Greetings, fellow SkyWatchers! Whoops! (she blushes) I got so lost this weekend in researching Comet ISON that I almost forgot to post the forecast! Ah, well… As they say, better late than never, eh? If you do nothing else this week, be sure to catch the close apparition of Mercury and the “Earthshine Moon” on Wednesday and stay up late Saturday night to watch the Orionid Meteor Shower! In case I forget, just meet me in the back yard…
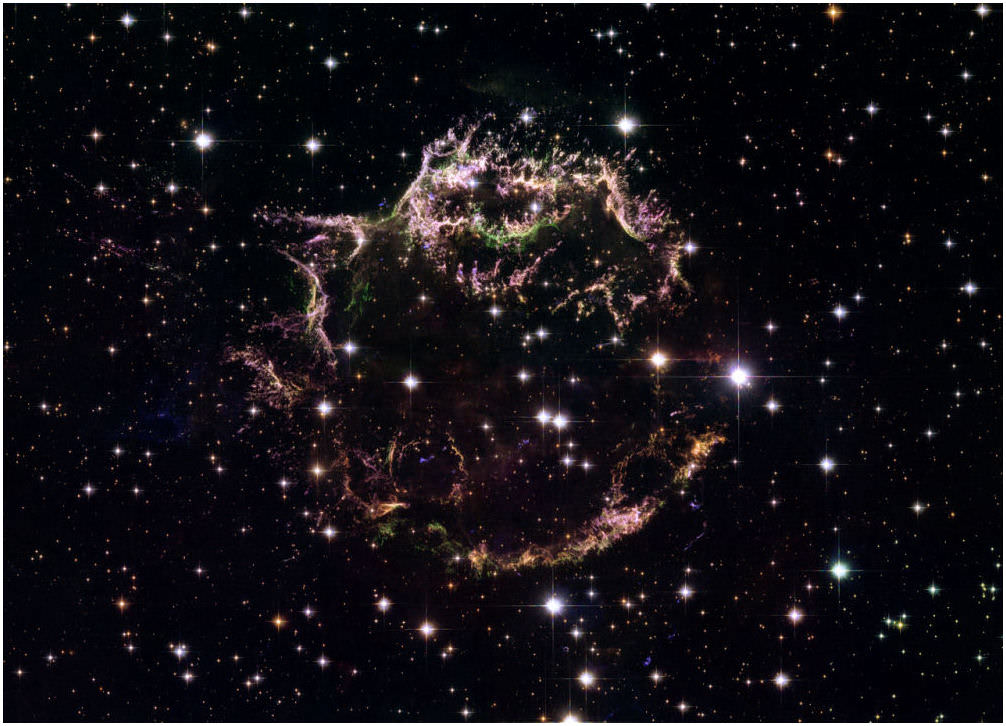
Monday, October 15 –Today in 1963 marks the first detection of an interstellar molecule. This discovery was made by Sander Weinreb (with Barrett, Meeks, and Henry) on the MIT Millstone Hill 84-foot dish. The discovery was made possible by new correlation receiver technology, and picked up a hydroxyl molecule in an absorption band. By using the radio galaxy Cas A as a background continuum source, the detection occurred at 1667.46 MHz and again at 1665.34 MHz. By the dawn of 2000, nearly 200 different interstellar molecules had been identified and many of these are classified as organic.
