[/caption]
A year ago, 2011 was proclaimed as the “Year of the Solar System” by NASA’s Planetary Science division. And what a year of excitement it was indeed for the planetary science community, amateur astronomers and the general public alike !
NASA successfully delivered astounding results on all fronts – On the Story of How We Came to Be.
“2011 was definitely the best year ever for NASA Planetary Science!” said Jim Green in an exclusive interview with Universe Today. Green is the Director of Planetary Science for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA HQ. “The Search for Life is a significant priority for NASA.”
This past year was without doubt simply breathtaking in scope in terms of new missions, new discoveries and extraordinary technical achievements. The comprehensive list of celestial targets investigated in 2011 spanned virtually every type of object in our solar system – from the innermost planet to the outermost reaches nearly touching interplanetary space.
There was even a stunningly evocative picture showing “All of Humanity” – especially appropriate now in this Holiday season !
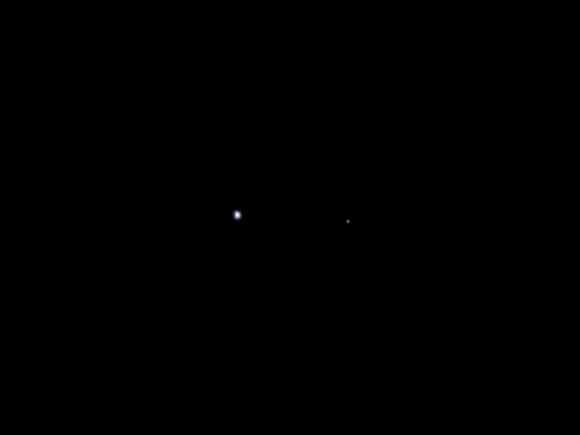

-- Earth & Moon Portrait by Juno from 6 Million miles away --
First Photo transmitted from Jupiter Bound Juno shows Earth (on the left) and the Moon (on the right). Taken on Aug. 26, 2011 when spacecraft was about 6 million miles (9.66 million kilometers) away from Earth. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Three brand new missions were launched and ongoing missions orbited a planet and an asteroid and flew past a comet.
“NASA has never had the pace of so many planetary launches in such a short time,” said Green.
And three missions here were awarded ‘Best of 2011’ for innovation !

Here’s the Top NASA Planetary Science Stories of 2011 – ‘The Year of the Solar System’ – in chronological order
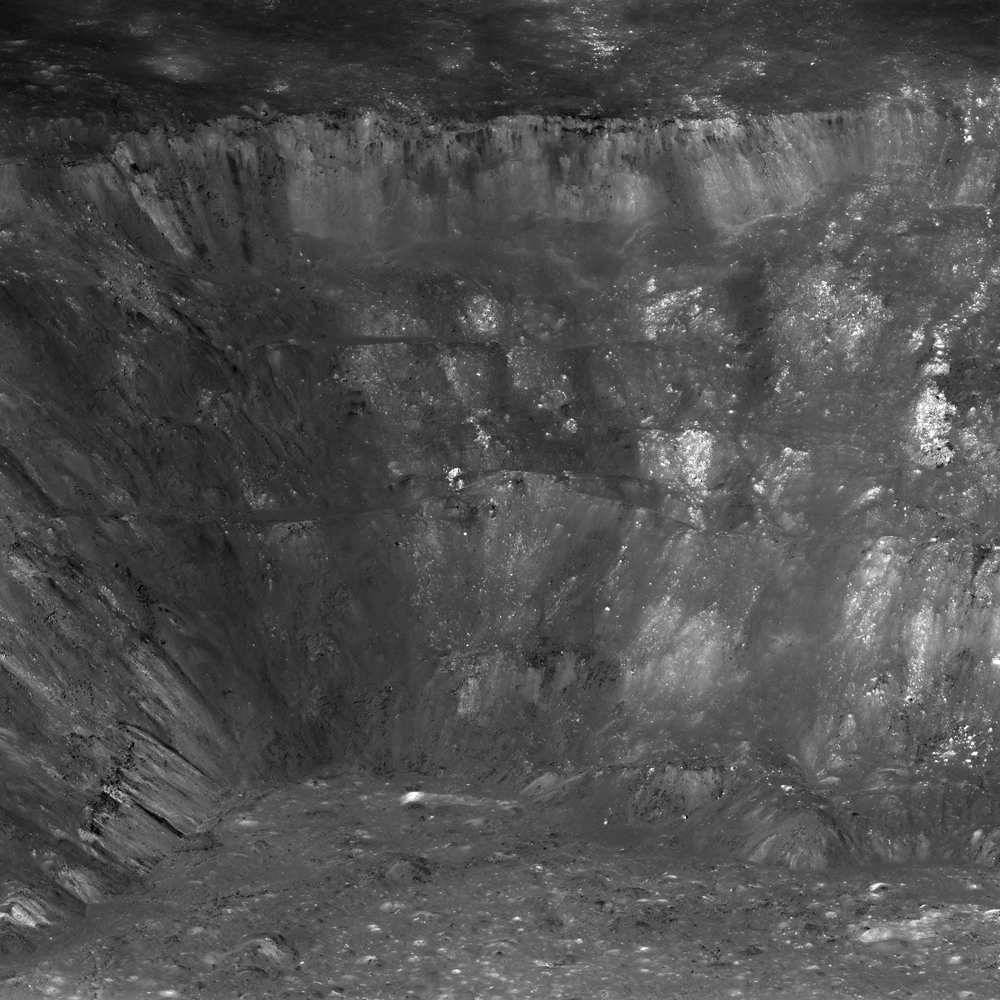
1. Stardust-NExT Fly By of Comet Tempel 1
