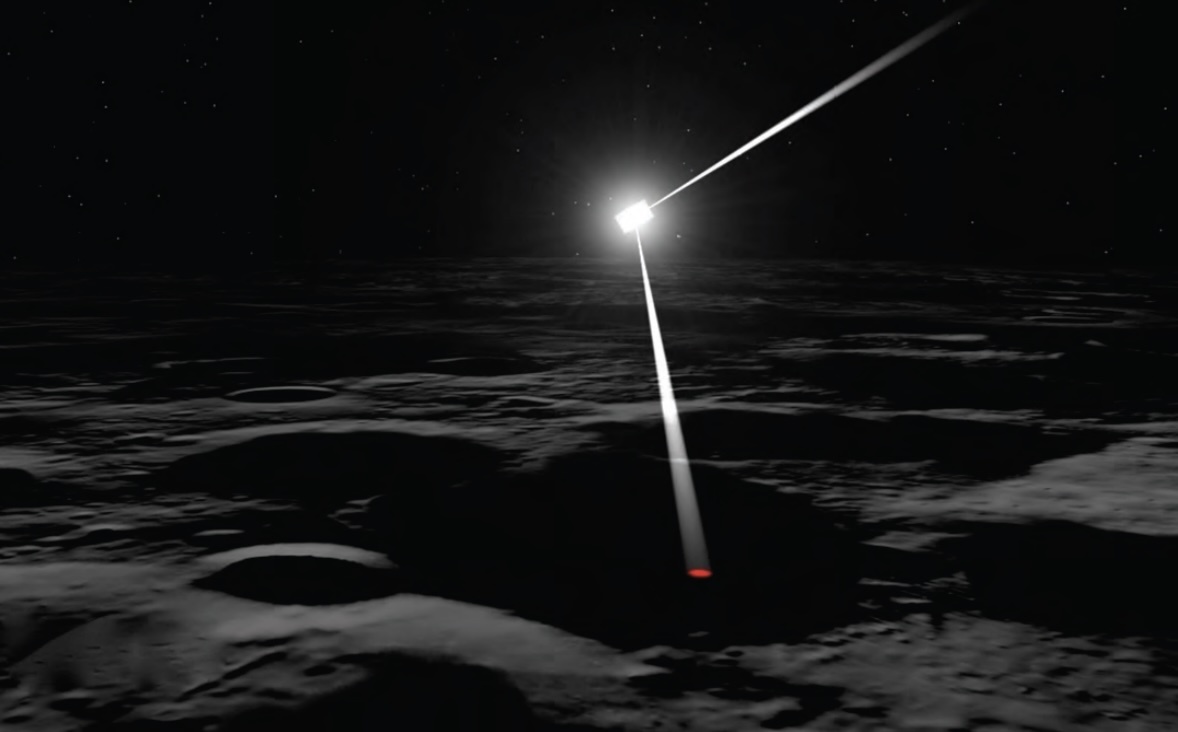
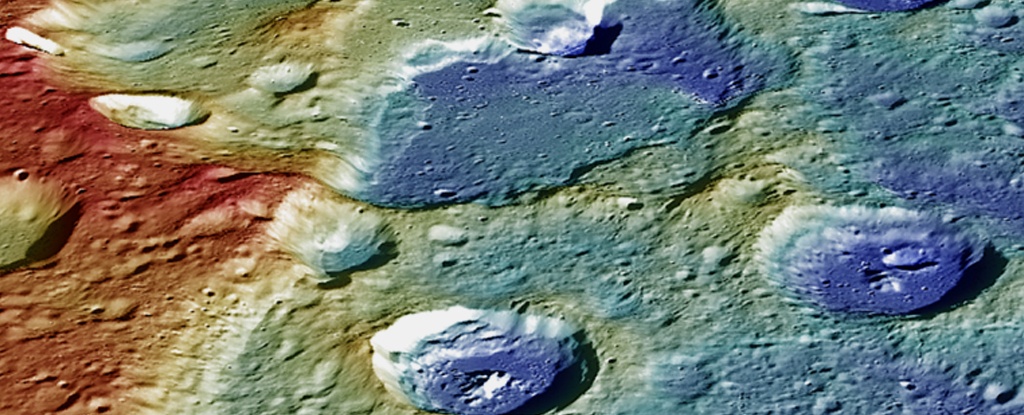
It’s not unusual for space probes to complete gravitational flyby manoeuvres en route to their destination. It’s a bit more unusual when the flyby is at the destination planet. ESA’s BepiColombo spacecraft is manoeuvring around Mercury into its final orbit. With each flyby it gets closer and closer and closer until its finally captured by Mercury’s gravity in 2026. During the latest flyby, stunning images of the nearest planet to the Sun were captured from just a few hundred km. Checkout the best and most stunning images of Mercury yet.