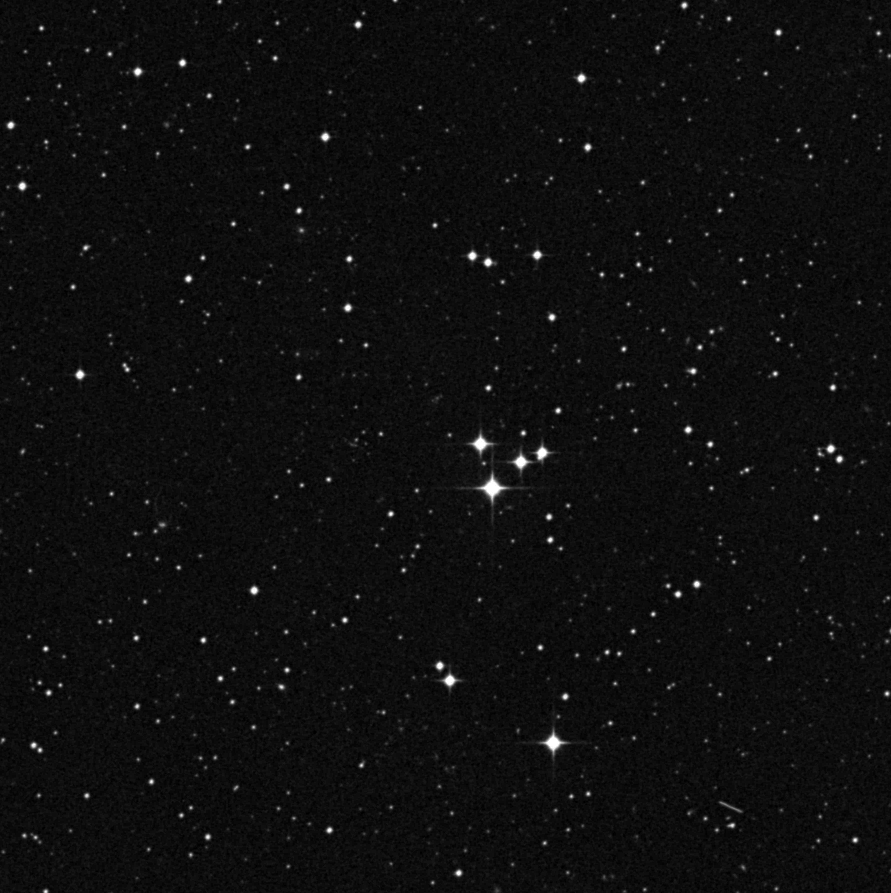
Tonight is New Moon! Let’s see what’s up there in the region of Cas A using visible light. The nearest bright star to Cas A is Beta Cassiopeiae – the bright star westward of the “W.” To locate the region of Cas A, go about three finger-widths due west of Beta and follow the subtle curve of three 5th magnitude stars. Cas A lies less than one degree south-southwest of the second star in the sequence of three. This star is a complex 5th magnitude multiple star system associated with variable star AR Cas.
Through binoculars, two stars of the AR system are easily resolved – the 4.9 magnitude primary is seen to be led across the sky by a 7.1 magnitude secondary (component C) which is a very tight double itself. Its 8.9 magnitude partner is resolvable in mid-sized scopes. Large aperture scopes may also be able to distinguish a 9.3 magnitude, second (B) component from the primary. Smaller scopes are back in the running again when attempting three 11th magnitude stars – none of which are close to the primary. Intermediate scopes can also hope to pick out a 12.9 magnitude H component northwest of C. 8.9 magnitude F also has a 9.1 magnitude near twin to the east-northeast. If you can see them all you should probably wrap an observatory building around your telescope – if one isn’t there already!
If you like to follow brightness changes in variables – AR Cas is not a good choice. This eclipsing type variable only fluctuates by a tenth of a magnitude over a period of 6 earth days.
Tuesday, October 16 – Let’s begin our evening by having a look at a radio source as we visit a pulsar located almost mid-way between Theta and Beta Capricorni – PSR2045+16.
While pulsars aren’t truly visible objects, there is still something undeniably cool about locating the field in which a rotating neutron star is sending out staccato pulses of radio waves anywhere between .001 and 4 seconds apart. If you have bright star 19 in the binocular field, then you know you’re in the right area for many radio sources, including many nearby quasars… Just imagine the possibilities!
Now let’s drop south-southeast of Beta Capricorni to have a look at a pair of doubles – Rho and Pi.
