Imagine a single mission that would allow you to explore the Milky Way and beyond, investigating cosmic chemistry, hunting planets, mapping galactic structure, probing dark energy and analyzing the expansion of the wider Universe. Enter the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, a massive scientific collaboration that enables one thousand astronomers from 51 institutions around the world to do just that.
At Tuesday’s AAS briefing in Seattle, researchers announced the public release of data collected by the project’s latest incarnation, SDSS-III. This data release, termed “DR12,” represents the survey’s largest and most detailed collection of measurements yet: 2,000 nights’ worth of brand-new information about nearly 500 million stars and galaxies.
One component of SDSS is exploring dark energy by “listening” for acoustic oscillation signals from the the acceleration of the early Universe, and the team also shared a new animated “fly-through” of the Universe that was created using SDSS data.
The SDSS-III collaboration is based at the powerful 2.5-meter Sloan Foundation Telescope at the Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico. The project itself consists of four component surveys: BOSS, APOGEE, MARVELS, and SEGUE. Each of these surveys applies different trappings to the parent telescope in order to accomplish its own, unique goal.
BOSS (the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey) visualizes the way that sound waves produced by interacting matter in the early Universe are reflected in the large-scale structure of our cosmos. These ancient imprints, which date back to the first 500,000 years after the Big Bang, are especially evident in high-redshift objects like luminous-red galaxies and quasars. Three-dimensional models created from BOSS observations will allow astronomers to track the expansion of the Universe over a span of 9 billion years, a feat that, later this year, will pave the way for rigorous assessment of current theories regarding dark energy.
At the press briefing, Daniel Eistenstein from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics explained how BOSS requires huge volumes of data and that so far 1.4 million galaxies have been mapped. He indicated the data analyzed so far strongly confirm dark energy’s existence.
This tweet from the SDSS twitter account uses a bit of humor to explain how BOSS works:
It turns out that in space, everyone can hear you scream, if you do it in the early Universe and set up acoustic oscillations #aas225
— SDSS — J. Johnson (@sdssurveys) January 6, 2015
APOGEE (the Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Experiment) employs a sophisticated, near-infrared spectrograph to pierce through thick dust and gather light from 100,000 distant red giants. By analyzing the spectral lines that appear in this light, scientists can identify the signatures of 15 different chemical elements that make up the faraway stars – observations that will help researchers piece together the stellar history of our galaxy.
MARVELS (the Multi-Object APO Radial Velocity Exoplanet Large-Area Survey) identifies minuscule wobbles in the orbits of stars, movements that betray the gravitational influence of orbiting planets. The technology itself is unprecedented. “MARVELS is the first large-scale survey to measure these tiny motions for dozens of stars simultaneously,” explained the project’s principal investigator Jian Ge, “which means we can probe and characterize the full population of giant planets in ways that weren’t possible before.”
At the press briefing, Ge said that MARVELS observed 5,500 stars repeatedly, looking for giant exoplanets around these stars. So far, the data has revealed 51 giant planet candidates as well as 38 brown dwarf candidates. Ge added that more will be found with better data processing.

