[/caption]
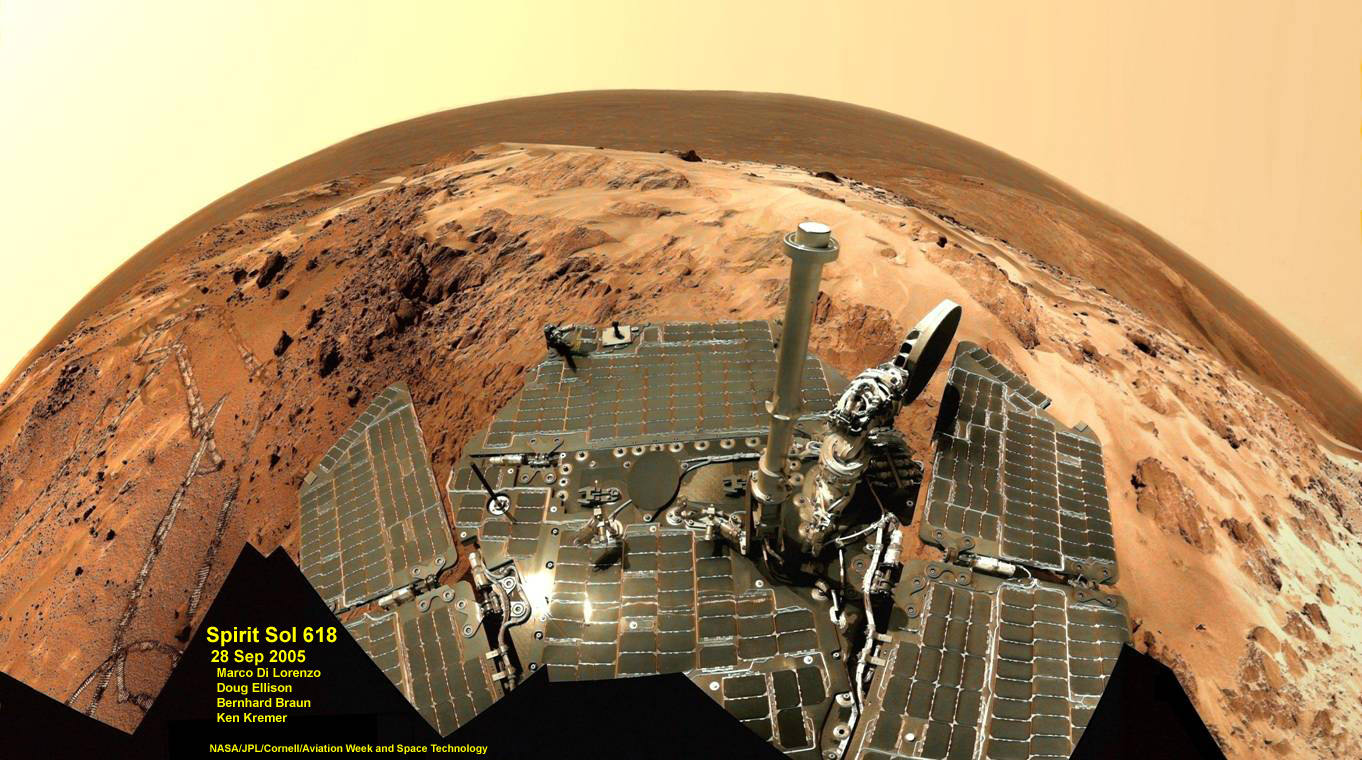
January 2012 marks the 8th anniversary since of the daring landing’s of “Spirit” and “Opportunity” – NASA’s now legendary twin Mars Exploration Rovers (MER), on opposite sides of the Red Planet in January 2004. They proved that early Mars was warm and wet – a key finding in the search for habitats conducive to life beyond Earth.
I asked the leaders of the MER team to share some thoughts celebrating this mind-boggling milestone of “8 Years on Mars” and the legacy of the rovers for the readers of Universe Today. This story focuses on Spirit, first of the trailblazing twin robots, which touched down inside Gusev Crater on Jan. 3, 2004. Opportunity set down three weeks later on the smooth hematite plains of Meridiani Planum.
“Every Sol is a gift. We push the rovers as hard as we can,” Prof. Steve Squyres informed Universe Today for this article commemorating Spirit’s landing. Squyres, of Cornell University, is the Scientific Principal Investigator for the MER mission.
“I seriously thought both Spirit and Opportunity would be finished by the summer of 2004,” Ray Arvidson told Universe Today. Arvidson, of Washington University in St. Louis, is the deputy principal investigator for the MER rovers.

