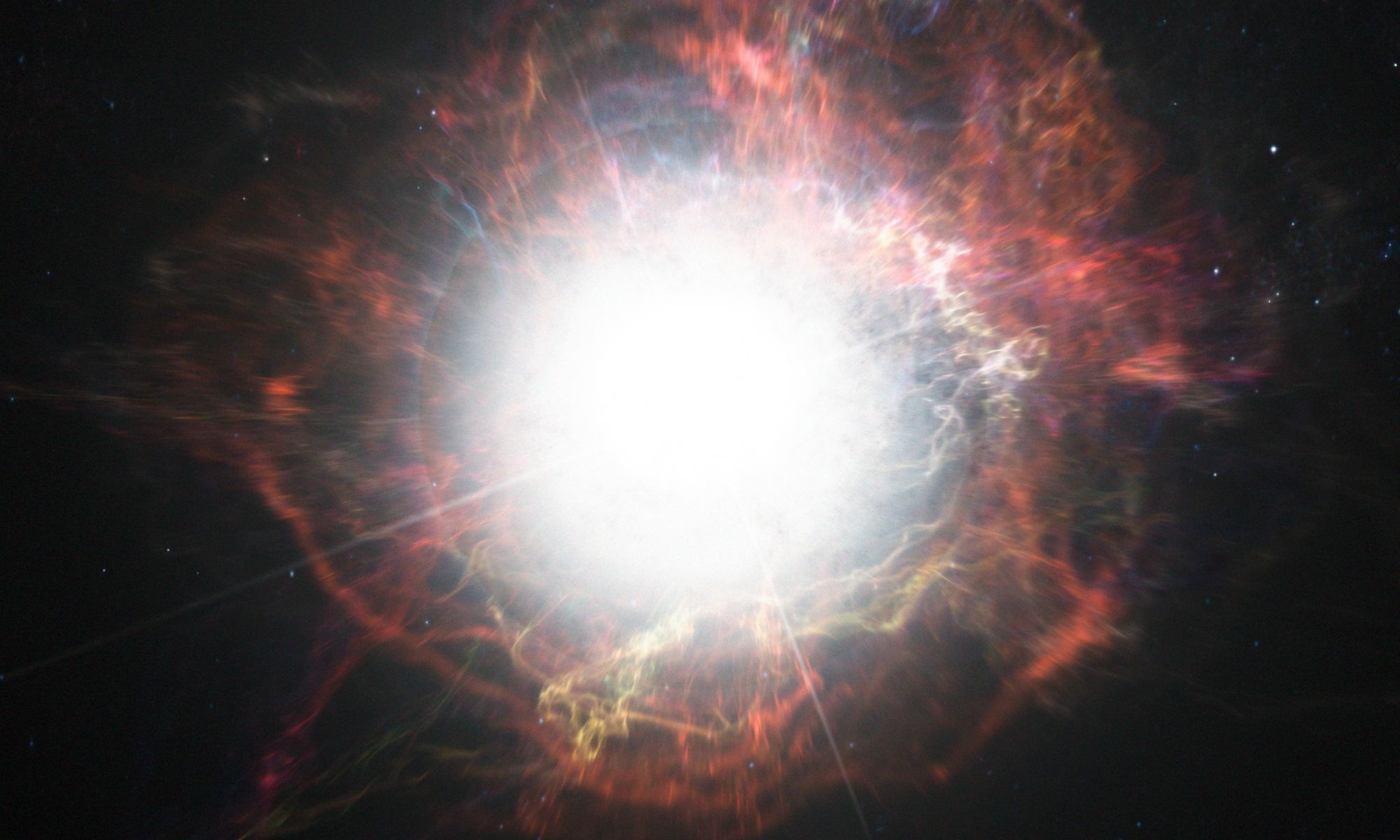

Life on our planet appeared early in Earth’s history. Surprisingly early, since in its early youth our planet didn’t have much of the chemical ingredients necessary for life to evolve. Since prebiotic chemicals such as sugars and amino acids are known to appear in asteroids and comets, one idea is that Earth was seeded with the building blocks of life by early cometary and asteroid impacts. While this likely played a role, a new study shows that cosmic dust also seeded young Earth, and it may have made all the difference.