Northernmost Pi is a multiple system slightly less than 100 light-years away, with each discernable member also being a spectroscopic double. Separated by about an eighth of a light-year, look for a 5th magnitude yellow/white giant with a very close 9th magnitude companion. Further south is Pi, a triple star system which has a traditional name – Okul. Located around 670 light-years away, look for a bright blue/white 5th magnitude primary that is also a spectroscopic double – and its much easier C component, which is around magnitude 8.
Wednesday, October 17 – For naked-eye observers, enjoy the beautiful “Earthshine” Moon and the close apparition of Mercury!
While you’re out, be sure to gaze upon one of the finest of stars, Vega. Facing West at just after sundown, Vega is bright enough to shine even in the city and will appear just slightly below the zenith. The name Vega means “Falling Eagle” and it is the fifth brightest star in the sky. Enjoyed in either telescopes or binoculars, Vega has a wonderful bluish appearance and a lovely halo of spectra. This magnificent star holds a place in ancient legend and blossomed in our imaginations even more recently as it became the “star” of the movie “Contact”. As the western-most point of the “Southern Triangle”, Vega holds a special appeal for those born in the year 1985. Why? Because Vega is 27 light years away, the light you see from it tonight left the year you were born!
Now point those binoculars towards the northwestern corner of Capricornus and have a look a spectacular Alpha!
Although the Alpha 1 and 2 pairing is strictly a visual binary, that won’t stop you from enjoying their slightly yellow and orange colors. Collectively they are named Al Giedi, and the brighter of the pair is Alpha 2 at about 100 light-years distant; while Alpha 1 is around five times further away. Now power up with a telescope and you’ll find that both stars are also visual doubles! While the companion stars to both are around the same magnitude, you’ll find that Alpha 2 is separated by three times as much distance. Be sure to mark your observation lists and enjoy!
Thursday, October 18 – Today in 1959, Soviet Luna 3 began returning the first photographs of the Moon’s far side. Also today – but in 1967 – the Soviets again made history as Venera 4 became the first spacecraft to probe Venus’ atmosphere.
Have you checked out Mars lately? Mars is now leaving the constellation Scorpius and entering Ophiuchus. At more than 2 AU away from Earth, Mars has become quite dim, and its minimal apparent visual brightness is +1.24 magnitude. Can you still spot a few of its more prominent features?
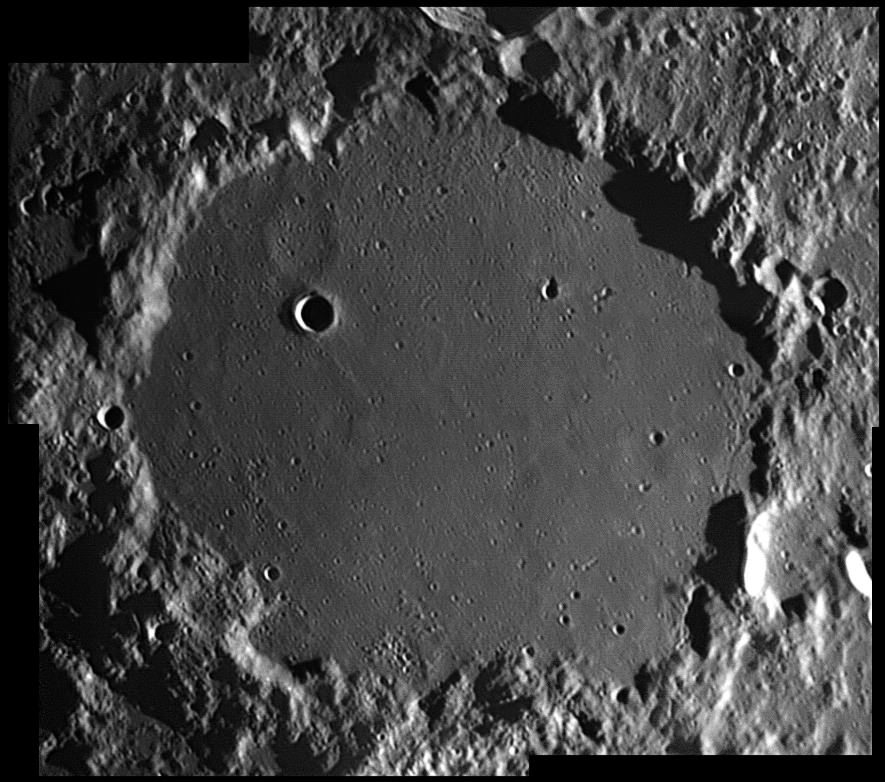
For a true telescope challenge, we’ll have to go out on a limb – the southeastern lunar limb – to have a look at an unusual crater. Named for the French agrochemist and botanist Jean-Baptiste Boussingault, this elliptical-appearing crater actually spans a handsome 71 kilometers. What makes Boussingault so unusual is that it is home to its own large interior crater – A. This double-ring formation gives it a unique stepped, concentric look that’s worth your time!
