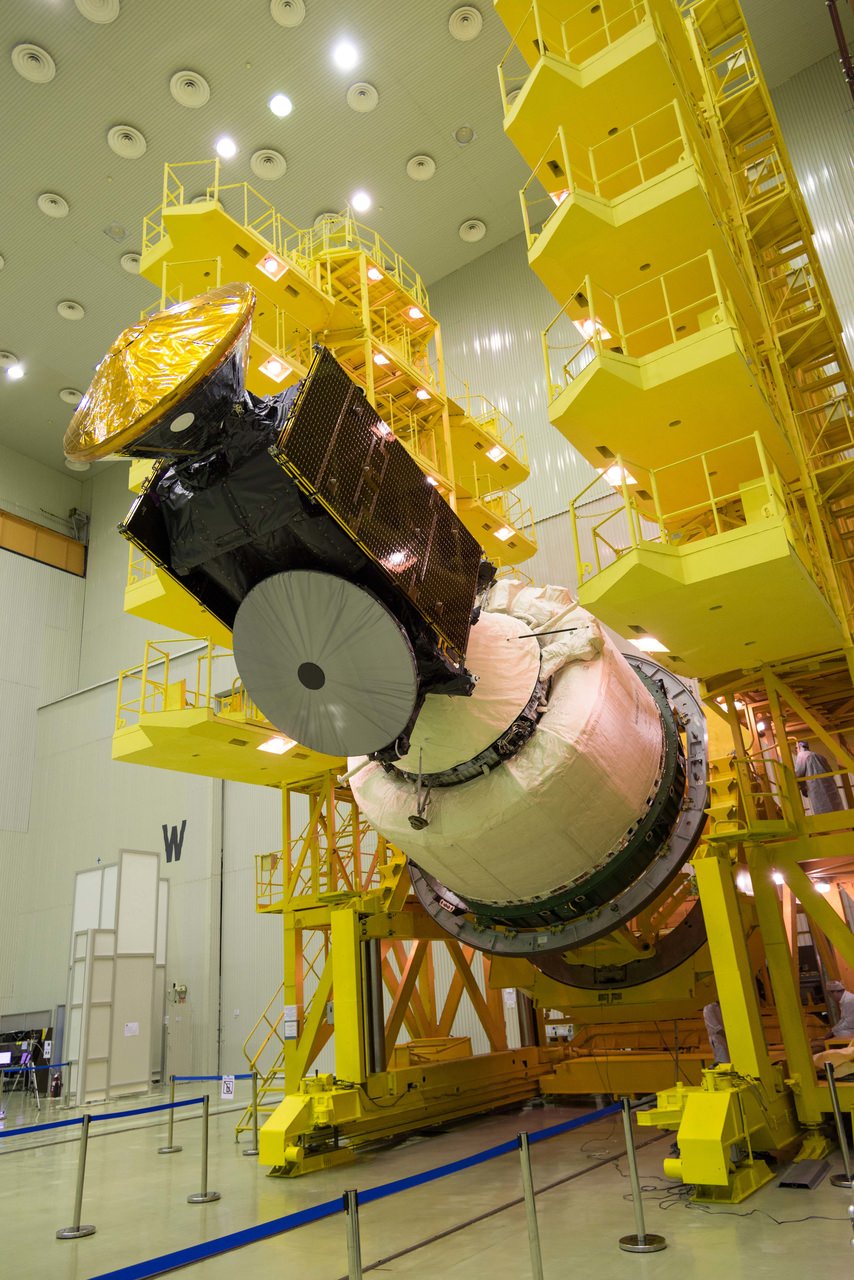
The cooperative Euro-Russian ExoMars 2016 expedition is now en route to the Red Planet after successfully firing its upper stage booster one final time on Monday evening, March 15, to blast free of the Earth’s gravitational tug and begin a 500 million kilometer interplanetary journey in a bold search of indications of life emanating from potential Martian microbes.
The vehicle is in “good health” with the solar panels unfurled, generating power and on course for the 500 Million kilometer (300 million mile) journey to Mars.
