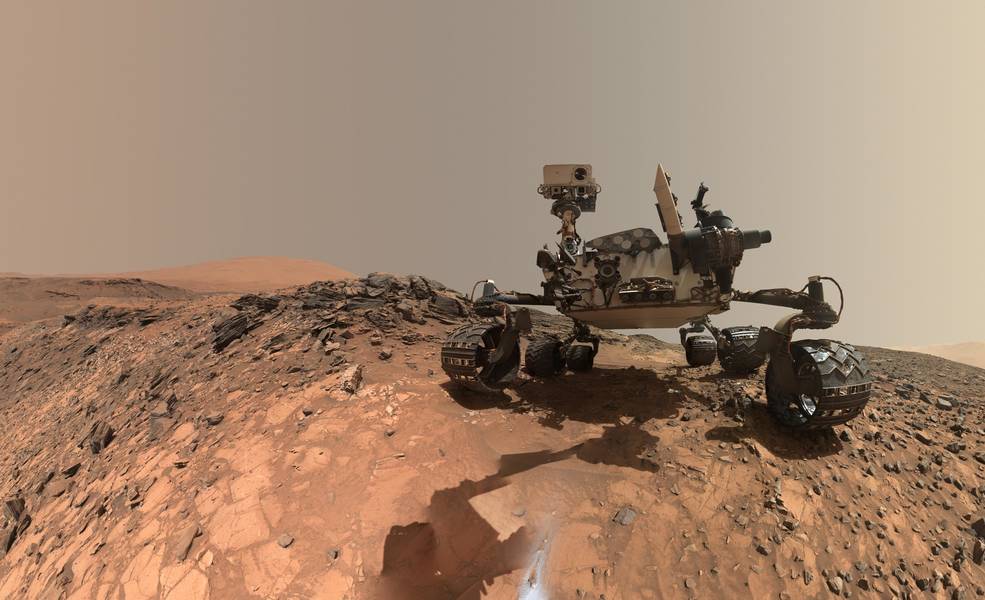
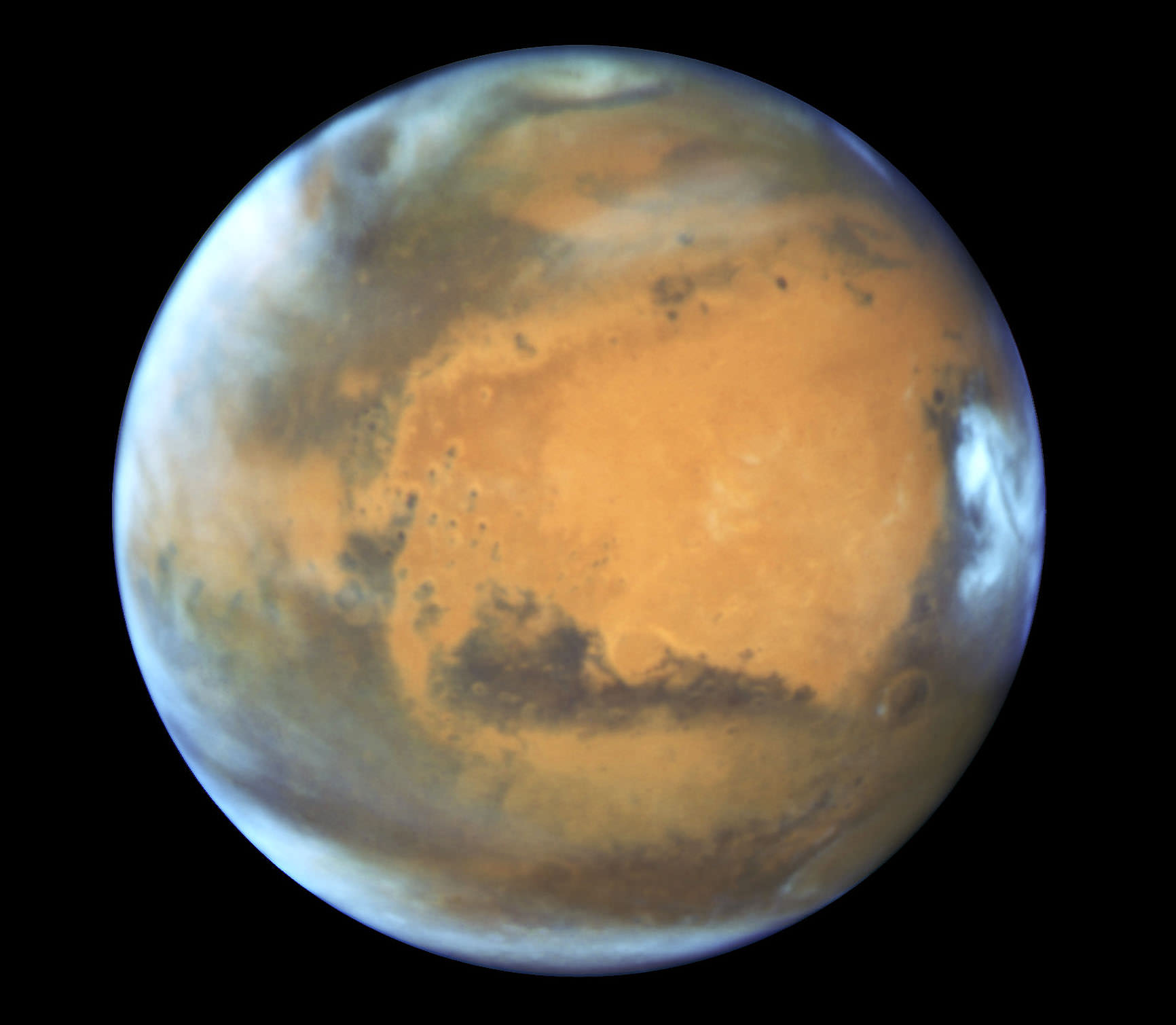
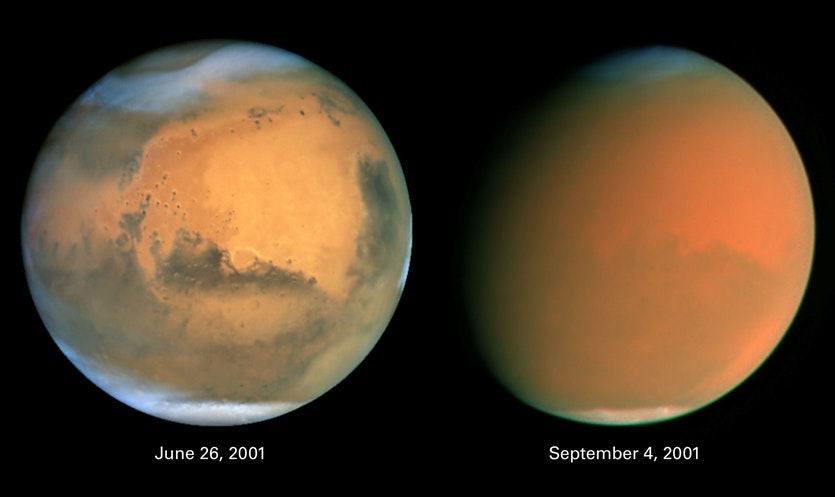
For centuries, scientists have speculated about the existence of life on Mars. But it was only within the past 15 years that the search for life (past and present) really began to heat up. It was at this time that methane, an organic molecule that is associated with many forms of life here on Earth (i.e. a “biosignature”) was detected in Mars’ atmosphere.
Since that time, attempts to study Mars’ atmospheric methane have produced varying results. In some cases, methane has been found that was several times its normal concentrations; in others, it was absent. Seeking to answer this mystery, an interdisciplinary team from Aarhus