Continue reading “Cosmic Dust Could Have Helped Get Life Going on Earth”Dying Stars Could Have Completely New Habitable Zones
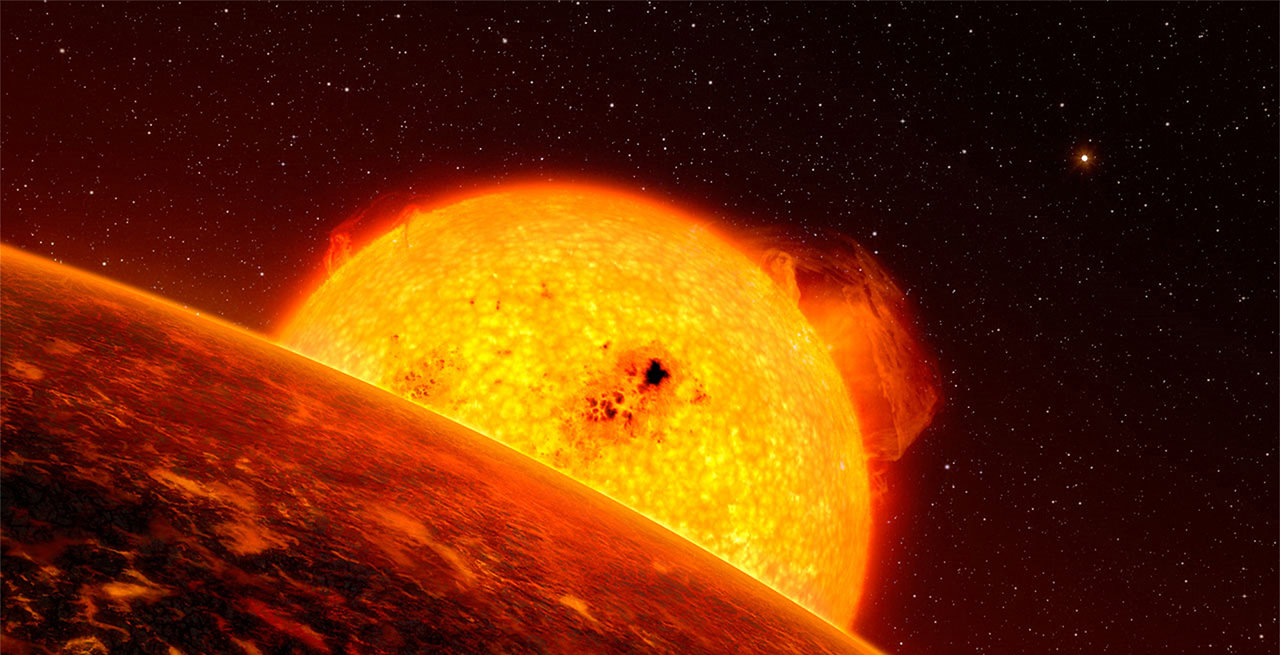
Aging stars that become red giants increase their luminosity and can wreak havoc on planets that were once in the star’s habitable zones. When the Sun becomes a red giant and expands, its habitable zone will move further outward, meaning Earth will likely lose its atmosphere, its water, and its life. But for planets further out, their time in the habitable zone will just begin.
Is there enough time for life to arise on these newly habitable planets?
Continue reading “Dying Stars Could Have Completely New Habitable Zones”Cosmic Dust Could Spread Life from World to World Across the Galaxy

Does life appear independently on different planets in the galaxy? Or does it spread from world to world? Or does it do both?
New research shows how life could spread via a basic, simple pathway: cosmic dust.
Continue reading “Cosmic Dust Could Spread Life from World to World Across the Galaxy”Could We Live Without Kilonovae?
It’s a classic statement shared at many public outreach events…’we are made of stardust’. It is true enough that the human body is mostly water with some other elelments like carbon which are formed inside stars just like the Sun. It’s not just common elements like carbon though for we also have slighly more rare elements like iodine and bromine. They don’t form in normal stars but instead are generated in collisions between neutron stars! It poses an interesting question, without the neutron star merger event; ‘would we exist?’
Continue reading “Could We Live Without Kilonovae?”The Seeming Impossibility of Life
The number of near misses, false starts, and legitimate disasters that have befallen our species since the day we took our first upright steps all those generations ago is too large to count and could honestly take up this entire book. I’ll give us humans this much, though: we’re survivors, through and through.
Continue reading “The Seeming Impossibility of Life”The Improbable Origins of Life on Earth
We do not yet know how, where, or why life first appeared on our planet. Part of the difficulty is that “life” has no strict, universally agreed-upon definition.
