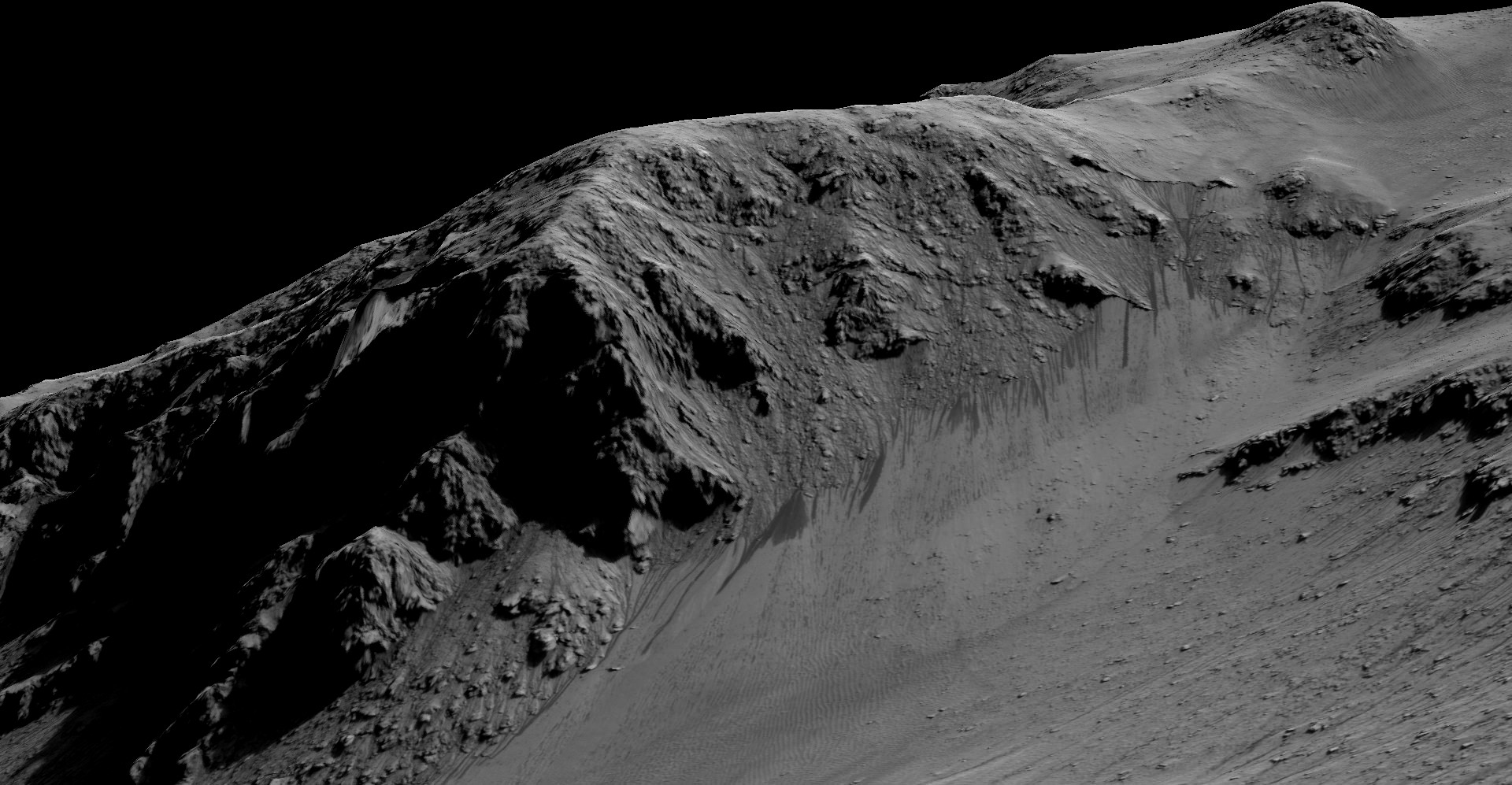
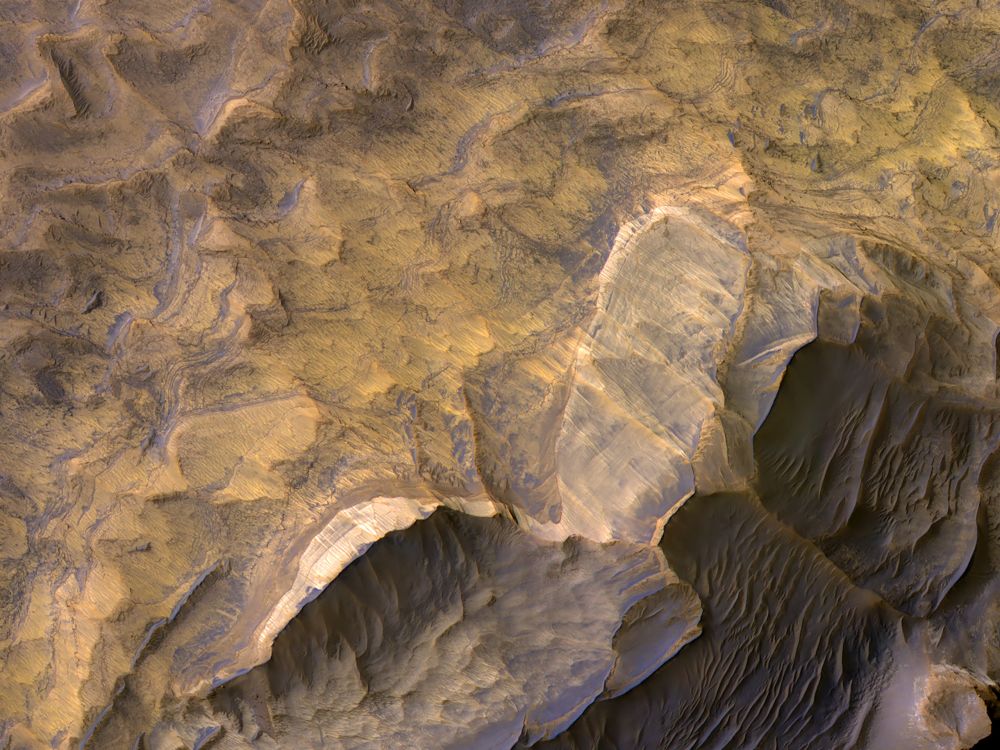
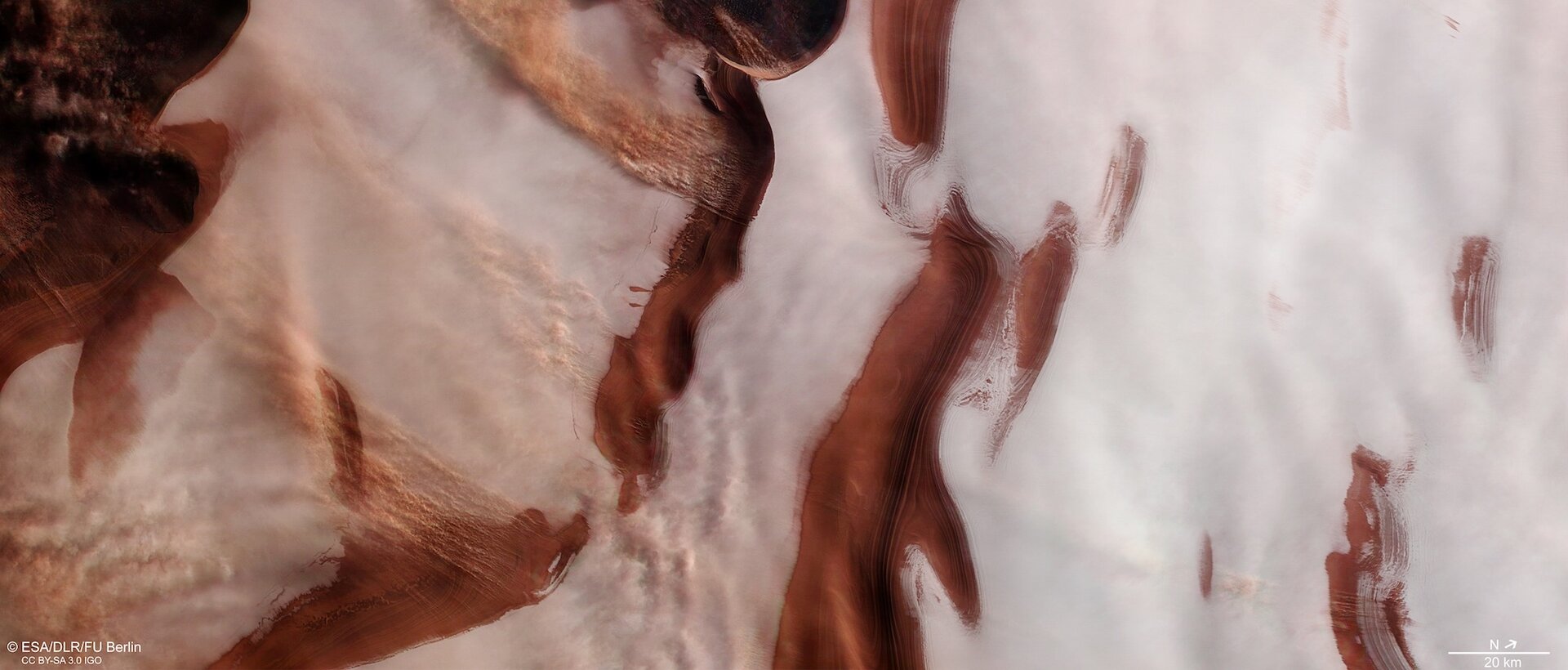
Billions of years ago, Mars had liquid water on its surface in the form of lakes, streams, and even an ocean that covered much of its northern hemisphere. The evidence of this warmer, wetter past is written in many places across the landscape in the form of alluvial fans, deltas, and mineral-rich clay deposits. However, for over half a century, scientists have been debating whether or not liquid water exists on Mars today.
According to new research by Norbert Schorghofer – the Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute – briny water may form intermittently on the surface of Mars. While very short-lived (just a few days a year), the potential presence of seasonal brines on the Martian surface would tell us much about the seasonal cycles of the Red Planet, as well as help to resolve one of its most enduring mysteries.
Continue reading “Salt Water Might Still be Able to Collect on the Surface of Mars a Few Days a Year”