When we’re done? Let’s go have a look at Gamma Aquilae just for the heck of it. Just northwest of bright Altair, Gamma has the very cool name of Tarazed and is believed to be over 300 light-years away. This K3 type giant will show just a slightly yellow coloration – but what really makes this one special is the low power field!
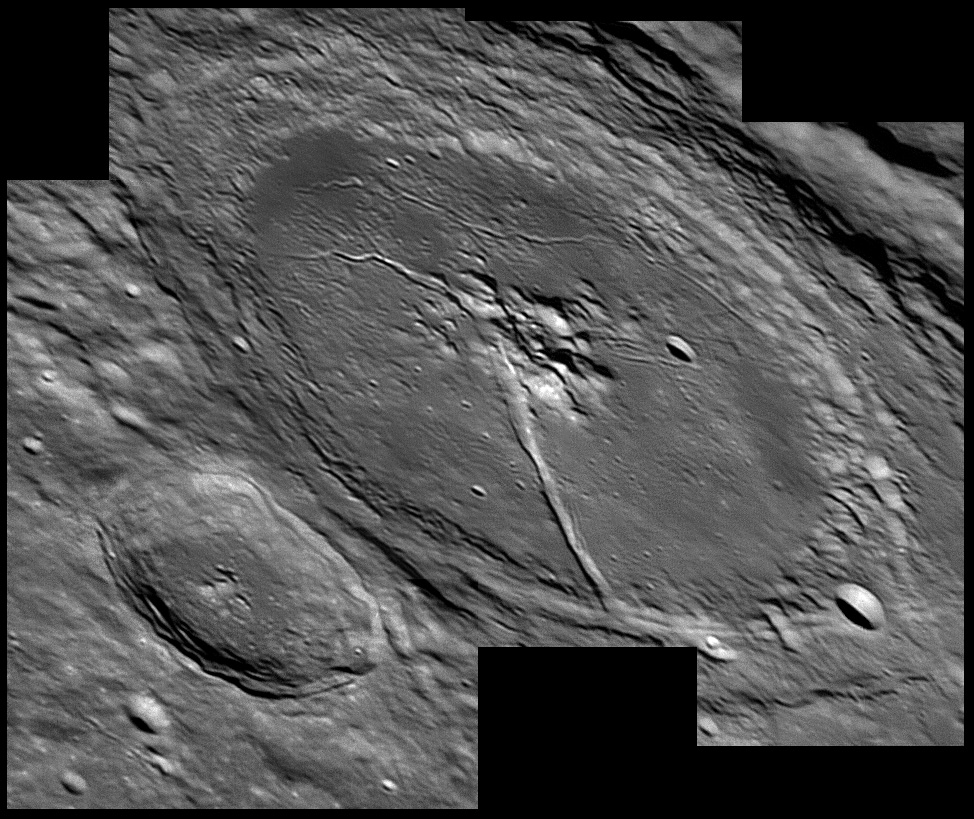
Friday, October 19 – Our lunar mission for tonight is a revisit on a crater named for historian and theologian Denis Pétau – Petavius! Located almost centrally along the terminator in the southeast quadrant, a lot will depend tonight on your viewing time and the age the Moon itself. Perhaps when you look, you’ll see 177 kilometer diameter Petavius cut in half by the terminator. If so, this is a great time to take a high magnification look at the small range of mountain peaks contained in its center, as well as a deep rima which runs for 80 kilometers across its otherwise fairly smooth surface. To the east lies a long furrow in the landscape. This deep runnel is Palitzsch and its Valles. While the primary crater which forms this deep gash is only 41 kilometers wide, the valley itself stretches for 110 kilometers. Look for crater Haas on Petavius’ southern edge with Snellius to the southwest and Wrottesley along its northwest wall.
