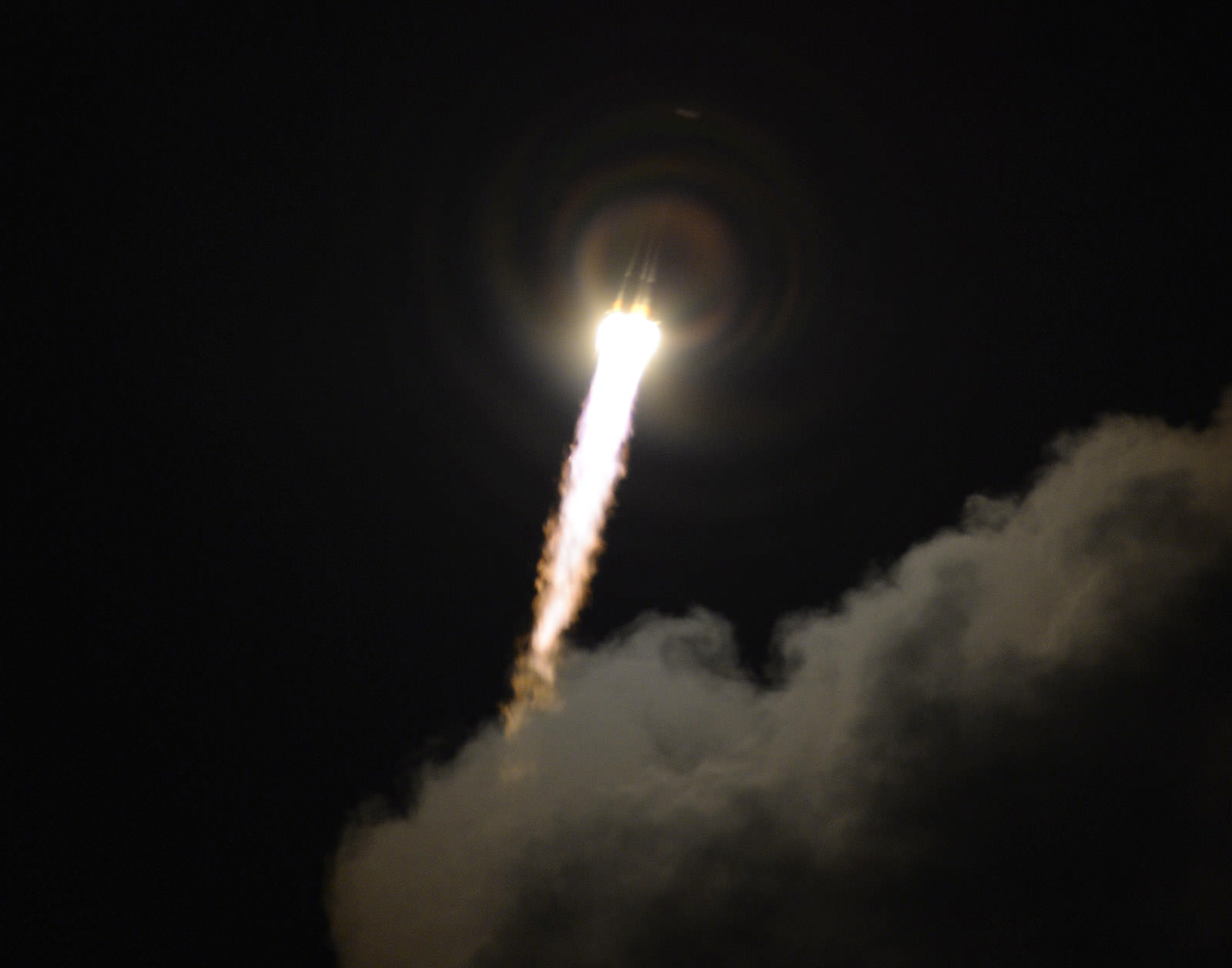
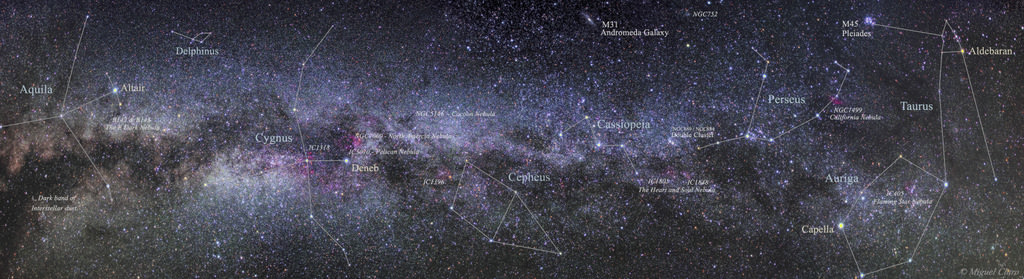
Early this morning, at 09:12 UTC, the cloudy pre-dawn sky above the coastal town of Kourou, French Guiana was brilliantly sliced by the fiery exhaust of a Soyuz VS06, which ferried ESA’s “billion-star surveyor” Gaia into space to begin its five-year mission to map the Milky Way.
Ten minutes after launch, after separation of the first three stages, the Fregat upper stage ignited, successfully delivering Gaia into a temporary parking orbit at an altitude of 175 km (108 miles). A second firing of the Fregat 11 minutes later took Gaia into its transfer orbit, followed by separation from the upper stage 42 minutes after liftoff. 46 minutes later Gaia’s sunshield was deployed, and the spacecraft is now cruising towards its target orbit around L2, a gravitationally-stable point in space located 1.5 million km (932,000 miles) away in the “shadow” of the Earth.
The launch itself was really quite beautiful, due in no small part to the large puffy clouds over the launch site. Watch the video below:
A global space astrometry mission, Gaia will make the largest, most precise three-dimensional map of our galaxy by surveying more than a billion stars over a five-year period.
“Gaia promises to build on the legacy of ESA’s first star-mapping mission, Hipparcos, launched in 1989, to reveal the history of the galaxy in which we live,” says Jean-Jacques Dordain, ESA’s Director General.
Repeatedly scanning the sky, Gaia will observe each of the billion stars an average of 70 times each over the five years. (That’s 40 million observations every day!) It will measure the position and key physical properties of each star, including its brightness, temperature and chemical composition.
By taking advantage of the slight change in perspective that occurs as Gaia orbits the Sun during a year, it will measure the stars’ distances and, by watching them patiently over the whole mission, their motions across the sky.
The motions of the stars can be put into “rewind” to learn more about where they came from and how the Milky Way was assembled over billions of years from the merging of smaller galaxies, and into “fast forward” to learn more about its ultimate fate.
“Gaia represents a dream of astronomers throughout history, right back to the pioneering observations of the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus, who catalogued the relative positions of around a thousand stars with only naked-eye observations and simple geometry. Over 2,000 years later, Gaia will not only produce an unrivaled stellar census, but along the way has the potential to uncover new asteroids, planets and dying stars.”
– Alvaro Giménez, ESA’s Director of Science and Robotic Exploration

Of the one billion stars Gaia will observe, 99% have never had their distances measured accurately. The mission will also study 500,000 distant quasars, search for exoplanets and brown dwarfs, and will conduct tests of Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity.
“Along with tens of thousands of other celestial and planetary objects,” said ESA’s Gaia project scientist Timo Prusti, “this vast treasure trove will give us a new view of our cosmic neighbourhood and its history, allowing us to explore the fundamental properties of our Solar System and the Milky Way, and our place in the wider Universe.”
Follow the status of Gaia on the mission blog here.
Source: ESA press release and Gaia fact sheet