Starting from the first moments of 2011 at the dawn of Jan. 1, hopes were already running high for planetary scientists and engineers busily engaged in setting up a romantic celestial date in space between a volatile icy comet and an aging, thrusting probe on Valentine’s Day.
The comet chasing Stardust-Next spacecraft successfully zoomed past Comet Tempel 1 on Feb. 14 at 10.9 km/sec (24,000 MPH) after flying over 6 Billion kilometers (3.5 Billion mi).
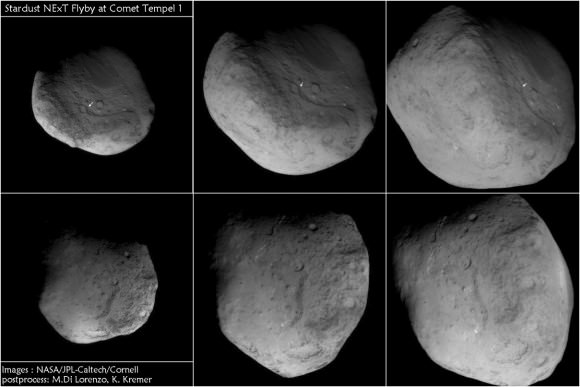
Arrows show location of man-made crater created in 2005 by NASA’s prior Deep Impact comet mission and newly imaged as Stardust-NExT zoomed past comet in 2011. The images progress in time during closest approach to comet beginning at upper left and moving clockwise to lower left. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Maryland. Post process and annotations by Marco Di Lorenzo & Kenneth Kremer
The craft approached within 178 km (111mi) and snapped 72 astonishingly detailed high resolution science images over barely 8 minutes. It also fulfilled the teams highest hopes by photographing the human-made crater created on Tempel 1 in 2005 by a cosmic collision with a penetrator hurled by NASA’s Deep Impact spacecraft. The probe previously flew by Comet Wild 2 in 2004 and returned cometary coma particles to Earth in 2006
Tempel 1 is the first comet to be visited by two spaceships from Earth and provided the first-ever opportunity to compare observations on two successive passages around the Sun.
Don Brownlee, the original Principal Investigator, summarized the results for Universe Today; “A great bonus of the mission was the ability to flyby two comets and take images and measurements. The wonderfully successful flyby of Comet Tempel 1 was a great cap to the 12 year mission and provided a great deal of new information to study the diversity among comets.”
“The new images of Tempel showed features that form a link between seemingly disparate surface features of the 4 comets imaged by spacecraft. Combining data on the same comet from the Deep Impact and Stardust missions has provided important new insights in to how comet surfaces evolve over time and how they release gas and dust into space”.