“Acquisition of signal confirmed. We have a mission to Mars!” announced Mission Control from the European Space Agency.
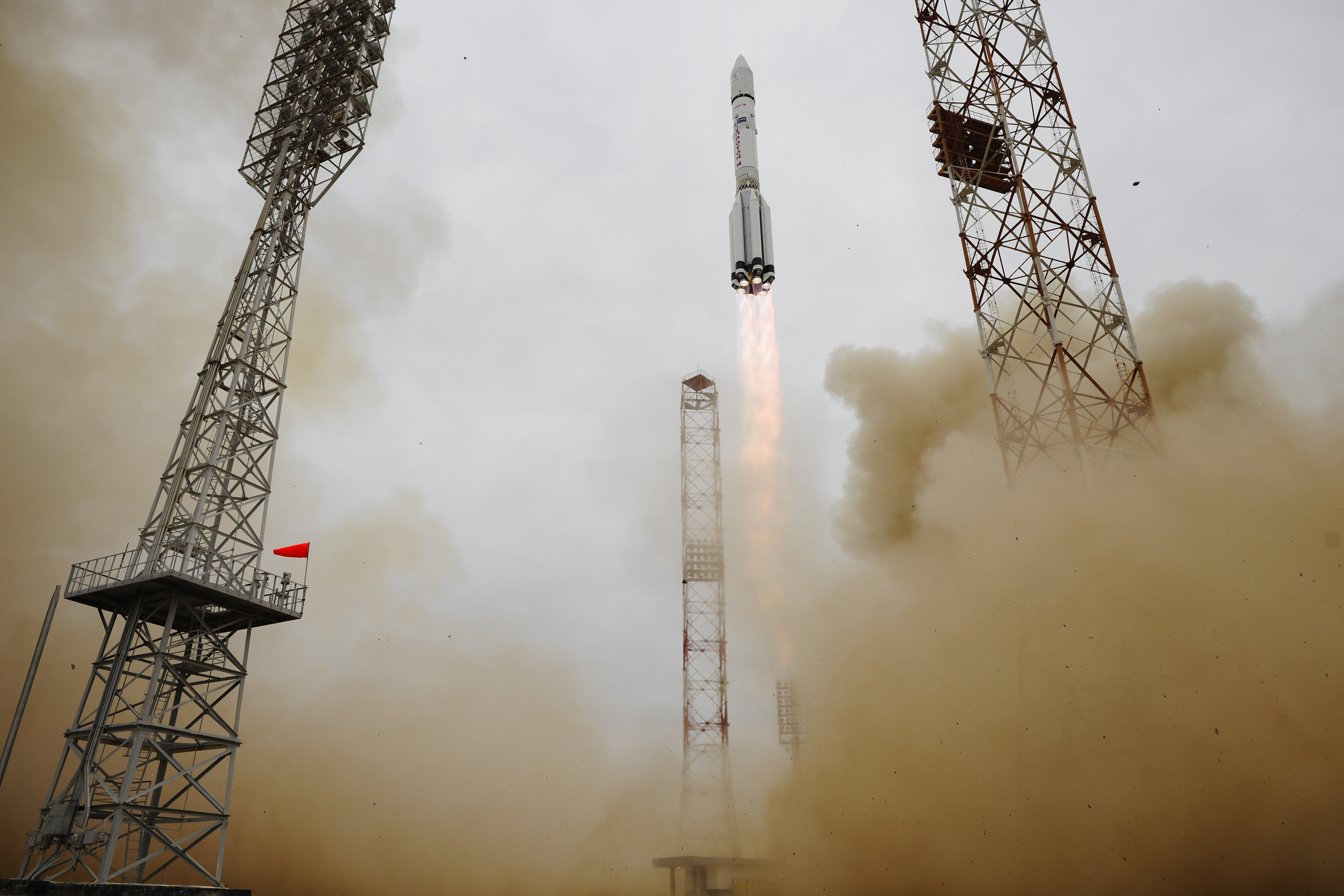
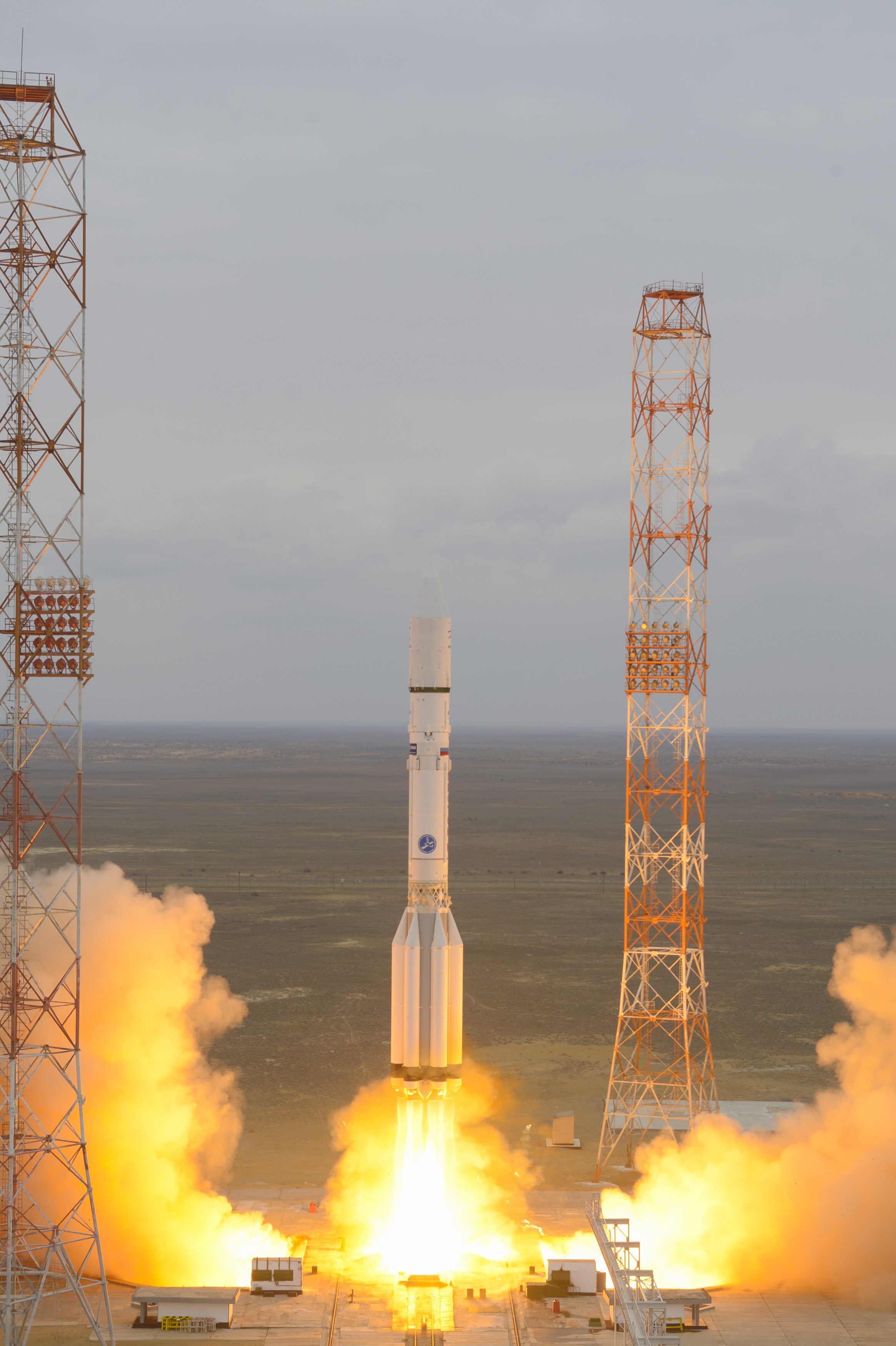
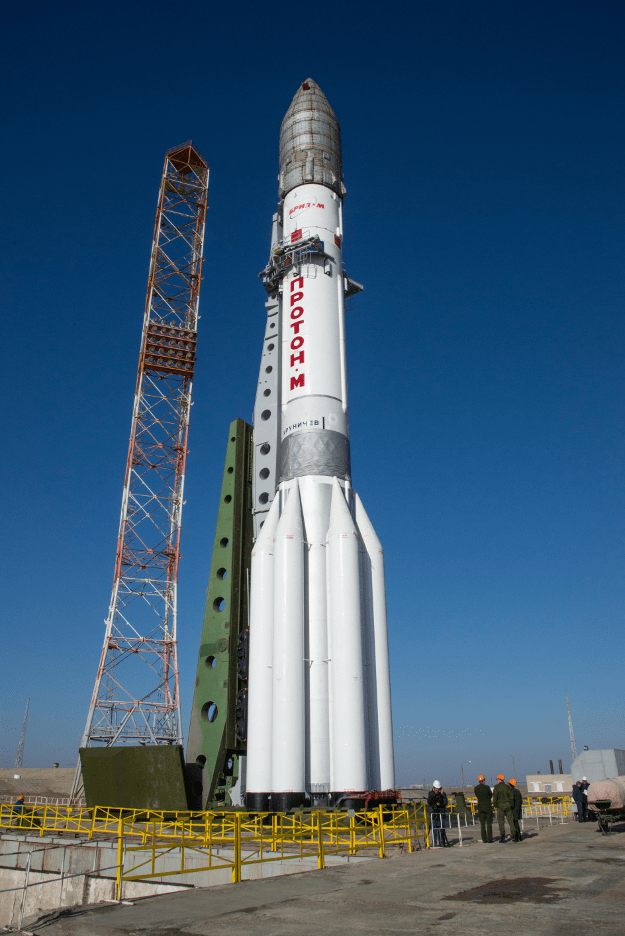
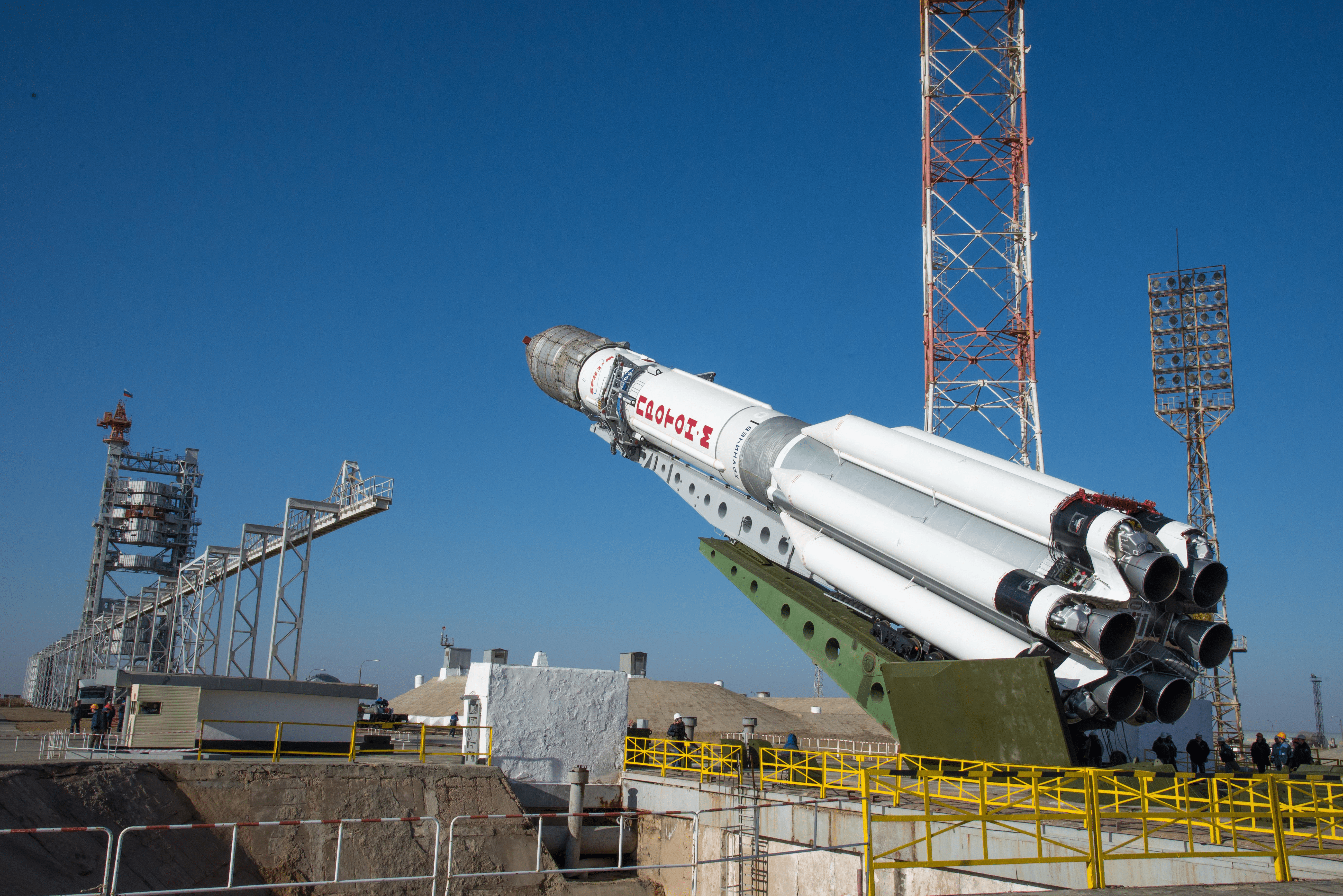
The joint European/Russian ExoMars spacecraft successfully blasted off from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan atop a Russian Proton-M rocket at 5:31:42 a.m. EDT (0931:42 GMT), Monday, March 14, with the goal of searching for possible signatures of life in the form of trace amounts of atmospheric methane on the Red Planet.