This full-circle view from the panoramic camera (Pancam) on NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit shows the terrain surrounding the location called "Troy," where Spirit became embedded in soft soil during the spring of 2009. The hundreds of images combined into this view were taken beginning on the 1,906th Martian day (or sol) of Spirit's mission on Mars (May 14, 2009) and ending on Sol 1943 (June 20, 2009). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell University
click to enlarge
Spirit endured for more than six years and Opportunity is still roving Mars today !
The dynamic robo duo were expected to last a mere three months, or 90 Martian days (sols). In reality, both robots enormously exceeded expectations and accumulated a vast bonus time of exploration and discovery in numerous extended mission phases.
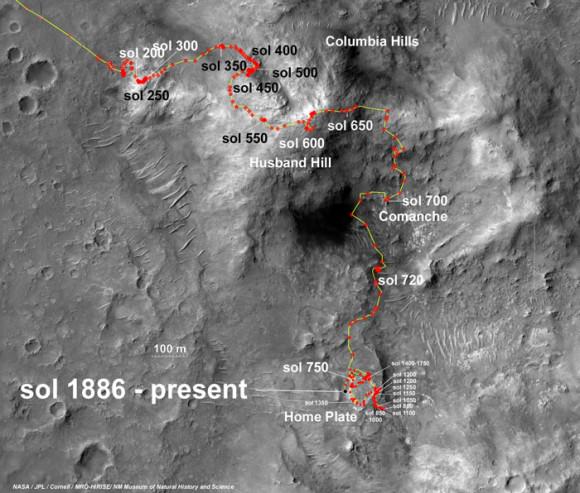
Spirit survived three harsh Martian winters and only succumbed to the Antarctic-like temperatures when she unexpectedly became mired in an unseen sand trap driving beside an ancient volcanic feature named ‘Home Plate’ that prevented the solar arrays from generating life giving power to safeguard critical electronic and computor components.
Spirit was heading towards another pair of volcanic objects named von Braun and Goddard and came within just a few hundred feet when she died.

It took Spirit three days, sols 620 to 622 (Oct. 1 to Oct. 3, 2005), to acquire all the images combined into this mosaic, called the "Everest Panorama". Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell University
Click to enlarge
“I never thought that we would still be planning sequences for Opportunity today and that we only lost Spirit because of her limited mobility and bad luck of breaking through crusty soil to get bogged down in loose sands,” said Arvidson
By the time of her last dispatch from Mars in March 2010, Spirit had triumphantly traversed the red planets terrain for more than six years of elapsed mission time – some 25 times beyond the three month “warranty” proclaimed by NASA as the mission began back in January 2004.

Husband Hill is 3.1 kilometers distant. Spirit took this mosaic of images with the panoramic camera at the beginning of February, 2004, less than a month after landing on Mars. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell
“I am feeling pretty good as the MER rover anniversaries approach in that Spirit had an excellent run, helping us understand without a doubt that early Mars had magmatic and volcanic activity that was “wet”, Arvidson explained.
“Magmas interacted with ground water to produce explosive eruptions – at Home Plate, Goddard, von Braun – with volcanic constructs replete with steam vents and perhaps hydrothermal pools.”
Altogether, the six wheeled Spirit drove over 4.8 miles (7.7 kilometers) and the cameras snapped over 128,000 images. NASA hoped the rovers would drive about a quarter mile during the planned 90 Sol mission.
“Milestones like 8 years on Mars always make me look forward rather than looking back,” Squyres told me.
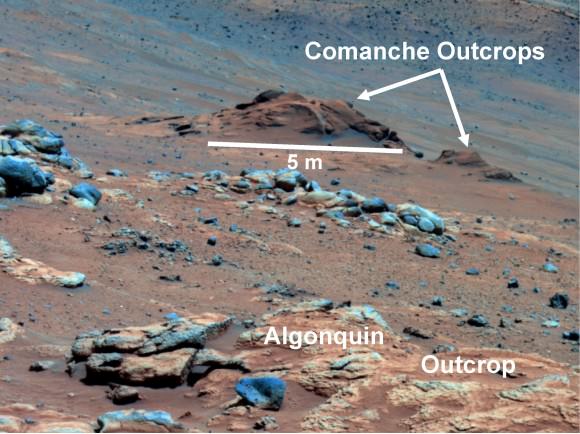

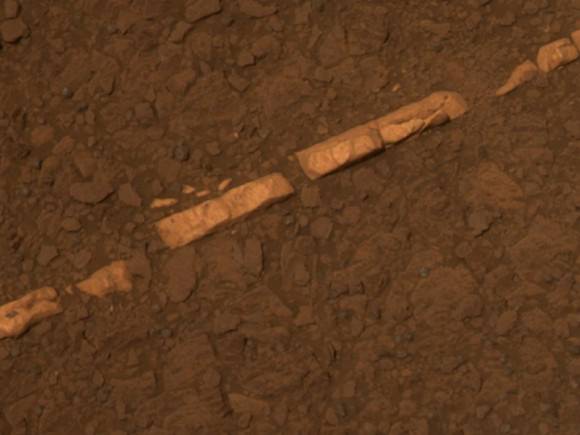
Spirit collected data in late 2005 which confirmed that the Comanche outcrop contains magnesium iron carbonate, a mineral indicating the past environment was wet and non-acidic, possibly favorable to life. This view was captured during Sol 689 on Mars (Dec. 11, 2005). The find at Comanche is the first unambiguous evidence from either Spirit or Opportunity for a past Martian environment that may have been more favorable to life than the wet but acidic conditions indicated by the rovers' earlier finds. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell University
Spirit became the first robotic emissary from humanity to climb a mountain beyond Earth, namely Husband Hill, a task for which she was not designed.
