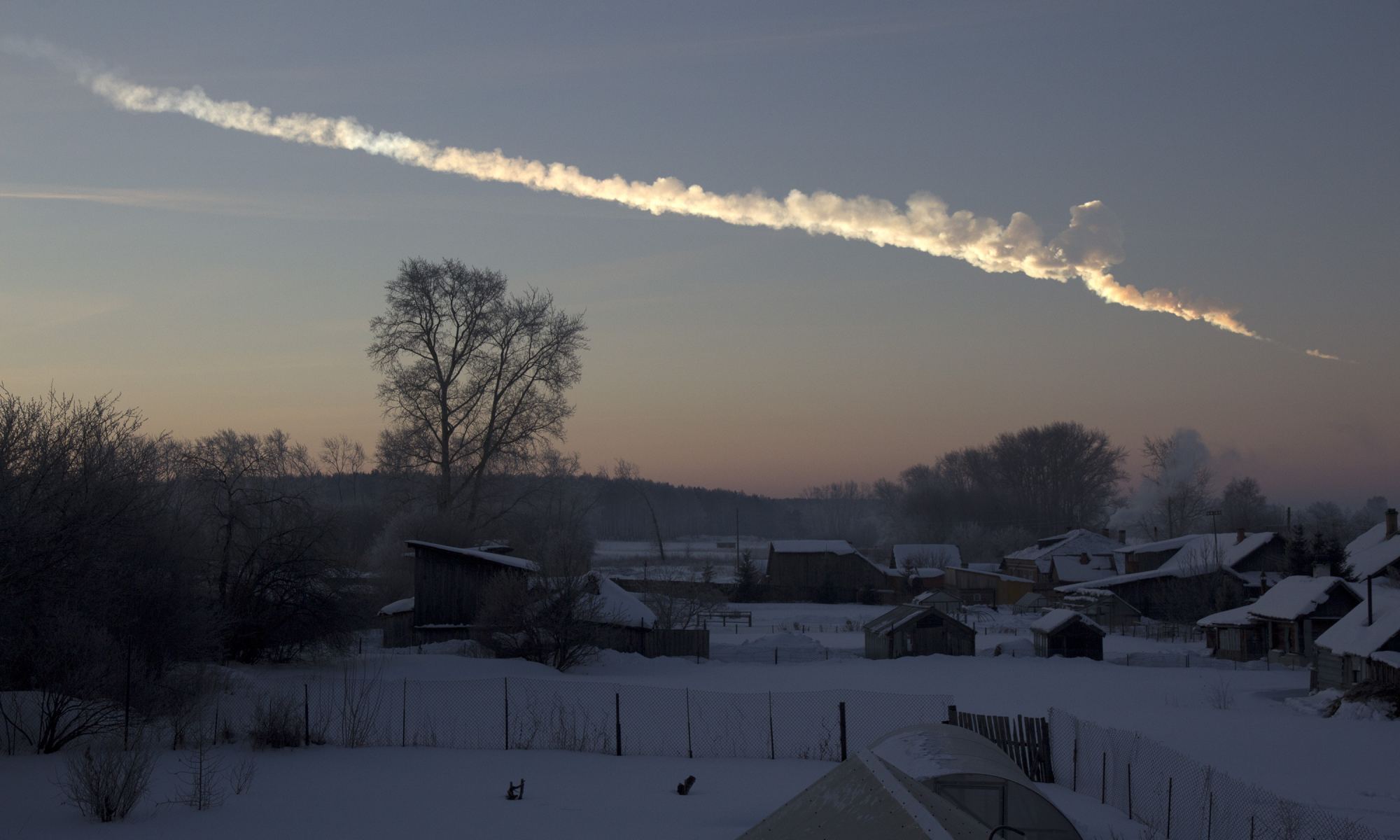
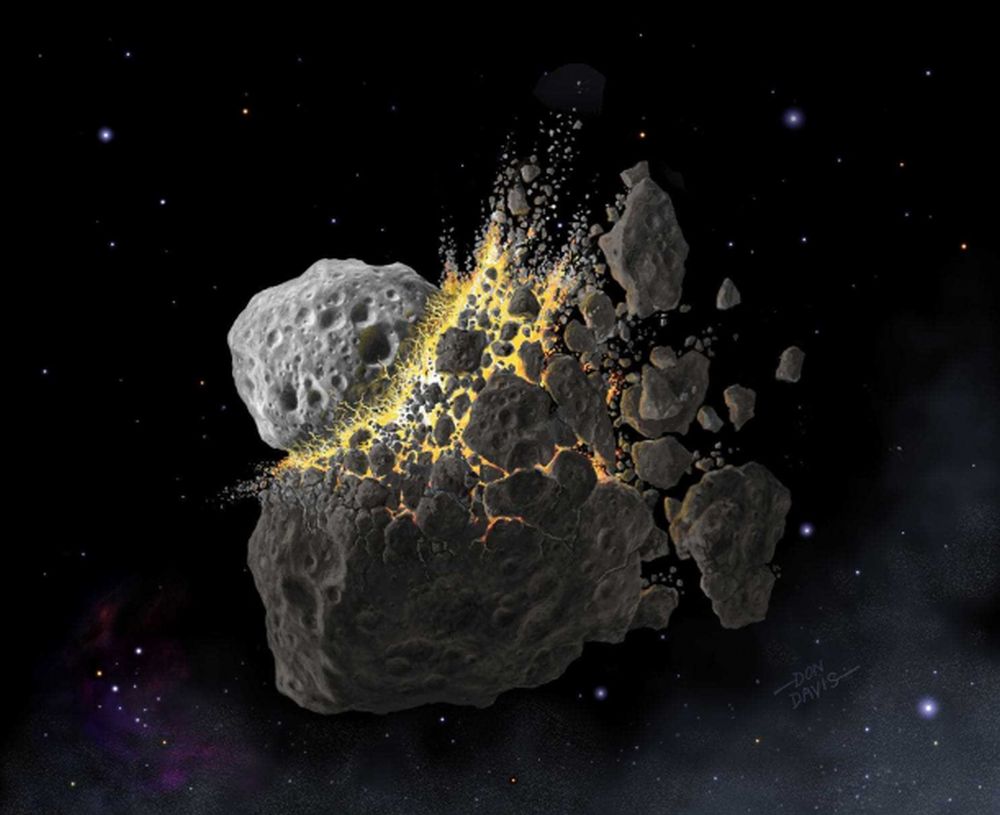
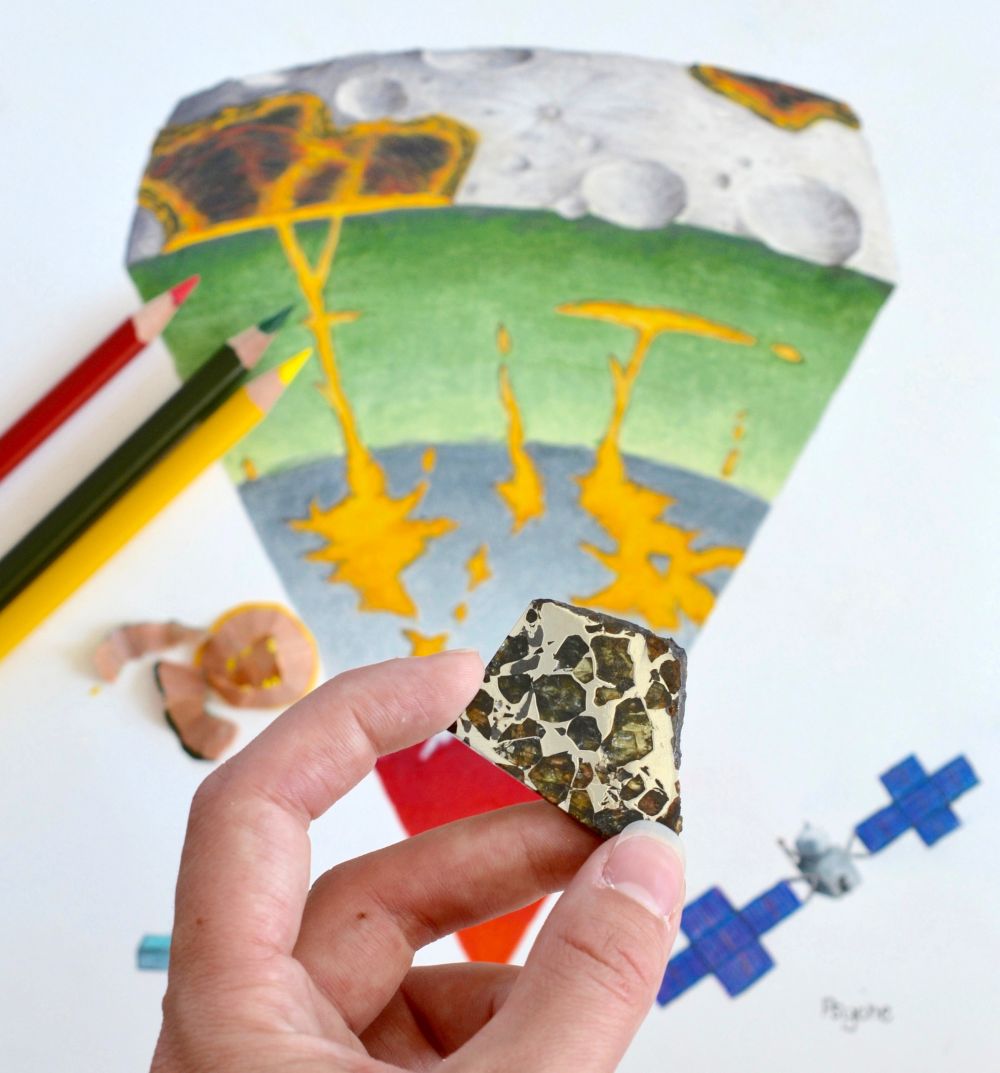
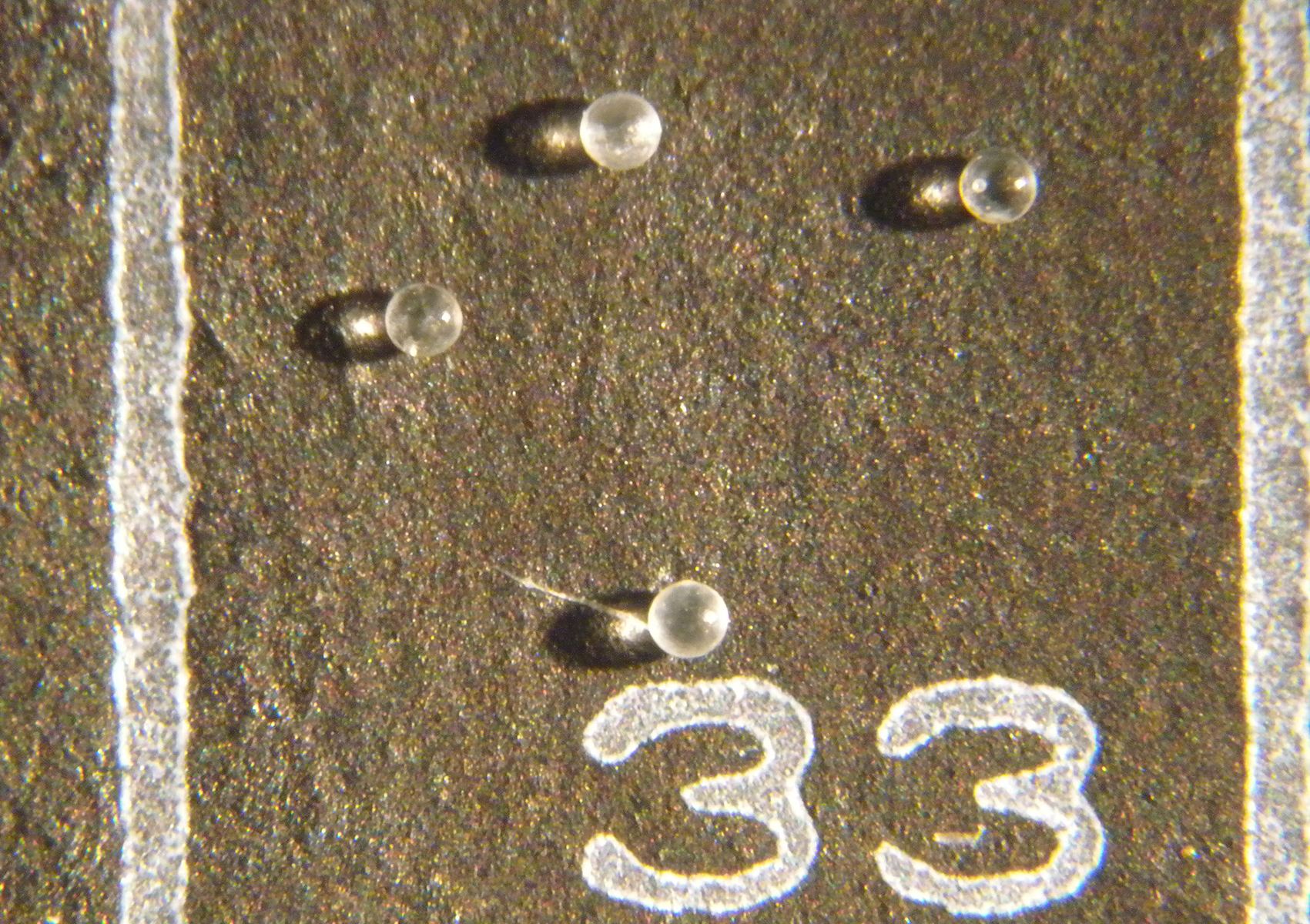
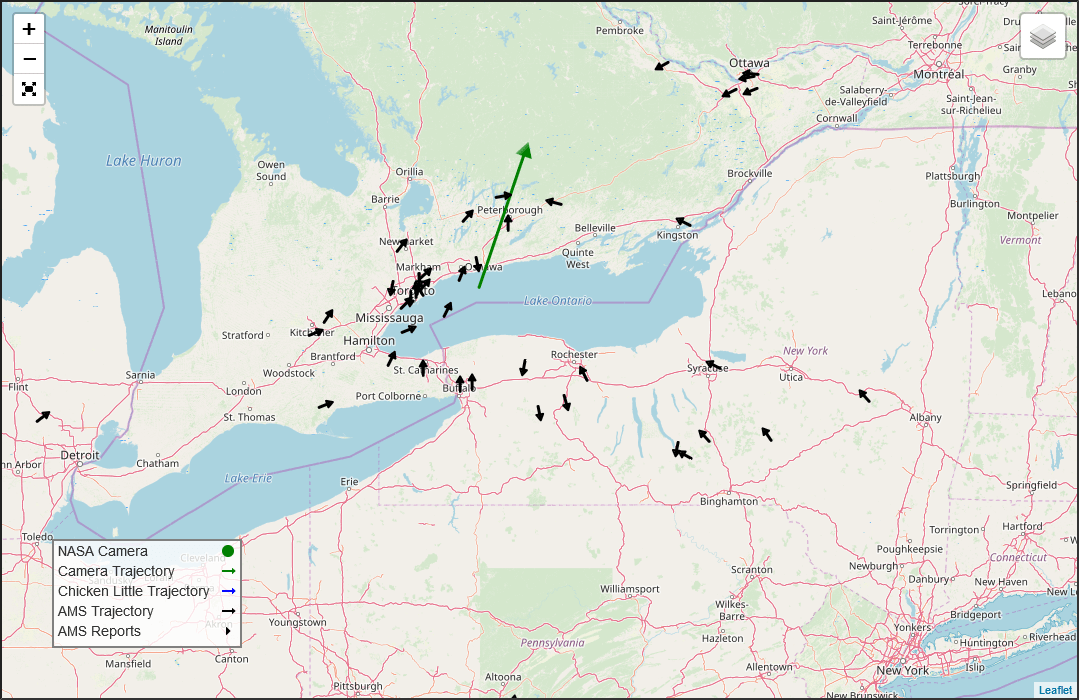
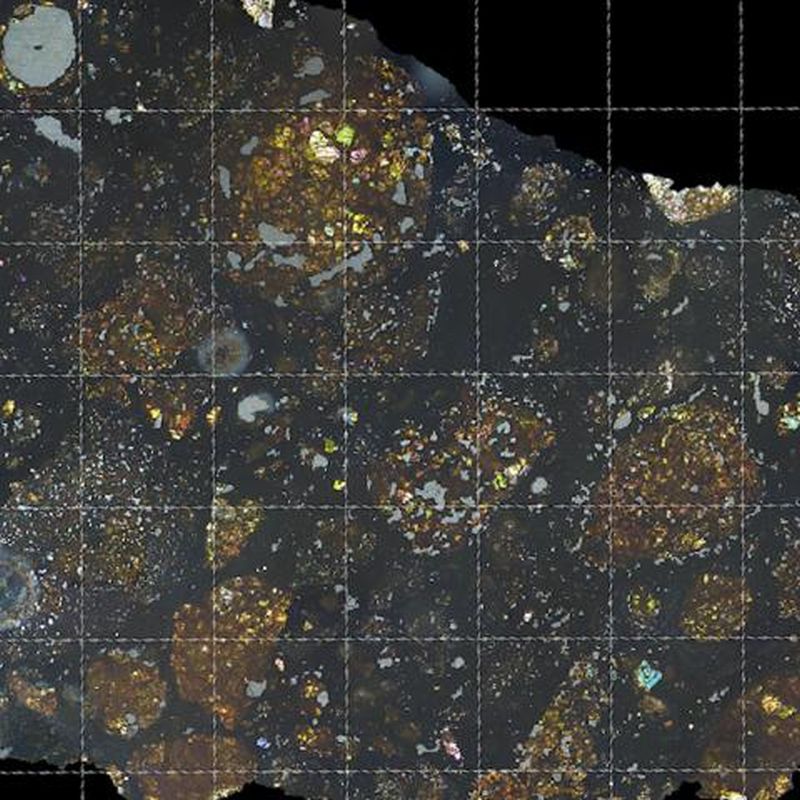
Before our Solar System had planets, it had planetesimals. Scientists think that most of the meteorites that have struck Earth are fragments of these planetesimals. Scientists also think that these planetesimals either melted completely, very early in their history, or that they remained as little more than collections of rocks, or “rubble piles.”
But one family of meteorites, that have been found spread around the world, appear to come from a planetesimal that bucked that trend.
Continue reading “A Group of Meteorites All Came From a Destroyed Planetesimal With a Magnetic Core”