Now, let’s go have a look at the northeastern corner of Capricornus as we learn about Delta…
Its proper name is Deneb Algedi and this nearly 3rd magnitude star is a stunning blue/ white. Curiously enough, it’s a rather close star – only about 50 light-years from Earth. Hovering so close to it that we cannot even correctly assess its spectral type is a binary companion whose eclipsing orbit causes Delta to be a very slight variable – with a period of just about one day. In its own way, Delta is rather historic… For it was only 4 degrees north of this star that Uranus was first sighted by Galle in 1846!
Saturday, October 20 – Tonight, let’s check out a lunar map and go hunting! First let’s start with a look at the Mare Fecunditatus region: (1)Taruntius, (2) Secchi, (3) Messier and Messier A, (4) Lubbock, (5) Guttenberg, (6) Montes Pyrenees, (7) Goclenius, (8) Magelhaens, (9) Columbo, (10) Webb, (11) Langrenus, (12) Lohse, (13) Lame, (14) Vendelinus, (15) the Luna 16 landing site

And here is a closer look at the area around Atlas and Hercules: (1) Mare Humboldtianum, (2) Endymion, (3) Atlas, (4) Hercules, (5) Chevalier, (6) Shuckburgh, (7) Hooke, (8) Cepheus, (9) Franklin, (10) Berzelius, (11) Maury, (12) Lacus Somniorum, (13) Daniel, (14) Grove, (15) Williams, (16) Mason, (17) Plana, (18) Burg, (19) Lacus Mortis, (20) Baily, (21) Atlas E, (22) Keldysh, (23) Mare Frigoris, (24) Democritus, (25) Gartner, (26) Schwabe, (27) Thales, (28) Strabo, (29) de la Rue, (30) Hayn.

Atlas and Hercules Region Photographic Map – Image Credit – Greg Konkel
Have fun marking off lunar challenge craters from your list!
After having looked at the Moon, take the time out to view a bright southern star – Fomalhaut (RA 22 57 39 Dec -29 37 20). Also known as “The Lonely One,” Alpha Piscis Austrini seems to sit in a rather empty area in the southern skies, some 23 light-years away. At magnitude 1, this main sequence A3 giant is the southernmost visible star of its type for northern hemisphere viewers, and is the 18th brightest star in the sky. The Lonely One is about twice the diameter of our own Sun, but 14 times more luminous! Just a little visual aid is all that it takes to reveal its optical companion…
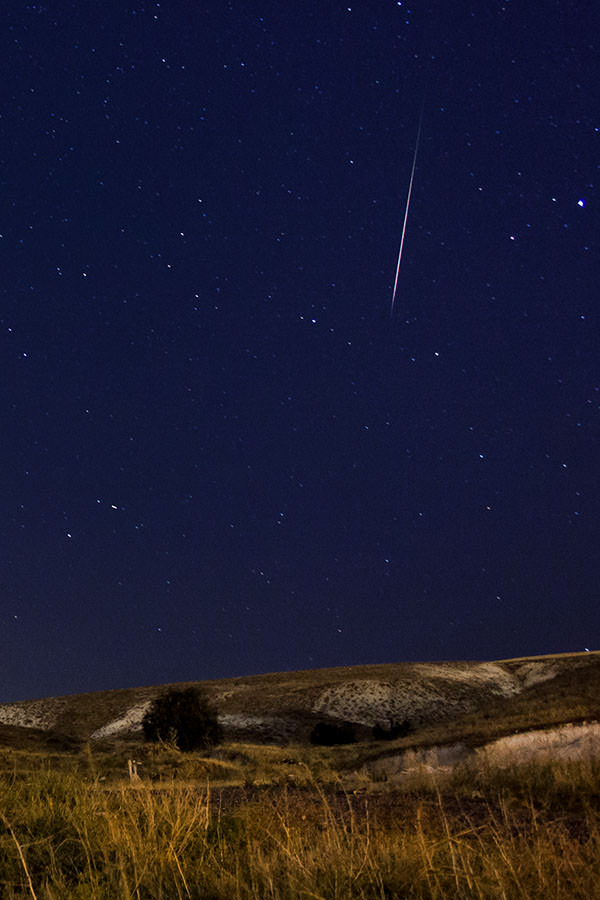
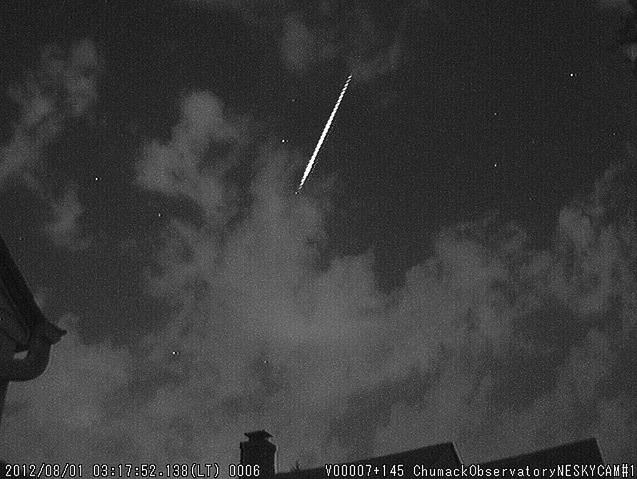
