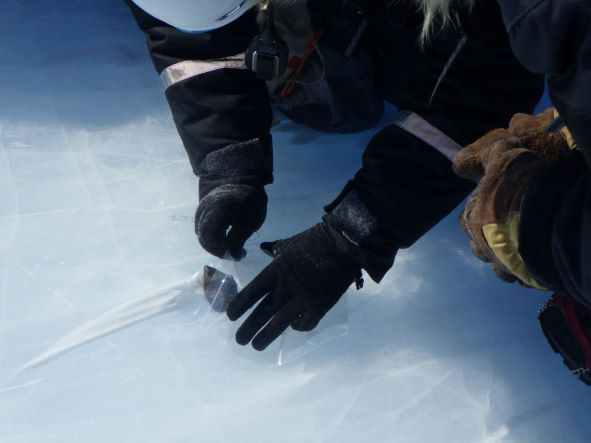
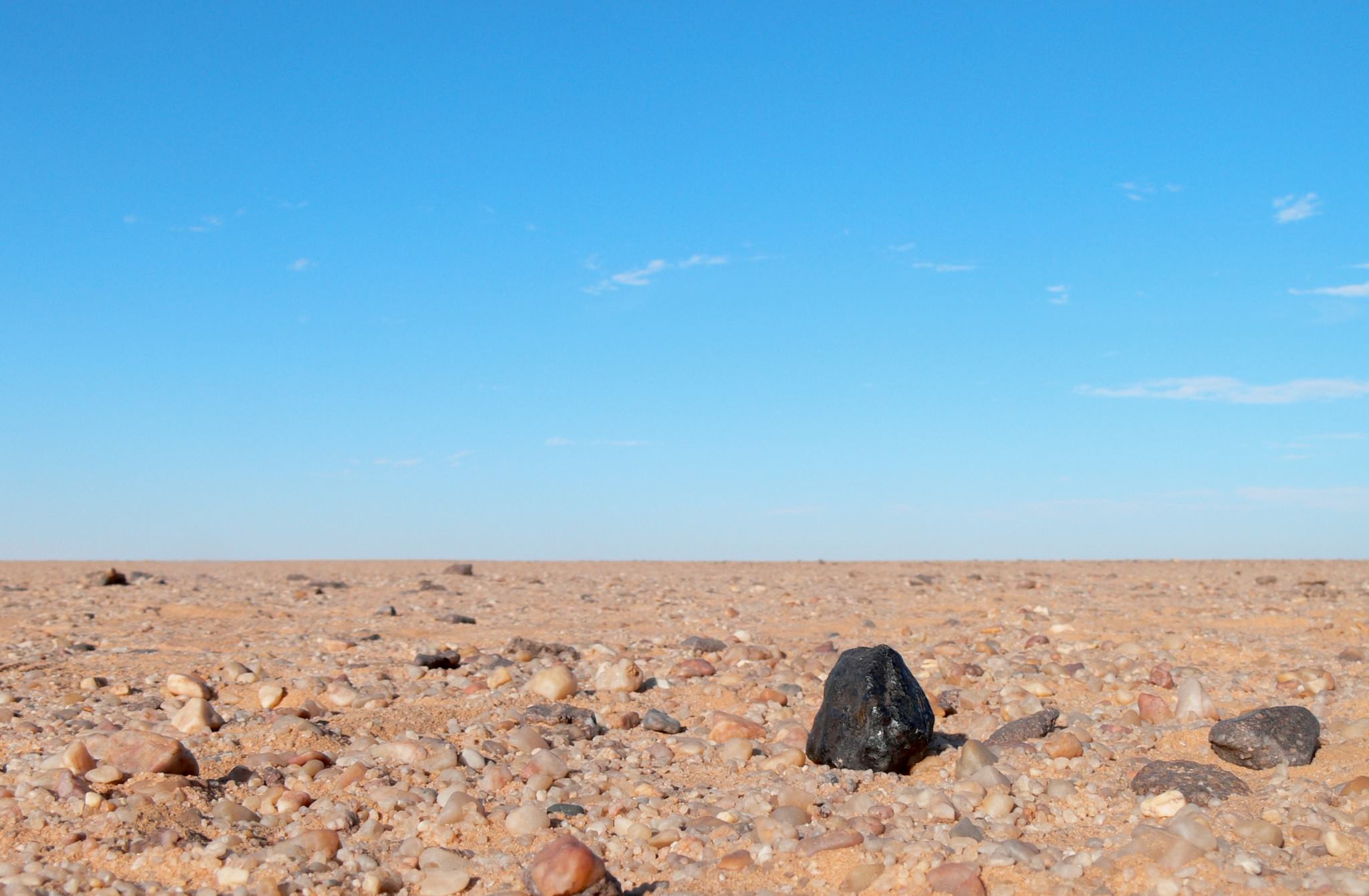
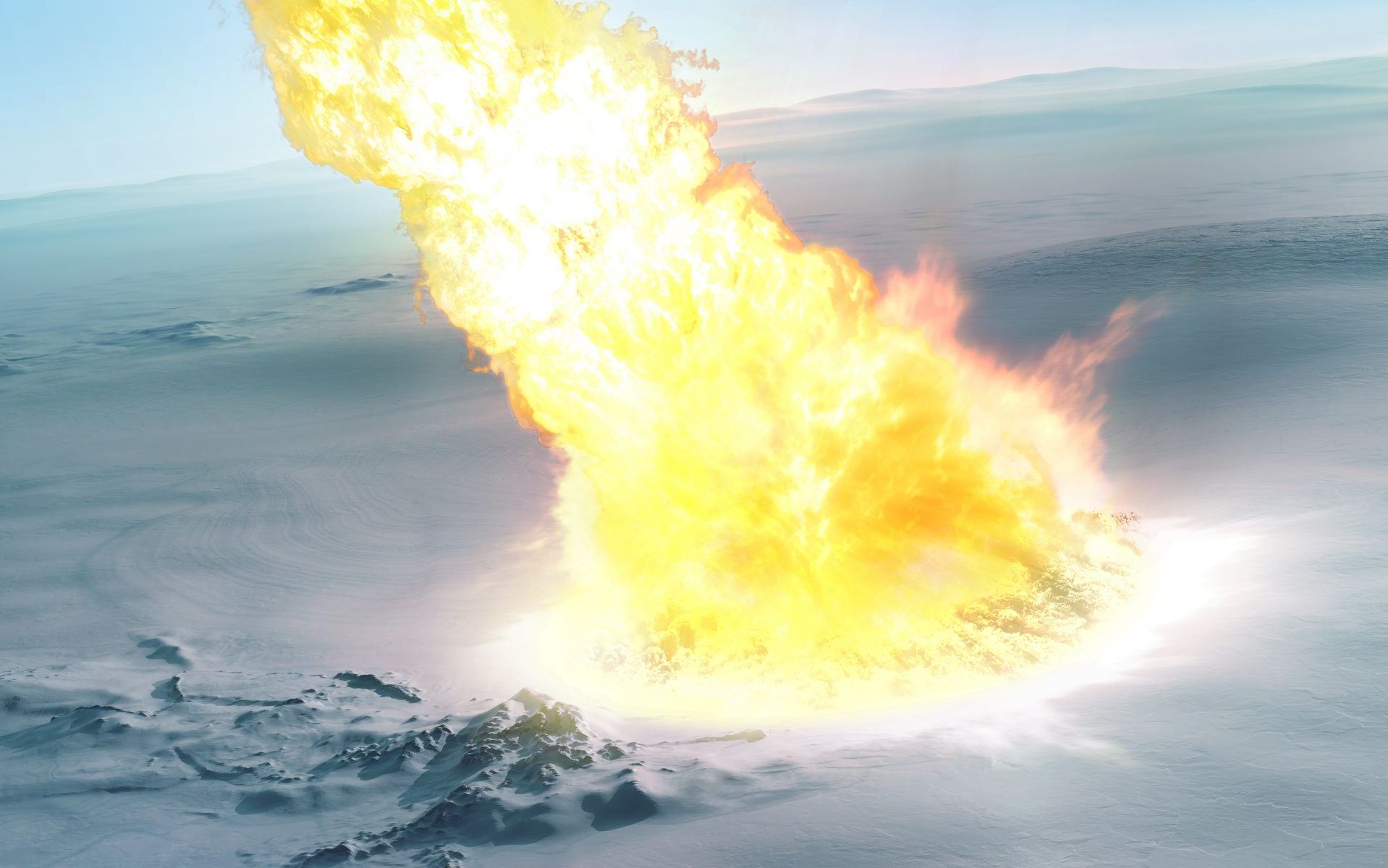
Comets visit the inner Solar System, and leave without saying goodbye. Maybe they leave a trail of dust behind, and when the Earth passes through it, we get a pretty light show in the night sky, in the form of a meteor shower. Likewise, asteroids frequently go whizzing by, though they don’t leave us with a pyrotechnic display.
