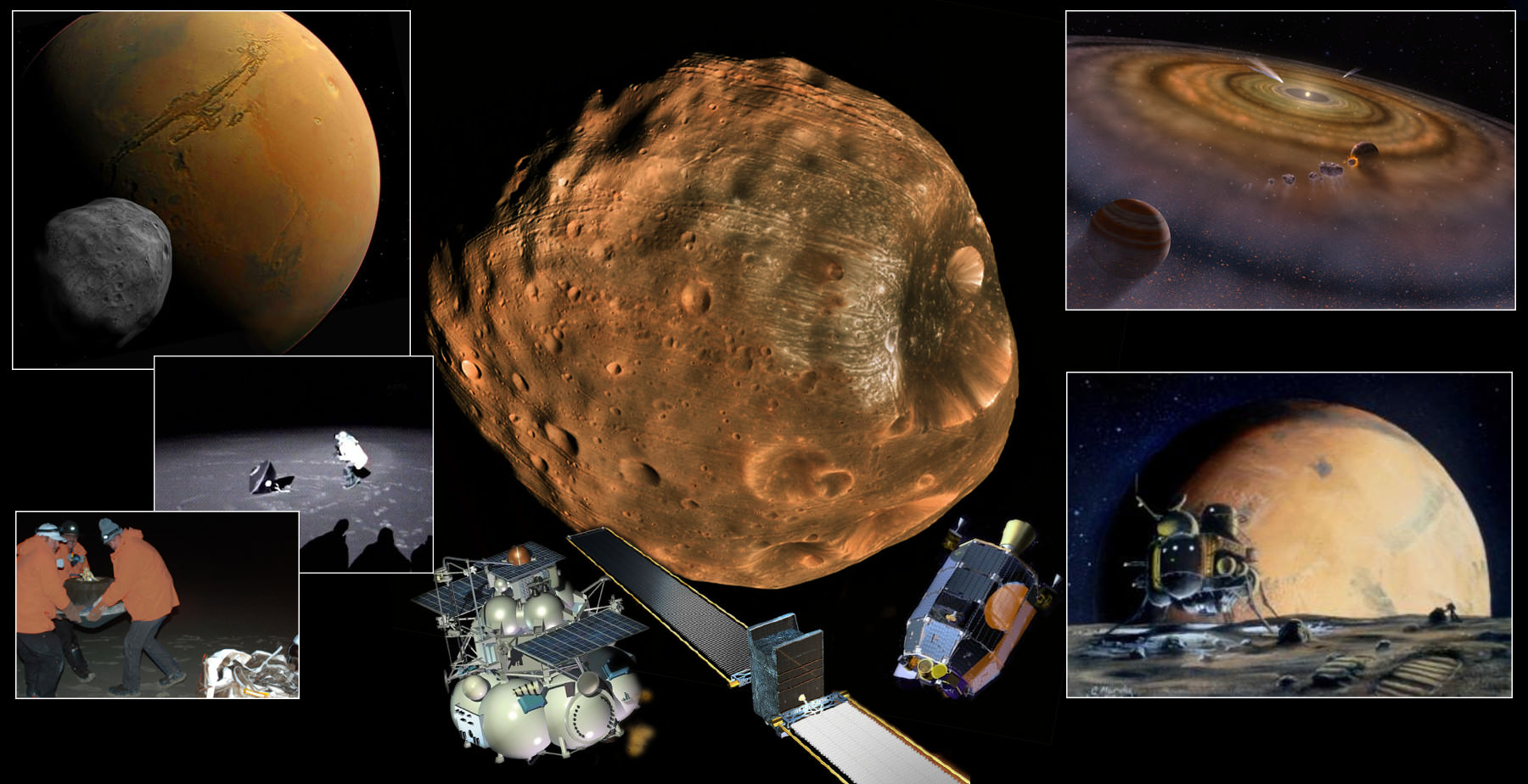
According to new research that appeared in the scientific journal Nature Geoscience, the larger of Mars’ two moons (Phobos) has an orbit that takes it through a stream of charged particles (ions) that flow from the Red Planet’s atmosphere. This process has been taking place for billions of years as the planet slowly lost its atmosphere, effectively establishing a record of Martian climate change on Phobos’ surface.
This research has provided yet another incentive for landing a mission on Phobos, something that has never been done successfully. In essence, this mission could gather sample data that would allow scientists to study this record more closely. In the process, they would be able to learn a great deal more about how Mars went from being a warmer world with liquid water to the extremely arid and cold environment it is today.
Continue reading “What Could We Learn From a Mission to Phobos?”