2. MESSENGER at Mercury
On March 18, the Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry, and Ranging, or MESSENGER, spacecraft became the first spacecraft inserted into orbit around Mercury, the innermost planet.
So far MESSENGER has completed 1 solar day – 176 Earth days- circling above Mercury. The probe has collected a treasure trove of new data from the seven instruments onboard yielding a scientific bonanza; these include global imagery of most of the surface, measurements of the planet’s surface chemical composition, topographic evidence for significant amounts of water ice, magnetic field and interactions with the solar wind.
“MESSENGER discovered that Mercury has an enormous core, larger than Earth’s. We are trying to understand why that is and why Mercury’s density is similar to Earth’s,” Jim Green explained to Universe Today.

After its first Mercury solar day (176 Earth days) in orbit, MESSENGER has nearly completed two of its main global imaging campaigns: a monochrome map at 250 m/pixel and an eight-color, 1-km/pixel color map. Small gaps will be filled in during the next solar day. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington
“The primary mission lasts 2 solar days, equivalent to 4 Mercury years.”
“NASA has granted a 1 year mission extension, for a total of 8 Mercury years. This will allow the team to understand the environment at Mercury during Solar Maximum for the first time. All prior spacecraft observations were closer to solar minimum,” said Green.
MESSENGER was launched in 2004 and the goal is to produce the first global scientific observations of Mercury and piece together the puzzle of how Mercury fits in with the origin and evolution of our solar system.
NASA’s Mariner 10 was the only previous robotic probe to explore Mercury, during three flyby’s back in the mid-1970’s early in the space age.
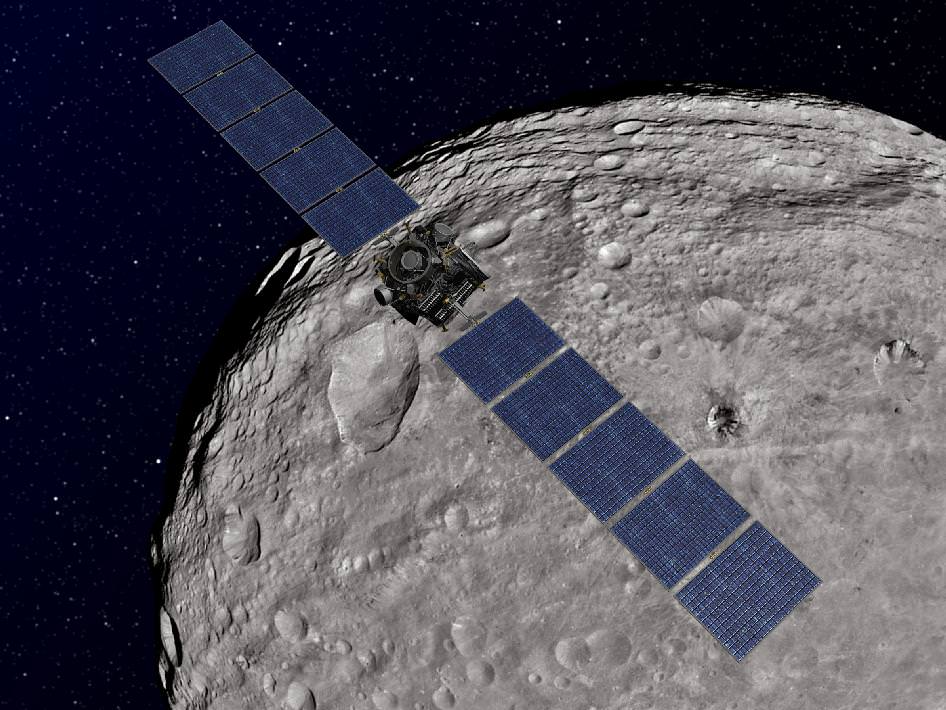
3. Dawn Asteroid Orbiter
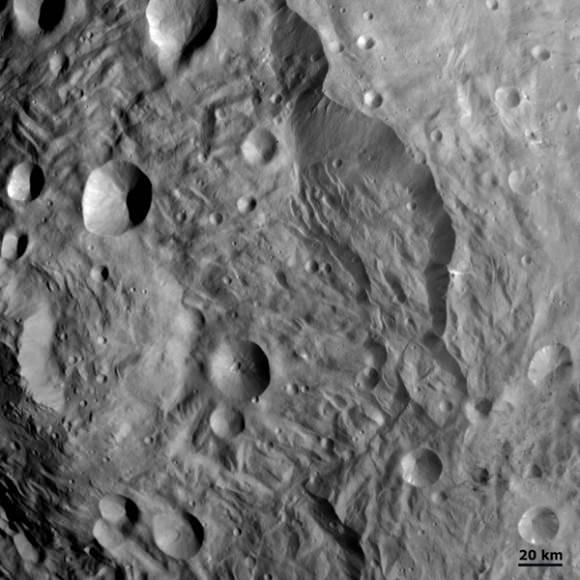
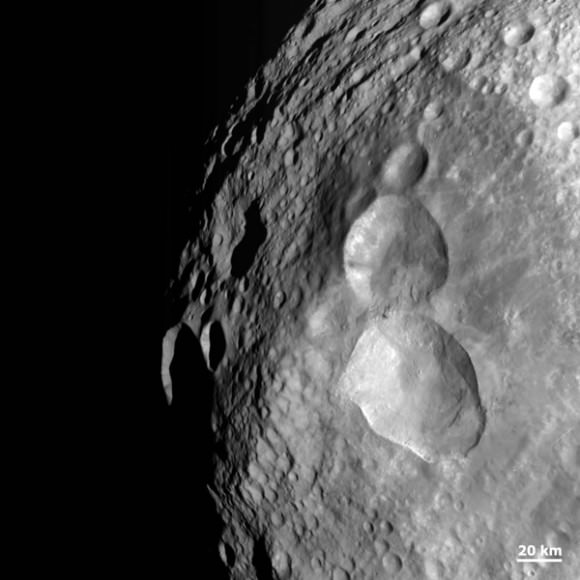
The Dawn spacecraft achieved orbit around the giant asteroid Vesta in July 2011 after a four year interplanetary cruise and began transmitting the history making first ever close-up observations of the mysteriously diverse and alien world that is nothing short of a ‘Space Spectacular’.
“We do not have a good analog to Vesta anywhere else in the Solar System,” Chris Russell said to Universe Today. Russell, from UCLA, is the scientific Principal Investigator for Dawn.
Before Dawn, Vesta was just another fuzzy blob in the most powerful telescopes. Dawn has completely unveiled Vesta as a remarkably dichotomous, heavily battered and pockmarked world that’s littered with thousands of craters, mountains and landslides and ringed by mystifying grooves and troughs. It will unlock details about the elemental abundances, chemical composition and interior structure of this marvelously intriguing body.
Cataclysmic collisions eons ago excavated Vesta so it lacks a south pole. Dawn discovered that what unexpectedly remains is an enormous mountain some 16 miles (25 kilometers) high, twice the height of Mt. Everest.
Dawn is now about midway through its 1 year mission at Vesta which ends in July 2012 with a departure for Ceres, the largest asteroid. So far the framing cameras have snapped more than 10,000 never-before-seen images.
“What can be more exciting than to explore an alien world that until recently was virtually unknown!. ” Dr. Marc Rayman said to Universe Today. Rayman is Dawn’s Chief Engineer from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif.
“Dawn is NASA at its best: ambitious, exciting, innovative, and productive.”