Continue reading “The Improbable Origins of Life on Earth”Early Life Was Radically Different Than Today
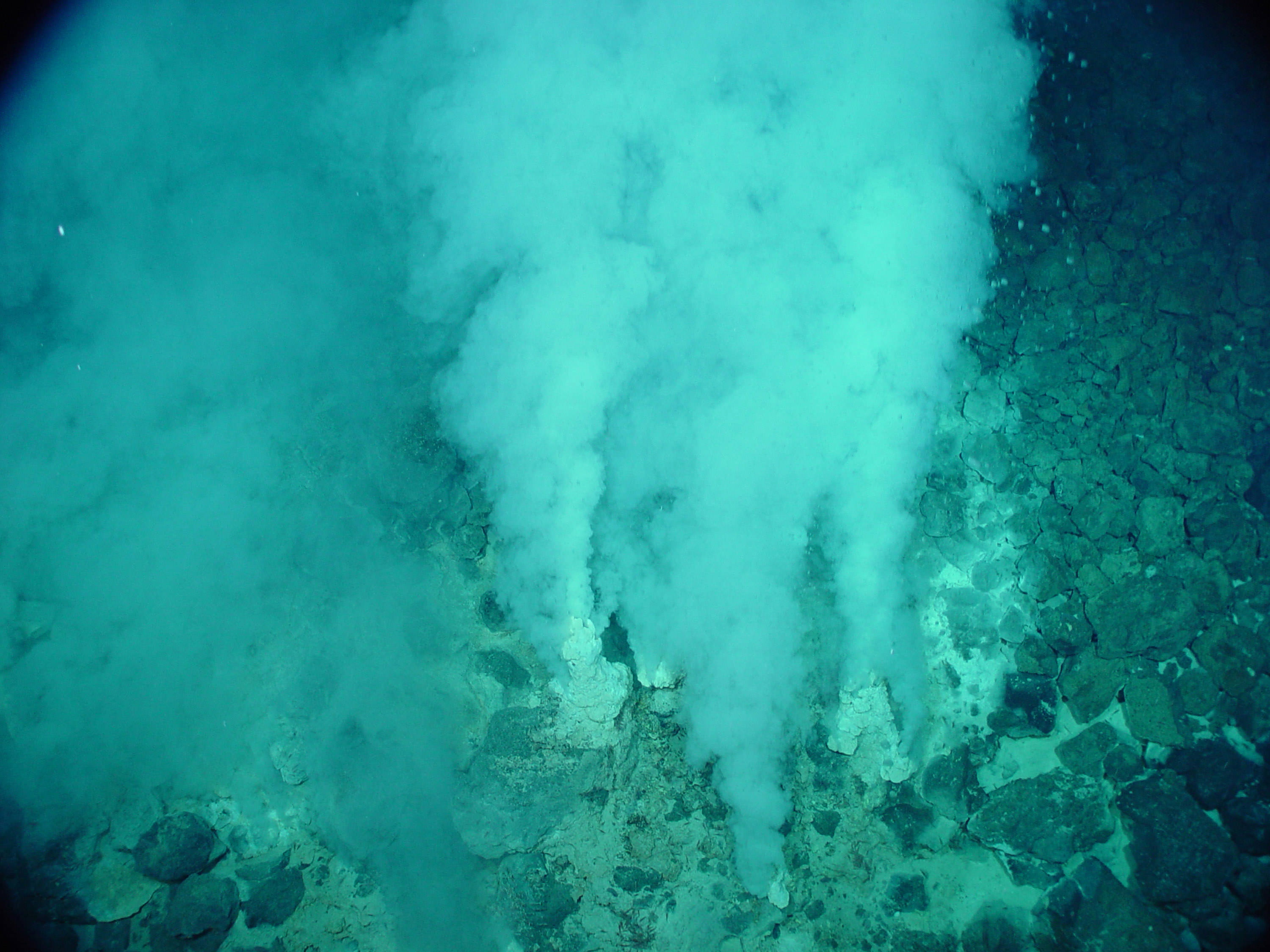

All modern life shares a robust, hardy, efficient system of intertwined chemicals that propagate themselves. This system must have emerged from a simpler, less efficient, more delicate one. But what was that system, and why did it appear on, of all places, planet Earth?
Continue reading “Early Life Was Radically Different Than Today”The Next Generation LIFE Telescope Could Detect Some Intriguing Biosignatures
The Large Interferometer for Exoplanets (LIFE) project is an ambitious plan to build a space telescope with four independent mirrors. The array would allow the individual mirrors to move closer or farther apart, similar to the way the Very Large Array (VLA) does with radio antennas. LIFE is still early in its planning stage, so it would likely be decades before it is built, but already the LIFE team is looking at ways it might discover life on other worlds. Much of this focuses on the detection of biogenic molecules in exoplanet atmospheres.
Continue reading “The Next Generation LIFE Telescope Could Detect Some Intriguing Biosignatures”



