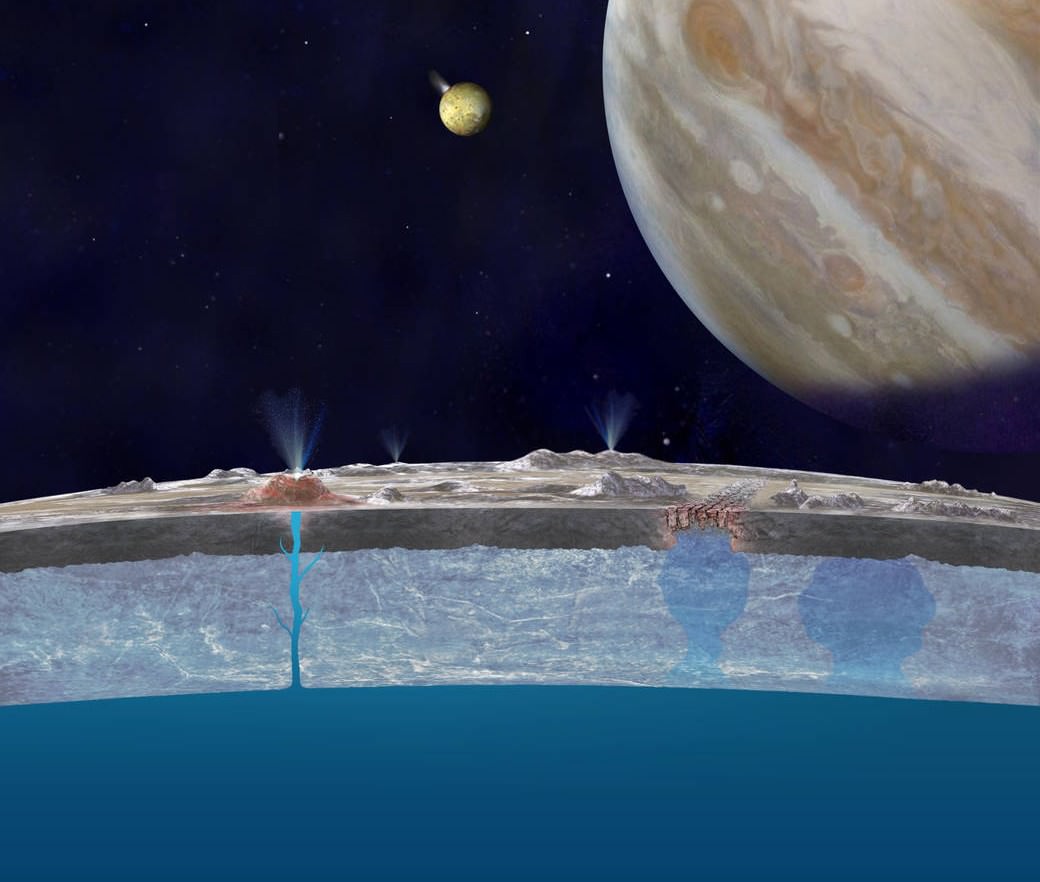
One of the most exciting aspects of space exploration today is how the field of astrobiology – the search for life in our Universe – has become so prominent. In the coming years, many robotic and even crewed missions will be bound for Mars that will aid in the ongoing search for life there. Beyond Mars, missions are planned for the outer Solar System that will explore satellites and bodies with icy exteriors and interior oceans – otherwise known as “Ocean Worlds.” These include the Jovian satellites Europa and Ganymede and Saturn’s moons Titan and Enceladus.
Similar to how missions to Mars have analyzed soil and rock samples for evidence of past life, the proposed missions will analyze liquid samples for the chemical signatures that we associate with life and biological processes (aka. “biosignatures”). To aid in this search, scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory have designed the Ocean Worlds Life Surveyor (OWLS), a suite of eight scientific instruments designed to sniff out biosignatures. In the coming decades, this suite could be used by robotic probes bound for “Ocean Worlds” all across the Solar System to search for signs of life.
Continue reading “NASA has Built a Collection of Instruments That Will Search for Life Inside Europa and Enceladus”