BepiColombo’s New Images of Mercury are Cool

The ESA/JAXA BepiColombo spacecraft made another flyby of its eventual target, Mercury. This is one of a series of Mercury flybys, as the spacecraft completes a complex set of maneuvers designed to deliver it to the innermost planet’s orbit. Its cameras captured some fantastic images of Mercury.
Continue reading “BepiColombo’s New Images of Mercury are Cool”Mercury Could be Housing a Megafortune Worth of Diamonds!

Mercury, the closest planet to our Sun, is also one of the least understood in the Solar System. On the one hand, it is similar in composition to Earth and the other rocky planets, consisting of silicate minerals and metals differentiated between a silicate crust and mantle and an iron-nickel core. But unlike the other rocky planets, Mercury’s core makes up a much larger part of its mass fraction. Mercury also has a mysteriously persistent magnetic field that scientists still cannot explain. In this respect, Mercury is also one of the most interesting planets in the Solar System.
But according to new research, Mercury could be much more interesting than previously thought. Based on new simulations of Mercury’s early evolution, a team of Chinese and Belgian geoscientists found evidence that Mercury may have a layer of solid diamond beneath its crust. According to their simulations, this layer is 15 km (9 mi) thick sandwiched between the core and the mantle hundreds of miles beneath the surface. While this makes the diamonds inaccessible (for now, at least), these findings could have implications for theories about the formation and evolution of rocky planets.
Continue reading “Mercury Could be Housing a Megafortune Worth of Diamonds!”The BepiColombo Mission To Mercury is Losing Power
BepiColombo is a joint ESA/JAXA mission to Mercury. It was launched in 2018 on a complex trajectory to the Solar System’s innermost planet. The ESA reports that the spacecraft’s thrusters have lost some power.
Continue reading “The BepiColombo Mission To Mercury is Losing Power”Mercury is the Perfect Destination for a Solar Sail
Solar sails rely upon pressure exerted by sunlight on large surfaces. Get the sail closer to the Sun and not surprisingly efficiency increases. A proposed new mission called Mercury Scout aims to take advantage of this to explore Mercury. The mission will map the Mercurian surface down to a resolution of 1 meter and, using the highly reflective sail surface to illuminate shadowed craters, could hunt for water deposits.
Continue reading “Mercury is the Perfect Destination for a Solar Sail”There Were Glaciers… on Mercury?

I have lost count of how many times I have given public lectures and explained the temperature differences between Mercury and Venus. How Mercury, surprisingly isn’t the hottest planet in the Solar System and how that badge goes to Venus, thick atmosphere blah blah blah. Mercury and its complex surface geology does of course get a good chunk of time but a recent paper has rather caught my attention and turned what I thought I knew about Mercury on its head! In short, a team of scientists have announced evidence for salt glaciers on Mercury!
Continue reading “There Were Glaciers… on Mercury?”The Solar Wind Whistles as it Passes Mercury
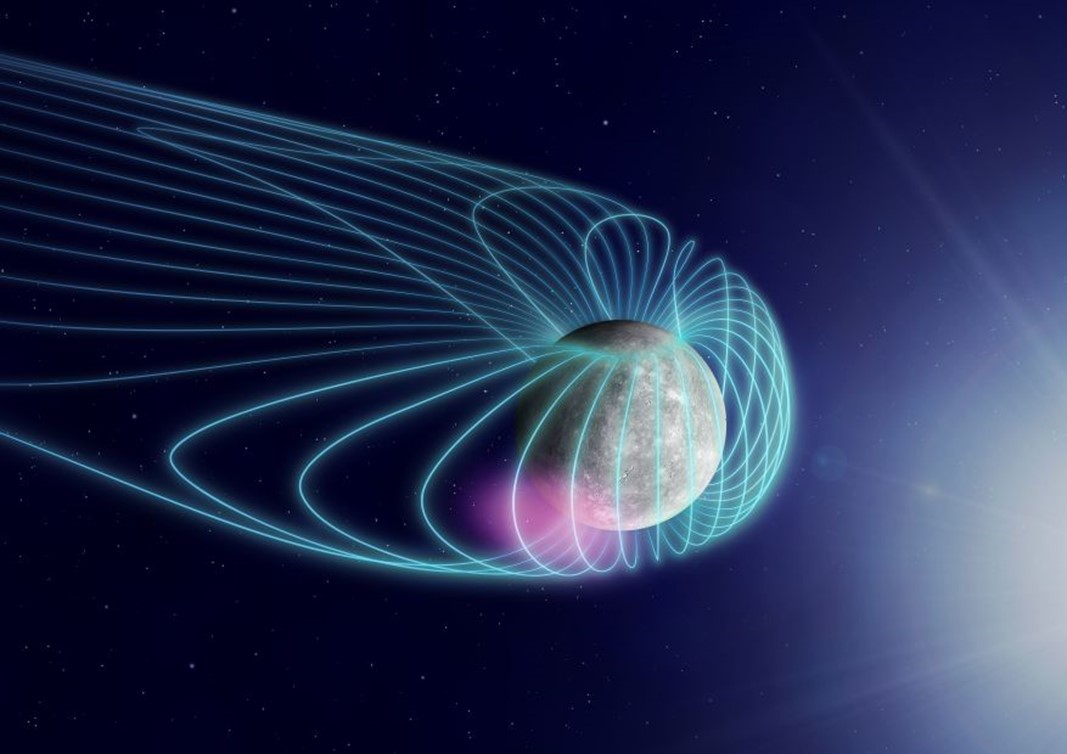
Mercury is the closest planet to our Sun, ranging from 46 million km (28.58 million mi) at perihelion to 69.82 million km (43.38 million mi) at aphelion. Because of its proximity, Mercury is strongly influenced by the steam of plasma constantly flowing from the Sun to the edge of the Solar System (aka. solar wind). Beginning with the Mariner 10 mission in 1974, robotic explorers have been sent to Mercury to measure how solar wind interacts with Mercury’s magnetic field to produce whistler-mode chorus waves – natural radio emissions that play a key role in electron acceleration in planetary magnetospheres.
In addition to being the cause of geomagnetic storms and auroras in planetary atmospheres, these waves also lead to electromagnetic vibrations at the same frequencies as sound, producing chirps and whistles. In a recent study, an international research team consulted data from the BepiColombo International Mercury Exploration Project, which gathered data on Mercury’s magnetosphere during its first and second flyby. Their results are the first direct probing of chorus waves in Mercury’s dawn sector, which showed evidence of possible background variations in magnetic field.
Continue reading “The Solar Wind Whistles as it Passes Mercury”Mercury is Still Shrinking
Mercury is considered a scorching, barren landscape that would literally melt your face off if you were standing on it in full sunlight. But scientists have also known for a long time that it was shrinking…because it was cold. New research based on distinct features in Mercury’s geography suggests that it might continue to do so even today.
Continue reading “Mercury is Still Shrinking”BepiColumbo Makes its Third Flyby of Mercury, Seeing the Planet's Night Side
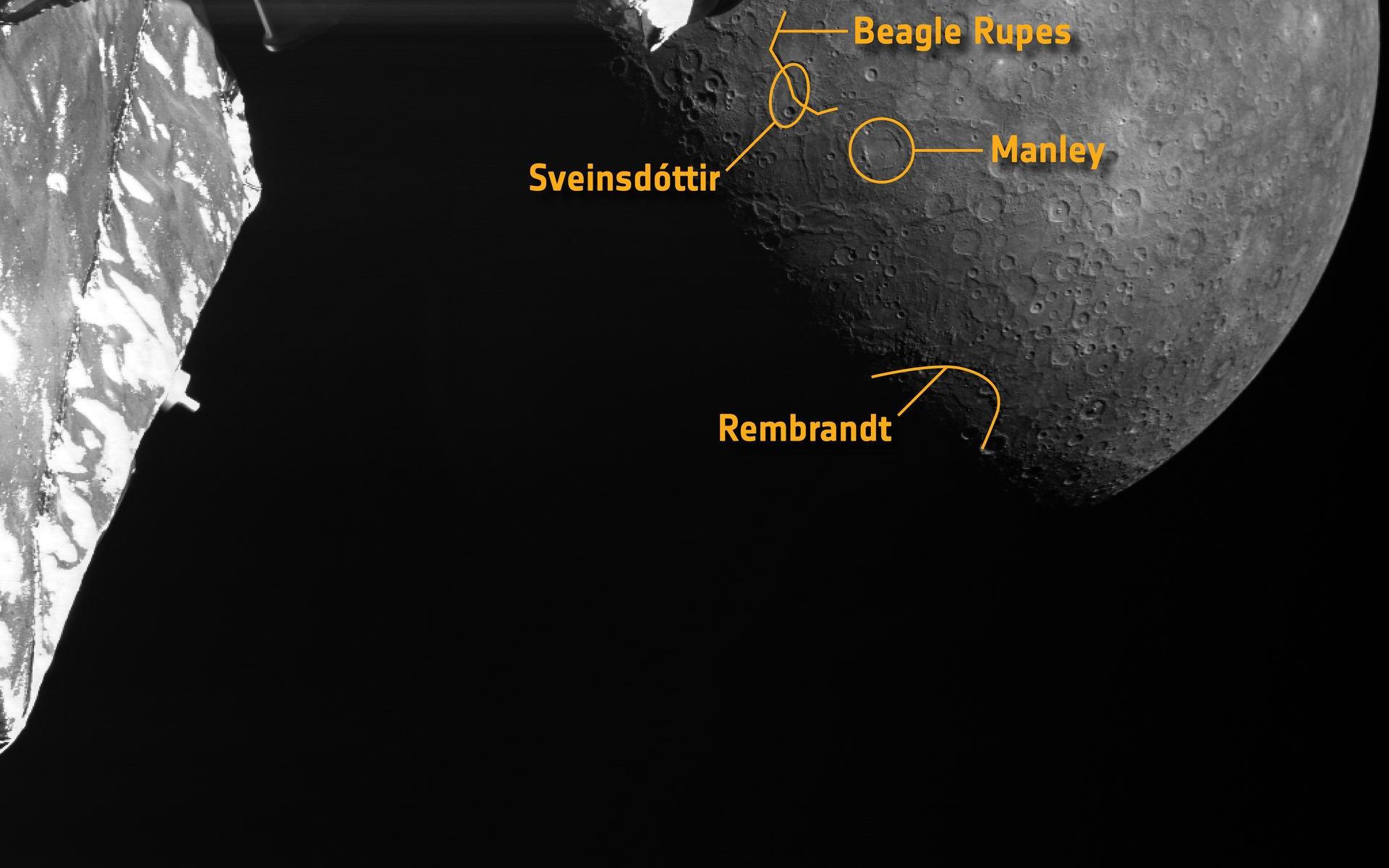

ESA’s BepiColumbo continues its journey to Mercury by making another flyby … of Mercury! This is the third of six planned flybys of its destination planet, each of which gives the spacecraft a gravitational deceleration. Eventually, it’ll slow down enough to go into its final operational orbit.
In the most recent flyby on June 19, 2023, the spacecraft sped past the planet’s night side and took a series of images from 236 km (145 miles) above Mercury’s surface. From these 217 images, the BepiColumbo team created a movie of the flyby, which includes a 3D scene.
Continue reading “BepiColumbo Makes its Third Flyby of Mercury, Seeing the Planet's Night Side”Astronomers Come Closer to Understanding How Mercury Formed
Simulations of the formation of the solar system have been largely successful. They are able to replicate the positions of all the major planets along with their orbital parameters. But current simulations have an extreme amount of difficulty getting the masses of the four terrestrial planets right, especially Mercury. A new study suggests that we need to pay more attention to the giant planets in order to understand the evolution of the smaller ones.
Continue reading “Astronomers Come Closer to Understanding How Mercury Formed”