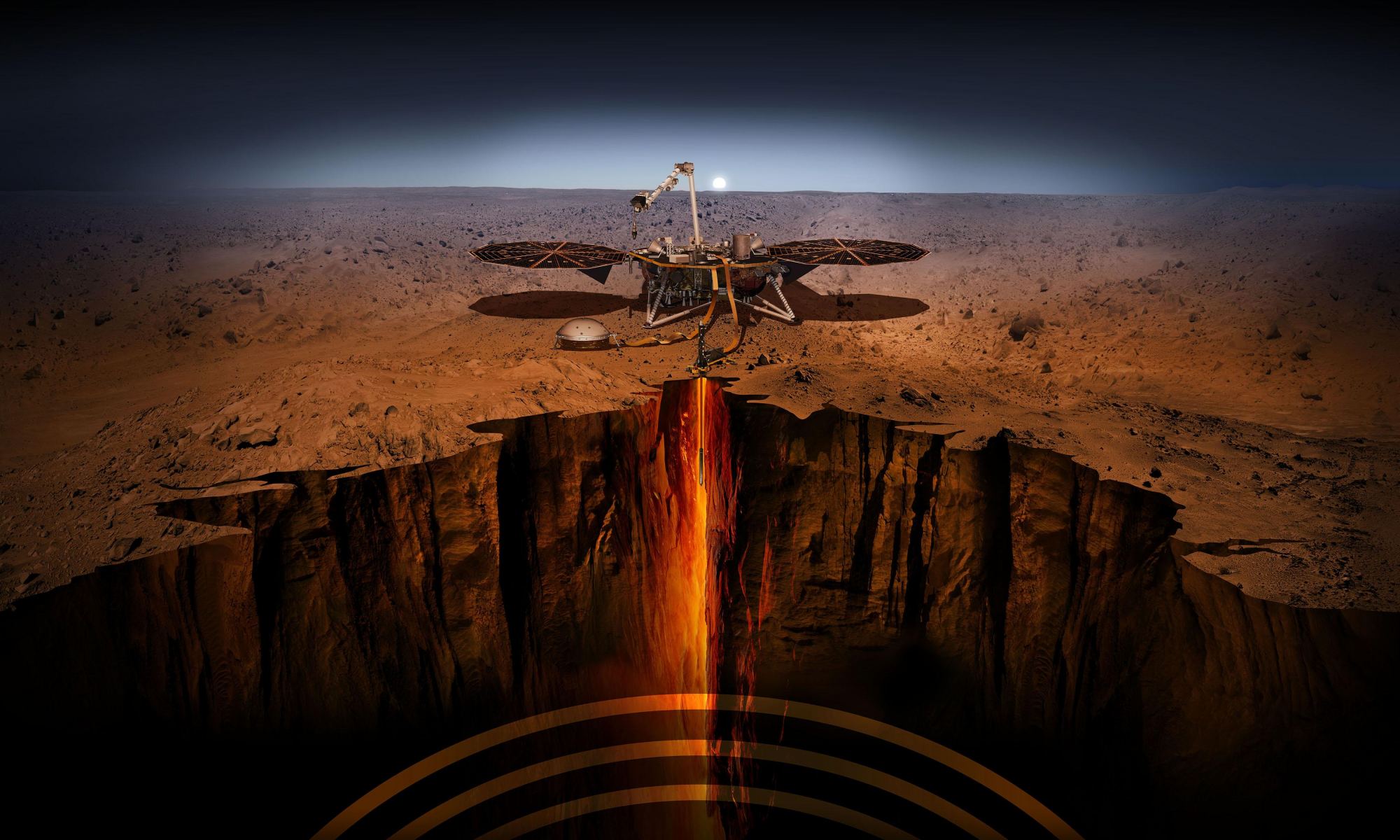
Since February 2019, NASA’s Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) lander has been making the first-ever measurements of tectonics on another planet. The key to this is InSight’s Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) instrument (developed by seismologists and geophysicists at ETH Zurich), which has been on the surface listening for signs of “marsquakes.” The dataset it has gathered (over 1,300 seismic events) has largely confirmed what planetary scientists have long suspected: that Mars is largely quiet.
However, a research team led by ETH Zurich recently analyzed a cluster of more than 20 recent marsquakes, which revealed something very interesting. Based on the location and spectral character of these events, they determined that most of Mars’ widely distributed surface faults are not seismically active. Nevertheless, most of the 20 seismic events observed originated in the vicinity of Cerberus Fossae, a region consisting of rifts (or graben). These results suggest that geological activity and volcanism still play an active role in shaping the Martian surface.
Continue reading “Mars is Mostly Dead. There's Still Magma Inside, so it's Slightly Alive”