Sometimes these rocky interlopers head straight for Earth. And when they do, the results can be cataclysmic, like when an asteroid struck Earth about 66 million years ago, wiping out the dinosaurs and 75% of life on Earth. Other times, it’s not quite as cataclysmic, but still devastating, like in about 2350 BC, when debris from a disintegrating comet may have caused the collapse of an ancient empire.
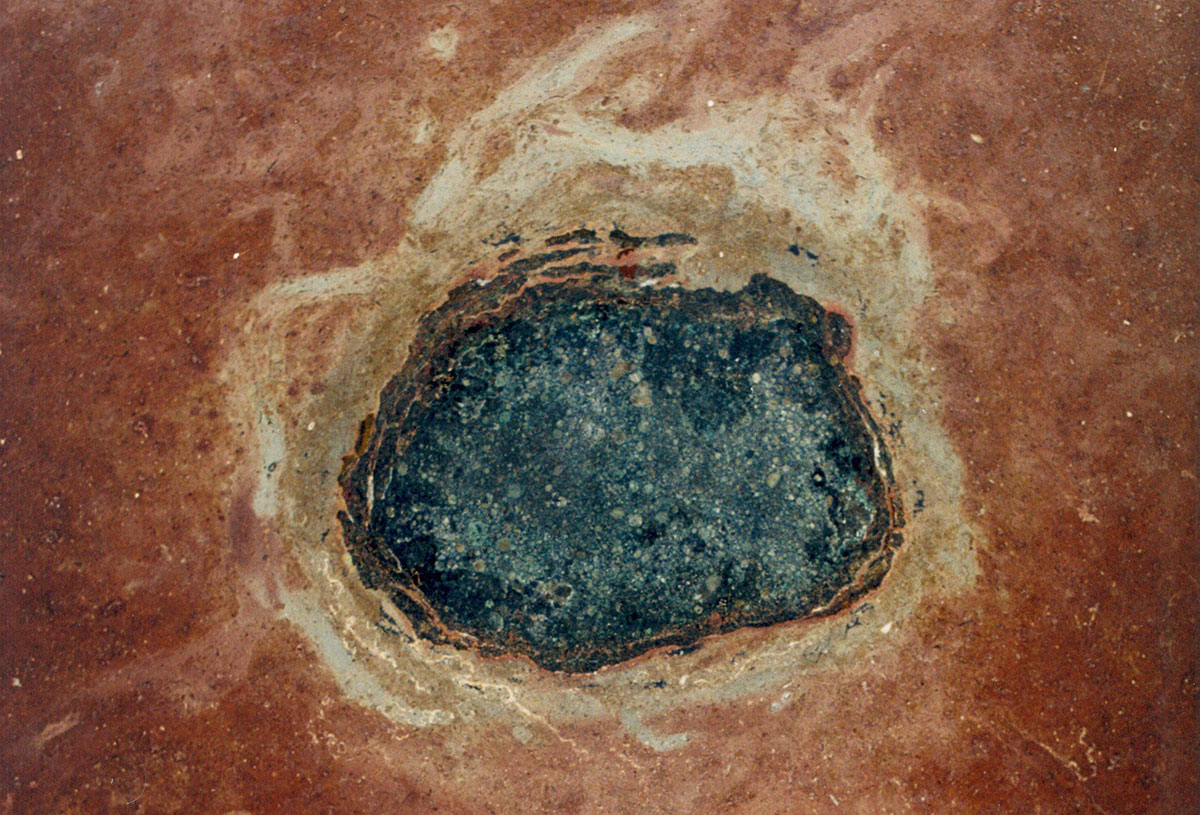
But regardless of the severity of any of these individual events, the conclusion is crystal clear: Earth’s history is intertwined with the coming and going of space rocks. The evidence is all around us, sort of.
Continue reading “Ancient Meteorites Can be Found Embedded in Rocks, Like Fossils”