How did life arise on Earth? How did we get from rocks and water to the abundance and variety that we see today? Perhaps the raw ingredients for life, amino acids, were delivered to Earth by a steady bombardment of meteorites. Researchers have turned up space rocks with concentrations of amino acids 10x higher than previously measured, raising hopes that the early Solar System was awash in organic material.
The study was done by Marilyn Fogel of Carnegie’s Geophysical Laboratory and Conel Alexander of the Department of Terrestrial Magnetism with Zita Martins of Imperial College London and two colleagues, and will be published in Meteoritics and Planetary Science.
If you’re like me, the astronomy stuff’s fine, but the biology news is a little baffling (I forward the kids’ biology questions to my wife). Amino acids are organic molecules that form the backbone of proteins, which make much of life’s structures and drive chemical reactions in cells. Amino acids are naturally occurring, but they somehow came together to make the first proteins in the Earth’s early days.
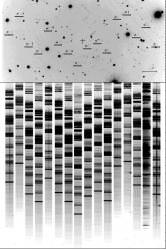
The researchers took samples from three meteorites collected during recent expeditions to Antarctica. The meteorites are from a type called CR chondrites, which are through to contain ancient organic materials that date back to the earliest times of the Solar System. At one point, these meteorites were part of a larger “parent body”, which was later shattered by impacts.
One sample had few amino acids, but the other two had the highest concentration ever seen in primitive meteorites.
“The amino acids probably formed within the parent body before it broke up,†says Alexander. “For instance. ammonia and other chemical precursors from the solar nebula, or even the interstellar medium, could have combined in the presence of water to make the amino acids. Then, after the break up, some of the fragments could have showered down onto the Earth and the other terrestrial planets. These same precursors are likely to have been present in other primitive bodies, such as comets, that were also raining material onto the early Earth. â€
So this points to the conclusion that the early Solar System was a much richer source of organic molecules than researchers previously believed. And the constant rain of amino acid-laden meteorites would have delivered this material to the primordial soup where life first emerged.
Exactly how the amino acids became the first proteins… that’s still one of the biggest mysteries in science.
Original Source: Carnegie Institution for Science News Release