“No one expected the rovers to last so long,” said Rob Manning to Universe Today. Manning, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion laboratory, Pasadena, CA. was the Mars Rover Spacecraft System Engineering team lead for Entry, Descent and Landing (EDL)
“Spirit surmounted many obstacles, including summiting a formidable hill her designers never intended her to attempt.”
“Spirit, her designers, her builders, her testers, her handlers and I have a lot to be thankful for,” Manning told me.
After departing the Gusev crater landing pad, Spirit traversed over 2 miles to reach Husband Hill. In order to scale the hill, the team had to create a driving plan from scratch with no playbook because no one ever figured that such a mouthwatering opportunity to be offered.
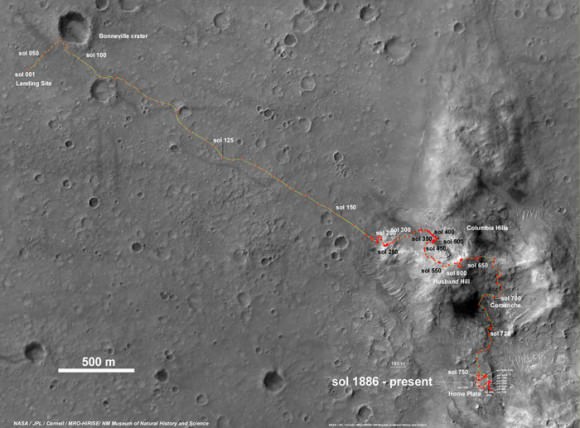

It took over a year to ascend to the hill’s summit. But the team was richly rewarded with a science bonanza of evidence for flowing liquid water on ancient Mars.
Spirit then descended down the other side of the hill to reach the feature dubbed Home Plate where she now rests and where she found extensive evidence of deposits of nearly pure silica, explosive volcanism and hot springs all indicative of water on Mars billions of years ago.
“Spirit’s big scientific accomplishments are the silica deposits at Home Plate, the carbonates at Comanche, and all the evidence for hydrothermal systems and explosive volcanism, Squyres explained. “ What we’ve learned is that early Mars at Spirit’s site was a hot, violent place, with hot springs, steam vents, and volcanic explosions. It was extraordinarily different from the Mars of today.”
“We’ve still got a lot of exploring to do [with Opportunity], but we’re doing it with a vehicle that was designed for a 90-sol mission,” Squyres concluded. “That means that ever sol is a gift at this point, and we have to push the rover and ourselves as hard as we can.”
NASA concluded the last attempt to communicate with Spirit in a transmission on May 25, 2011.

Spirit’s last panorama from Gusev Crater was taken during February 2010 before her death from extremely low temperatures during her 4th Martian winter. Spirit was just 500 feet from her next science target - dubbed Von Braun – at center, with Columbia Hills as backdrop.
Mosaic Credit: Marco De Lorenzo/ Kenneth Kremer/ NASA/JPL/Cornell University
Mosaic featured on Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) on 30 May 2011 - http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap110530.html
Meanwhile, the Curiosity Mars Science Lab rover, NASA’s next Red Planet explorer, continues her interplanetary journey on course for a 6 August 2012 landing at Gale Crater.
Read continuing features about the Mars Rovers, Curiosity and GRAIL by Ken Kremer here:
Two new Moons join the Moon – GRAIL Twins Achieve New Year’s Orbits
2011: Top Stories from the Best Year Ever for NASA Planetary Science!