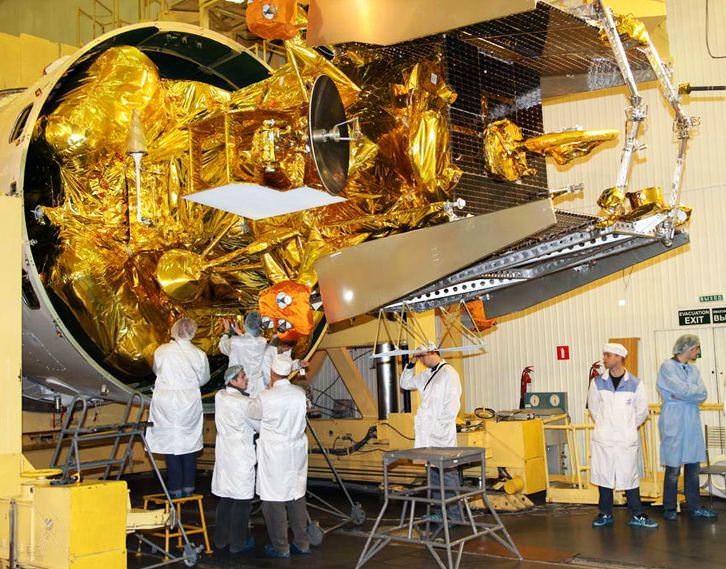
4. Juno Jupiter Orbiter
The solar powered Juno spacecraft was launched on Aug. 5 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, to embark on a five year, 2.8 billion kilometer (1.7 Billion mi) trek to Jupiter, our solar system’s largest planet. It was the first of three NASA planetary science liftoffs scheduled in 2011.

Juno’s goal is to map to the depths of the planets interior and elucidate the ingredients of Jupiter’s genesis hidden deep inside. These measurements will help answer how Jupiter’s birth and evolution applies to the formation of the other eight planets.
The 4 ton spacecraft will arrive at the gas giant in July 2016 and fire its braking rockets to go into a polar orbit and circle the planet 33 times over about one year.
The suite of nine instruments will scan the gas giant to find out more about the planets origins, interior structure and atmosphere, measure the amount of water and ammonia, observe the aurora, map the intense magnetic field and search for the existence of a solid planetary core.
“Jupiter is the Rosetta Stone of our solar system,” said Scott Bolton, Juno’s principal investigator from the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio. “It is by far the oldest planet, contains more material than all the other planets, asteroids and comets combined and carries deep inside it the story of not only the solar system but of us. Juno is going there as our emissary — to interpret what Jupiter has to say.”
5. Opportunity reaches Endeavour Crater on Mars
The long lived Opportunity rover finally arrived at the rim of the vast 14 mile (22 kilometer) wide Endeavour Crater in mid-August 2011 following an epic three year trek across treacherous dune fields – a feat once thought unimaginable. All told, Opportunity has driven more than 34 km ( 21 mi) since landing on the Red Planet way back in 2004 for a mere 90 sol mission.

Opportunity arrived at the rim of Endeavour on Sol 2681, August 9, 2011 after a three year trek. The robot photographed segments of the huge craters eroded rim in this panoramic vista. Endeavour Crater is 14 miles (22 kilometers) in diameter. Mosaic Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Kenneth Kremer
In November, the rover discovered the most scientifically compelling evidence yet for the flow of liquid water on ancient Mars in the form of a water related mineral vein at a spot dubbed “Homestake” along an eroded ridge of Endeavour’s rim.
Read my story about the Homestake discovery here, along with our panoramic mosaic showing the location – created by Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo and published by Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) on 12 Dec. 2011.
Watch for my upcoming story detailing Opportunity’s accomplishments in 2011.