Video caption: Blastoff of Russian Proton rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome carrying ExoMars 2016 mission on March 14, 2016. Credit: Roscosmos
The first three stages of the 191-foot-tall (58-meter) Russian-built rocket fired as scheduled over the first ten minutes and lofted the 9,550-pound (4,332-kilogram) ExoMars to orbit.
Three more firings from the Breeze-M fourth stage quickly raised the probe into progressively higher temporary parking orbits around Earth.
But the science and engineering teams from the European Space Agency (ESA) and Roscosmos had to keep their fingers crossed and endure an agonizingly long wait of more than 10 hours before the fourth and final ignition of the Proton’s Breeze-M upper stage required to break the bonds of Earth.
The do or die last Breeze-M upper stage burn with ExoMars still attached was finally fired exactly as planned.
The probe was released at last from the Breeze at 20:13 GMT.
However, it took another long hour to corroborate the missions true success until the first acquisition of signal (AOS) from the spacecraft was received at ESA’s control centre in Darmstadt, Germany via the Malindi ground tracking station in Africa at 5:21:29 p.m. EST (21:29 GMT), confirming a fully successful launch with the spacecraft in good health.
It was propelled outwards to begin a seven-month-long journey to the Red Planet to the great relief of everyone involved from ESA, Roscosmos and other nations participating. An upper stage failure caused the total loss of Russia’s prior mission to Mars; Phobos-Grunt.
“Only the process of collaboration produces the best technical solutions for great research results. Roscosmos and ESA are confident of the mission’s success,” said Igor Komarov, General Director of the Roscosmos State Space Corporation, in a statement.