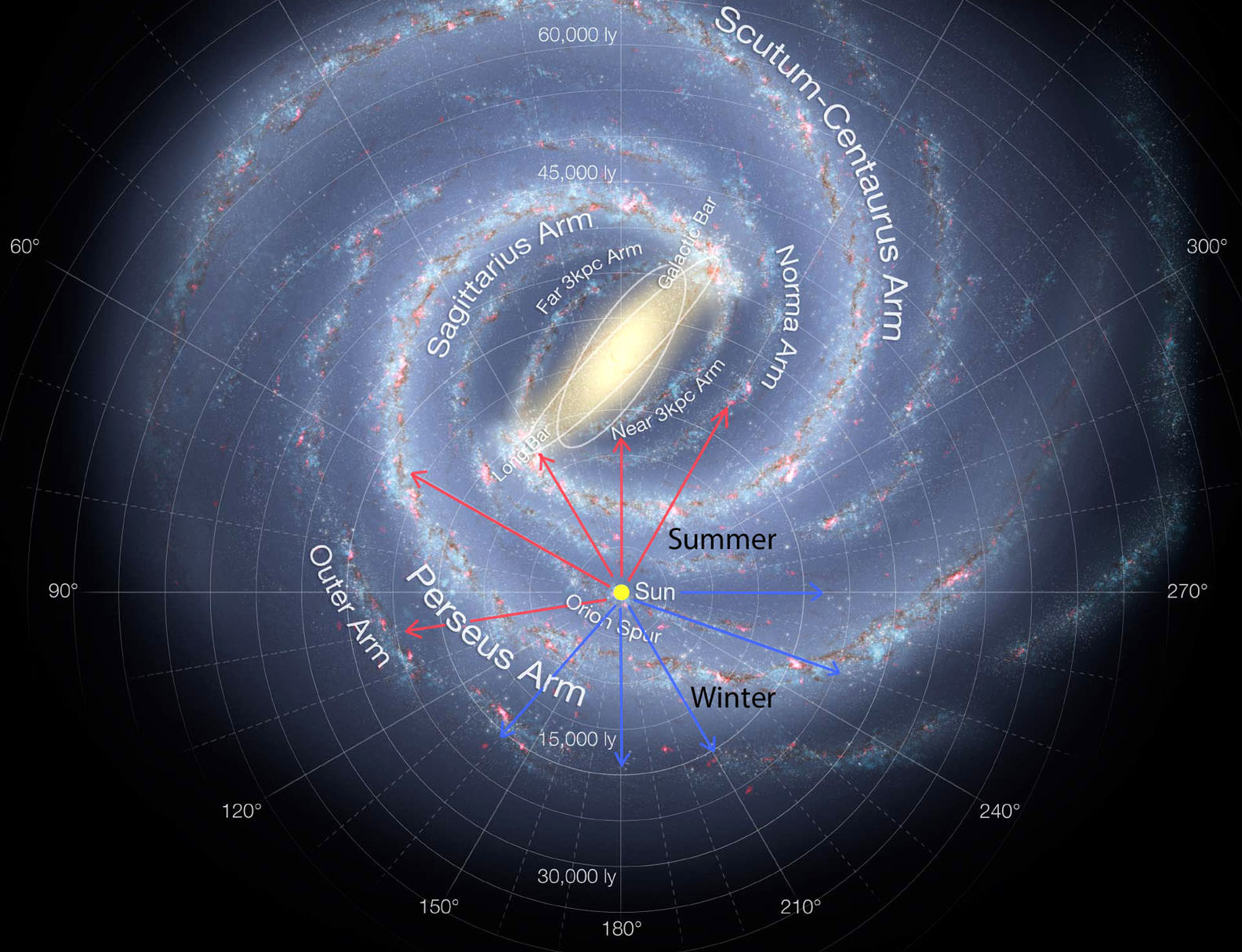
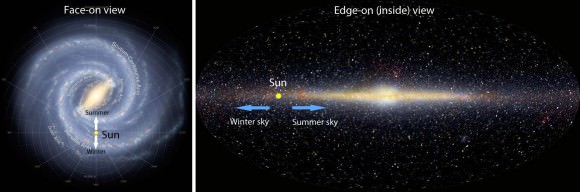
SEGUE (the Sloan Extension for Galactic Understanding and Exploration) rounds out the quartet by analyzing visible light from 250,000 stars in the outer reaches of our galaxy. Coincidentally, this survey’s observations “segue” nicely into work being done by other projects within SDSS-III. Constance Rockosi, leader of the SDSS-III domain of SEGUE, recaps the importance of her project’s observations of our outer galaxy: “In combination with the much more detailed view of the inner galaxy from APOGEE, we’re getting a truly holistic picture of the Milky Way.”
One of the most exceptional attributes of SDSS-III is its universality; that is, every byte of juicy information contained in DR12 will be made freely available to professionals, amateurs, and lay public alike. This philosophy enables interested parties from all walks of life to contribute to the advancement of astronomy in whatever capacity they are able.
As momentous as the release of DR12 is for today’s astronomers, however, there is still much more work to be done. “Crossing the DR12 finish line is a huge accomplishment by hundreds of people,” said Daniel Eisenstein, director of the SDSS-III collaboration, “But it’s a big universe out there, so there is plenty more to observe.”
DR12 includes observations made by SDSS-III between July 2008 and June 2014. The project’s successor, SDSS-IV, began its run in July 2014 and will continue observing for six more years.
Here is the video animation of the fly-through of the Universe: