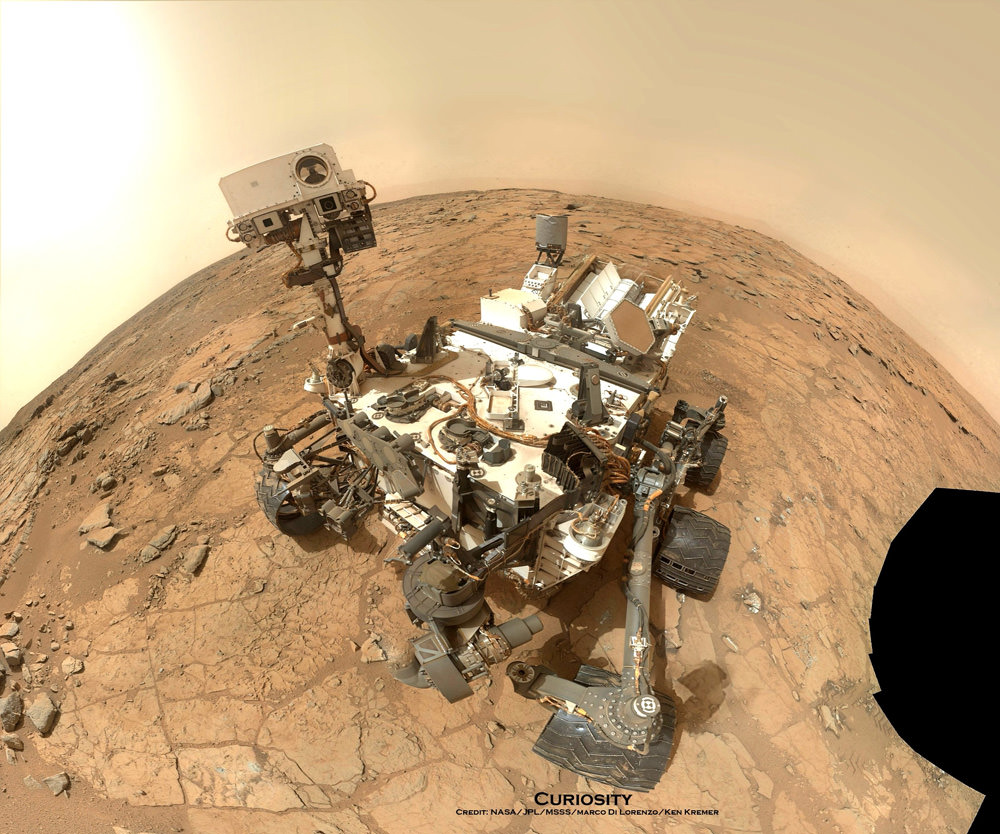
NASA’s planetary senior review panel harshly criticized the scientific return of the Curiosity rover in a report released yesterday (Sept. 3), saying the mission lacks focus and the team is taking actions that show they think the $2.5-billion mission is “too big to fail.”
While the review did recommend the mission receive more funding — along with the other six NASA extended planetary missions being scrutinized — members recommended making several changes to the mission. One of them would be reducing the distance that Curiosity drives in favor of doing more detailed investigations when it stops.
The role of the senior review, which is held every two years, is to help NASA decide what money should be allocated to its extended missions. This is important, because the agency (as with many other departments) has limited funds and tries to seek a balance between spending money on new missions and keeping older ones going strong.
Engineering acumen means that many missions are now operating well past their expiry dates, such as the Cassini orbiter at Saturn and the Opportunity rover on Mars. In examining the seven missions being reviewed, the panel did recommend keeping funding for all, but said that 4/7 are facing significant problems.

In the case of Curiosity, the panel called out principal investigator John Grotzinger for not showing up in person on two occasions, preferring instead to interact by phone. The review also said there is a “lack of science” in its extended mission proposal with regard to “scientific questions to be answered, testable hypotheses, and proposed measurements and assessment of uncertainties and limitations.”
Other concerns were the small number of samples over the prime and extended missions (13, a “poor science return”), and a lack of clarity on how the ChemCam and Mastcam instruments will play into the extended mission. Additionally, the panel expressed concern that NASA would cut short its observations of clays (which could help answer questions of habitability) in favor of heading to Mount Sharp, the mission’s ultimate science destination.
“In summary, the Curiosity … proposal lacked scientific focus and detail,” the panel concluded, adding in its general recommendations for the reviews that principal investigators must be present to avoid confusion while answering questions. The other missions facing concern from the panel included the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, Mars Express and Mars Odyssey.

LRO: Its extended mission (the second) is supposed to look at how the moon’s surface, subsurface and exosphere changes through processes such as meteorites and interaction with space. The panel was concerned with a “lack of detail” in the proposal and in answers to follow-up questions. The panel also recommended turning off certain instruments “at the end of their useful science mission”.
Mars Express: The extended mission is focusing on the ionosphere and atmosphere as well as the planet’s surface and subsurface. Concerns were raised about matters such as why funding is needed to calibrate its high-resolution stereo camera after 11 years — especially given the instrument has been rarely cited in published journal reports lately — and how people involved in the extended mission would meet the goals. The panel also saw a “lack of communication” in the team.
Mars Odyssey: If approved, the spacecraft will move to the day/night line of Mars to look at the planet’s radiation, gamma rays, distribution of water/carbon dioxide/dust in the atmosphere, and the planet’s surface. The panel, however, said there are no “convincing arguments” as to how the new science relates to the Decadal Survey objectives for planetary science. Odyssey, which is in its 11th year, may also be nearing the end of its productive lifespan given fewer publications using its data in recent years, the panel said.
The panel also weighed in on the success of the Cassini and Opportunity missions:

Cassini received the highest rating — “Excellent” — due to its scientific merit, the only mission this time around to do so. The panel was particularly excited about seasonal changes that will be seen on Titan in the coming years, as well as measurements of Saturn’s rings and magnetosphere and its icier moons (such as Enceladus). The spacecraft is noted to be in good condition and the new mission will be a success because of “the unique aspect of the new observations.”
Opportunity, which is more than 10 years into its Mars exploration, is still “in sufficiently good condition” to do science, although the panel raised concerns about software and communication problems. The panel, however, said more time with the rover would allow it to look for evidence of past water on Mars that would not be visible from orbit — even though it’s unclear if phyllosilicates around its current location (Endeavour crater) are from the Noachian period, the earliest period in Mars’ history.
The panel is just one step along the road to figuring out how NASA chooses to spend its money in the coming years. Funding availability depends on how much money Congress allocates to the agency.