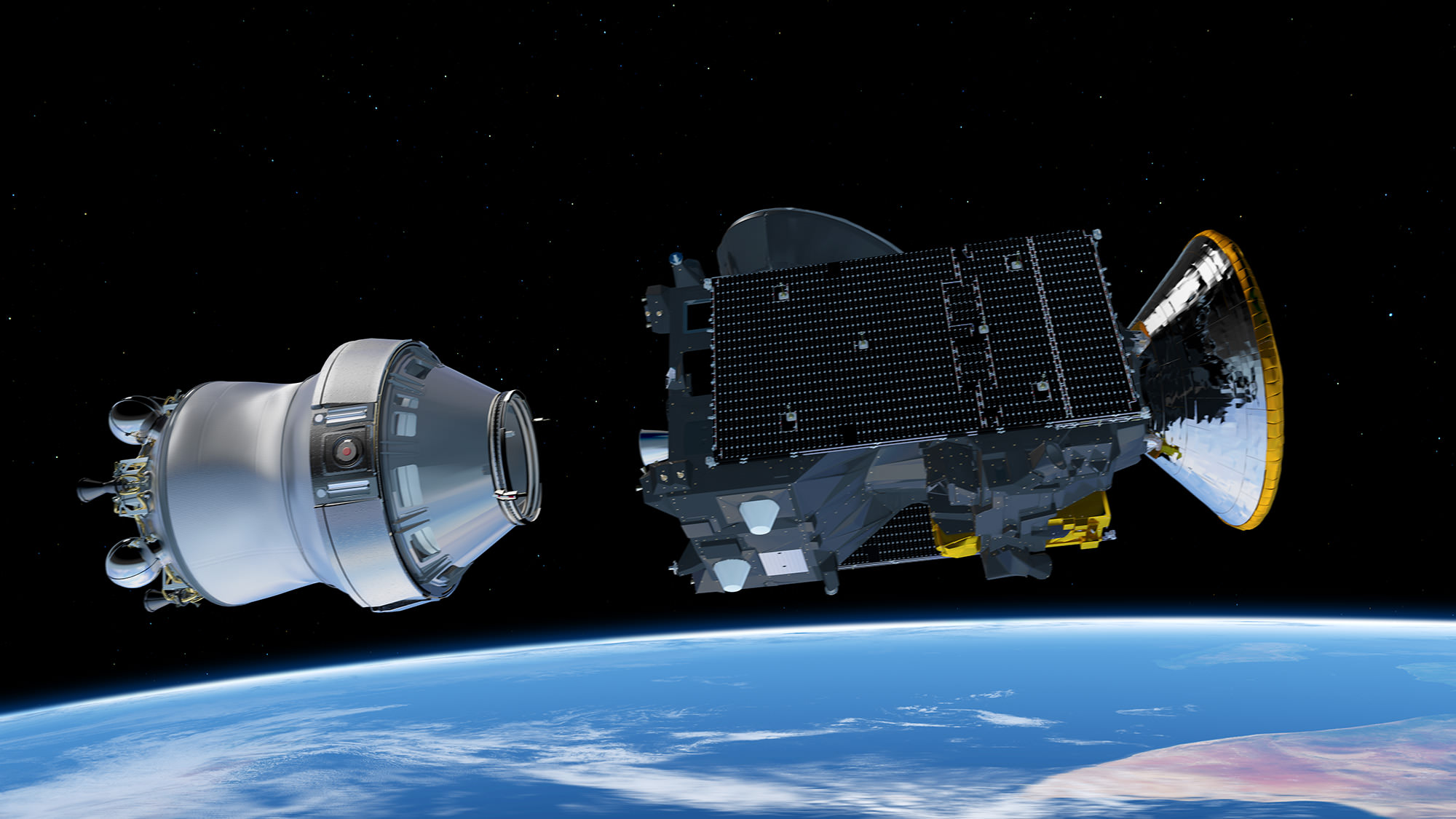
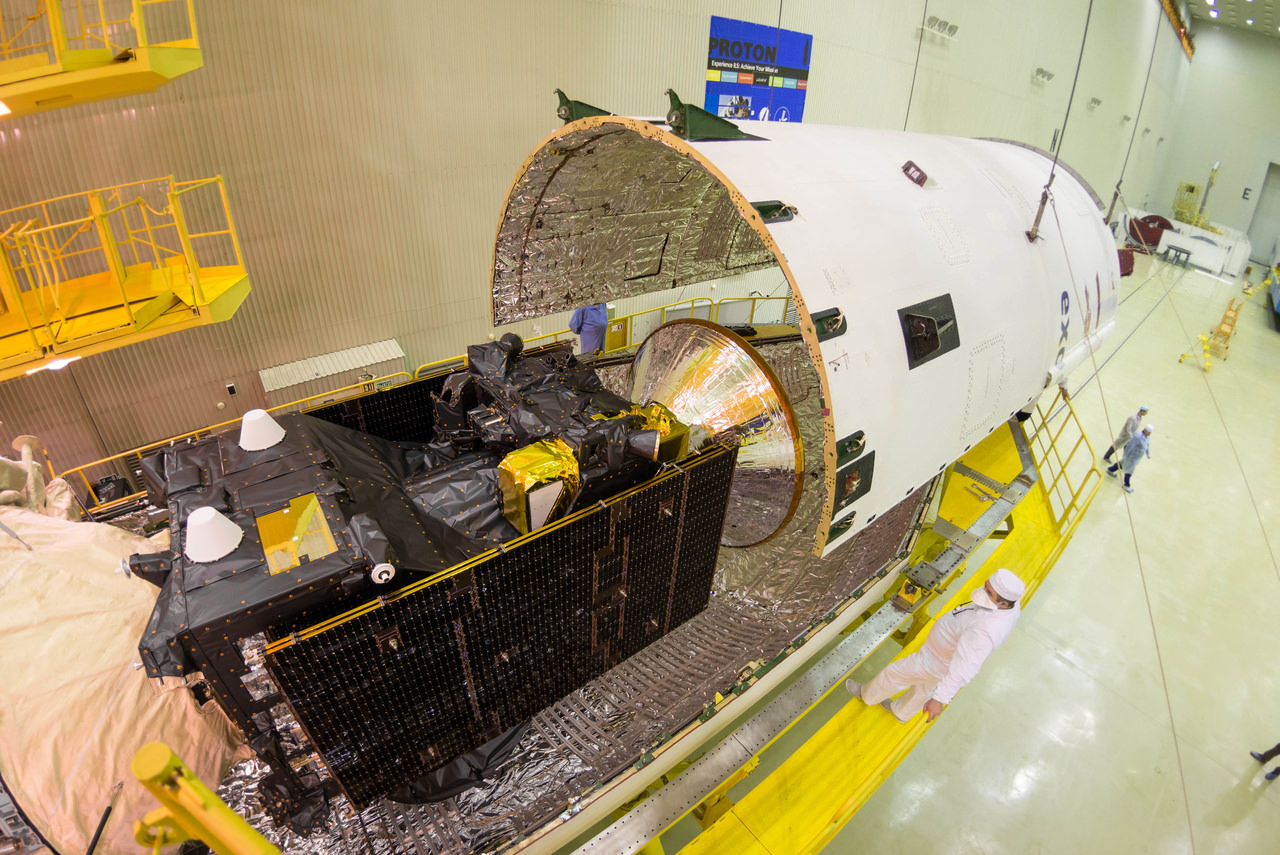
The ExoMars 2016 mission is comprised of a joined pair of European-built spacecraft consisting of the Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) plus the Schiaparelli entry, descent and landing demonstrator module, built and funded by ESA.
“It’s been a long journey getting the first ExoMars mission to the launch pad, but thanks to the hard work and dedication of our international teams, a new era of Mars exploration is now within our reach,” says Johann-Dietrich Woerner, ESA’s Director General.
“I am grateful to our Russian partner, who have given this mission the best possible start today. Now we will explore Mars together.”

The cooperative mission includes significant participation from the Russian space agency Roscosmos who provided the Proton-M launcher, part of the science instrument package, the surface platform and ground station support.
The Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and Schiaparelli lander are speeding towards Mars joined together, on a collision course for the Red Planet. They will separate on October 16, 2016 at distance of 900,000 km from the planet, three days before arriving on October 19, 2016.
TGO will fire thrusters to alter course and enter an initial four-day elliptical orbit around the fourth planet from the sun ranging from 300 km at its perigee to 96 000 km at its apogee, or furthest point.
Over the next year, engineers will command TGO to fire thrusters and conduct a complex series of ‘aerobraking’ manoeuvres that will gradually lower the spacecraft to circular 400 km (250 mi) orbit above the surface.
The science mission to analyse for rare gases, including methane, in the thin Martian atmosphere at the nominal orbit is expected to begin in December 2017.
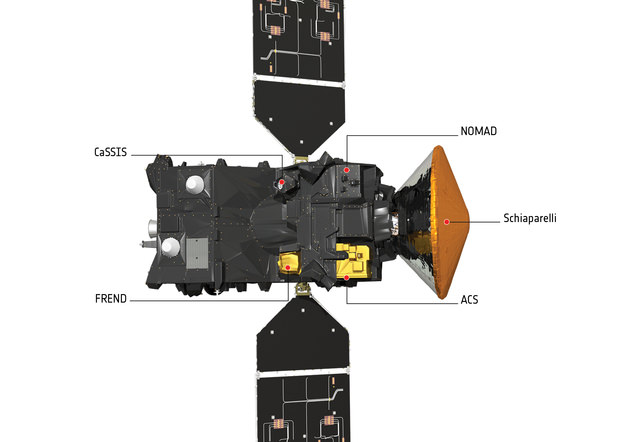
ESA/ATG medialab
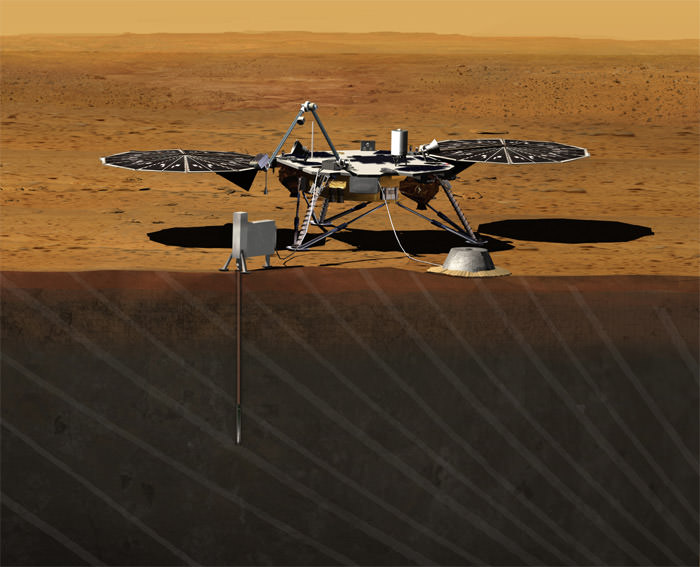
As TGO enters orbit, the Schiaparelli lander will smash into the atmosphere and begin a harrowing six minute descent to the surface.
The main purpose of Schiaparelli is to demonstrate key entry, descent, and landing technologies for the follow on 2nd ExoMars mission in 2018 that will land the first European rover on the Red Planet.
The battery powered lander is expected to operate for perhaps four and up to eight days until the battery is depleted.
It will conduct a number of environmental science studies such as “obtaining the first measurements of electric fields on the surface of Mars that, combined with measurements of the concentration of atmospheric dust, will provide new insights into the role of electric forces on dust lifting – the trigger for dust storms,” according to ESA.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.











 Martian Eye Candy: A beautiful picture of some dunes on the surface of Mars. Thanks MRO! (Image: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona)
Martian Eye Candy: A beautiful picture of some dunes on the surface of Mars. Thanks MRO! (Image: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona)