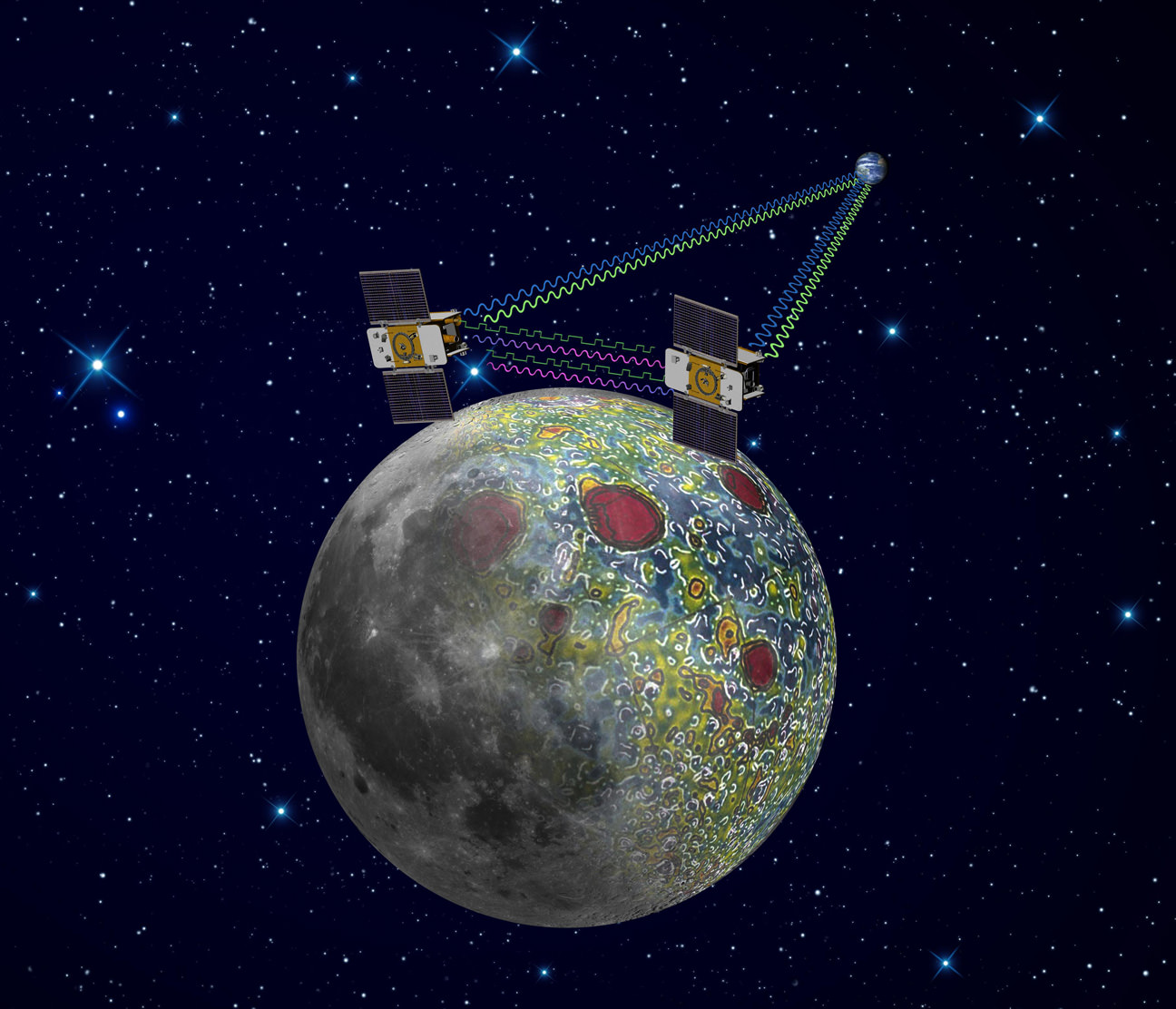
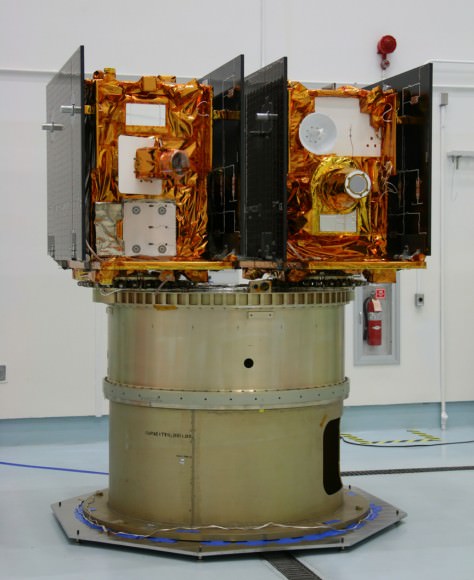
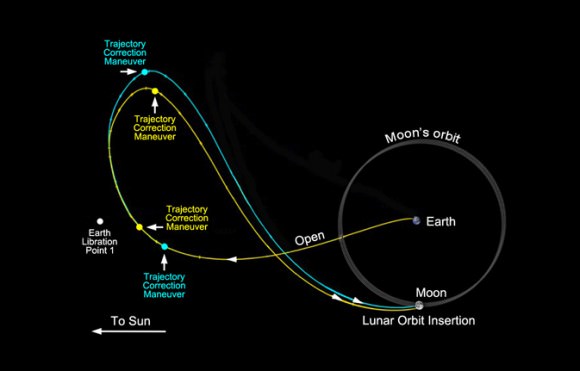
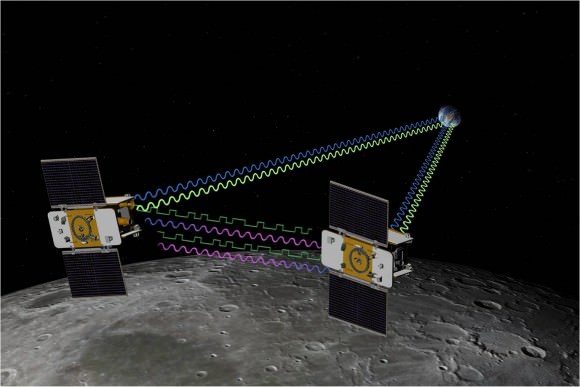
6. GRAIL Moon Mappers
The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory, or GRAIL mission is comprised of twin spacecraft tasked to map the moon’s gravity and study the structure of the lunar interior from crust to core.
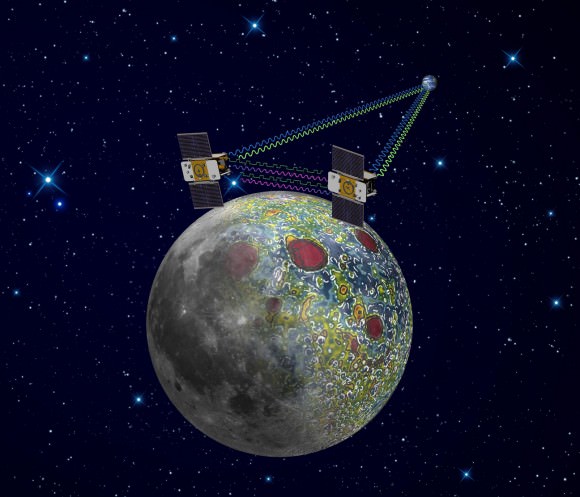

GRAIL spacecraft will map the moon's gravity field and interior composition. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The dynamic duo lifted off from Cape Canaveral on September 10, 2011 atop the last Delta II rocket that will likely soar to space from Florida. After a three month voyage of more than 2.5 million miles (4 million kilometers) since blastoff, the two mirror image GRAIL spacecraft dubbed Grail-A and GRAIL-B are sailing on a trajectory placing them on a course over the Moon’s south pole on New Year’s weekend.
Each spacecraft will fire the braking rockets for about 40 minutes for insertion into Lunar Orbit about 25 hours apart on New Year’s Eve and New Year’s Day.
Engineers will then gradually lower the satellites to a near-polar near-circular orbital altitude of about 34 miles (55 kilometers).
The spacecraft will fly in tandem and the 82 day science phase will begin in March 2012.
“GRAIL is a Journey to the Center of the Moon”, says Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). “GRAIL will rewrite the book on the formation of the moon and the beginning of us.”
“By globally mapping the moon’s gravity field to high precision scientists can deduce information about the interior structure, density and composition of the lunar interior. We’ll evaluate whether there even is a solid or liquid core or a mixture and advance the understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon and the solar system,” explained co-investigator Sami Asmar to Universe Today. Asmar is from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL)
7. Curiosity Mars Rover
The Curiosity Mars Science Lab (MSL) rover soared skywards on Nov. 26, the last of 2011’s three planetary science missions. Curiosity is the newest, largest and most technologically sophisticated robotic surveyor that NASA has ever assembled.
“MSL packs the most bang for the buck yet sent to Mars.” John Grotzinger, the Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist of the California Institute of Technology, told Universe Today.
The three meter long robot is the first astrobiology mission since the Viking landers in the 1970’s and specifically tasked to hunt for the ‘Ingredients of Life’ on Mars – the most Earth-like planet in our Solar System.