Now we are slipping into the stream of Comet Halley and into one of the finest meteor showers of the year. If skies are clear tonight, this would be the perfect chance to begin your observations of the Orionid meteor shower. But, wait for the Moon to set!
Sunday, October 21 – Be sure to be outdoors before dawn to enjoy one of the year’s most reliable meteor showers. The offspring of Comet Halley will grace the early morning hours as they return once again as the Orionid meteor shower. This dependable shower produces an average of 10-20 meteors per hour at maximum and the best activity begins before local midnight on the 20th, and reaches its best as Orion stands high to the south at about two hours before local dawn on the 21st. With the Moon nearly out of the morning picture, this is gonna’ be great!
Although Comet Halley has long since departed our Solar System, the debris left from its trail still remain scattered in Earth’s orbital path around the Sun, allowing us to predict when this meteor shower will occur. We first enter the “stream” at the beginning of October and do not leave it until the beginning of November, making your chances of “catching a falling star” even greater! These meteors are very fast, and although they are faint, it is still possible to see an occasional fireball that leaves a persistent trail.
For best success, try to get away from city lights. Facing south-southeast, simply relax and enjoy the stars of the winter Milky Way. The radiant, or apparent point of origin, for this shower will be near the red giant Alpha Orionis (Betelguese), but meteors may occur from any point in the sky. You will make your meteor watching experience much more comfortable if you take along a lawn chair, a blanket and a thermos of your favorite beverage.
Clouded out? Don’t despair. You don’t always need your eyes or perfect weather to meteor watch. By tuning an FM radio to the lowest frequency possible that does not receive a clear signal, you can practice radio meteor listening! An outdoor FM antenna pointed at the zenith and connected to your receiver will increase your chances, but it’s not necessary. Simply turn up the static and listen. Those hums, whistles, beeps, bongs, and occasional snatches of signals are our own radio signals being reflected off the meteor’s ion trail! Pretty cool, huh?
Por amour du ciel… ~Tammy