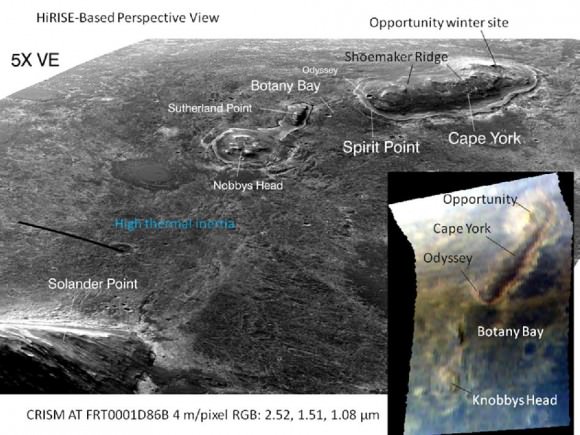
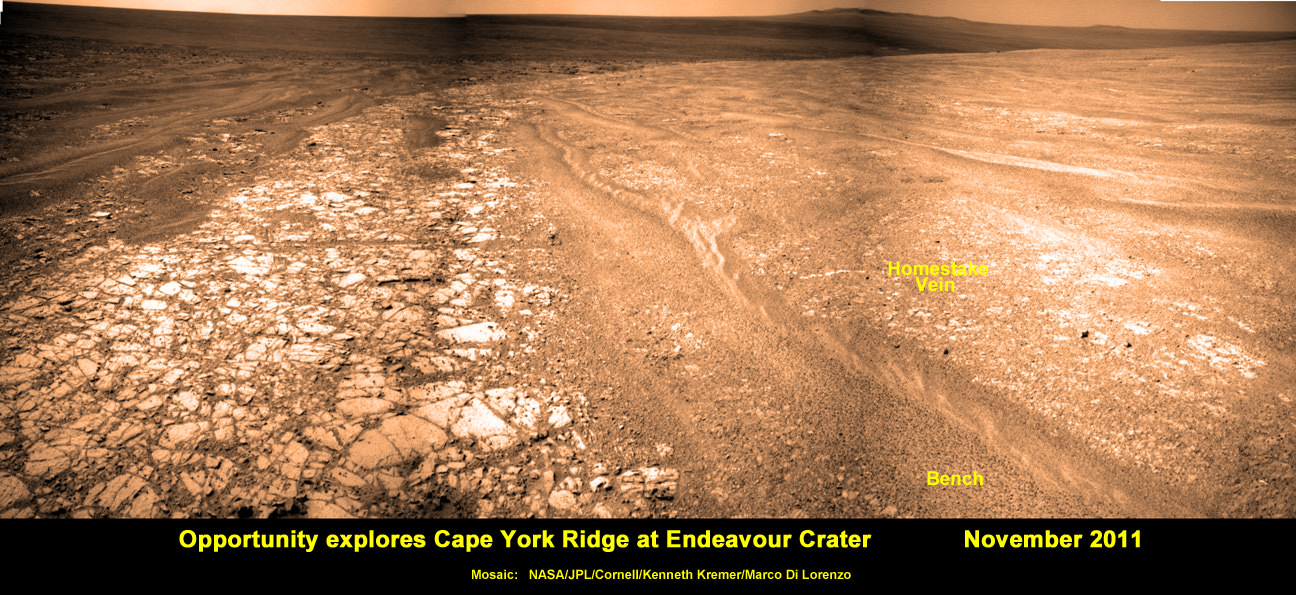
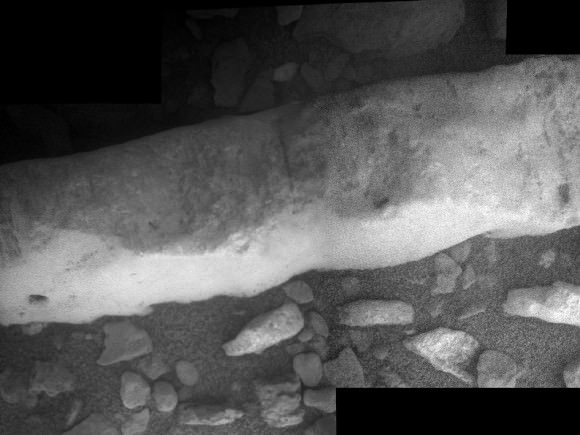
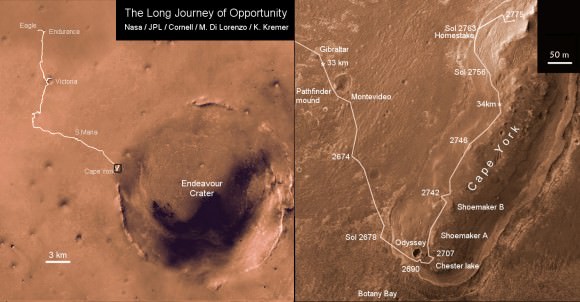
Opportunity Discovers Most Powerful Evidence Yet for Martian Liquid Water
Curiosity Starts First Science on Mars Sojurn – How Lethal is Space Radiation to Life’s Survival
Jan 11: Free Lecture by Ken Kremer at the Franklin Institute, Philadelphia, PA at 8 PM for the Rittenhouse Astronomical Society. Topic: Mars & Vesta in 3 D – Plus Search for Life & GRAIL