Video caption: Action packed animation depicts sequences of Curiosity departing Earth, the nail biting terror of the never before used entry, descent and landing on the Martian surface and then looking for signs of life at Gale Crater during her minimum two year expedition across hitherto unseen and unexplored Martian landscapes, mountains and craters. Credit: NASA
Curiosity will gather and analyze samples of Martian dirt in pursuit of the tell-tale signatures of life in the form of organic molecules – the carbon based building blocks of life as we know it.
NASA is targeting Curiosity to a pinpoint touch down inside the 154 km (96 mile) wide Gale Crater on Aug. 6, 2012. The crater exhibits exposures of phyllosilicates and other minerals that may have preserved evidence of ancient or extant Martian life and is dominated by a towering 3 mile (5 km) high mountain.
“10 science instruments are all aimed at a mountain whose stratigraphic layering records the major breakpoints in the history of Mars’ environments over likely hundreds of millions of years, including those that may have been habitable for life,” Grotzinger told me.
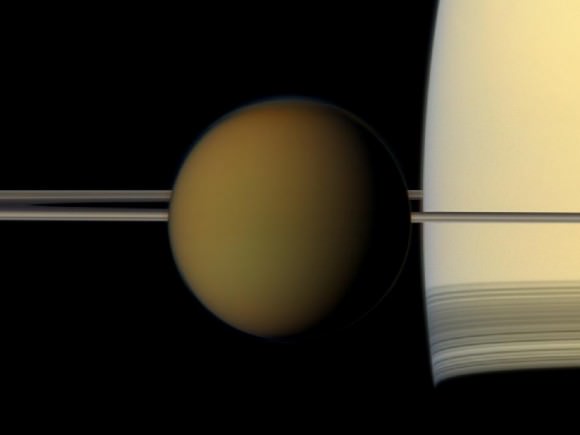
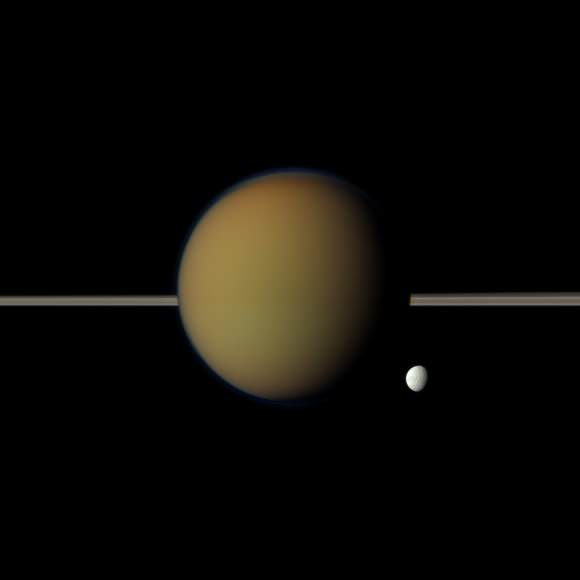
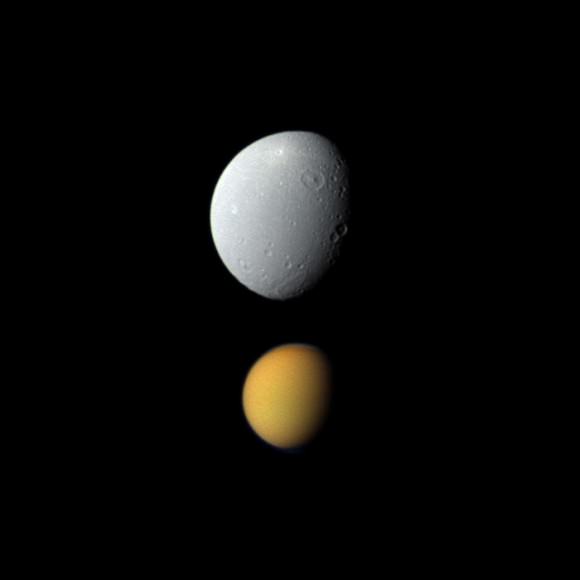
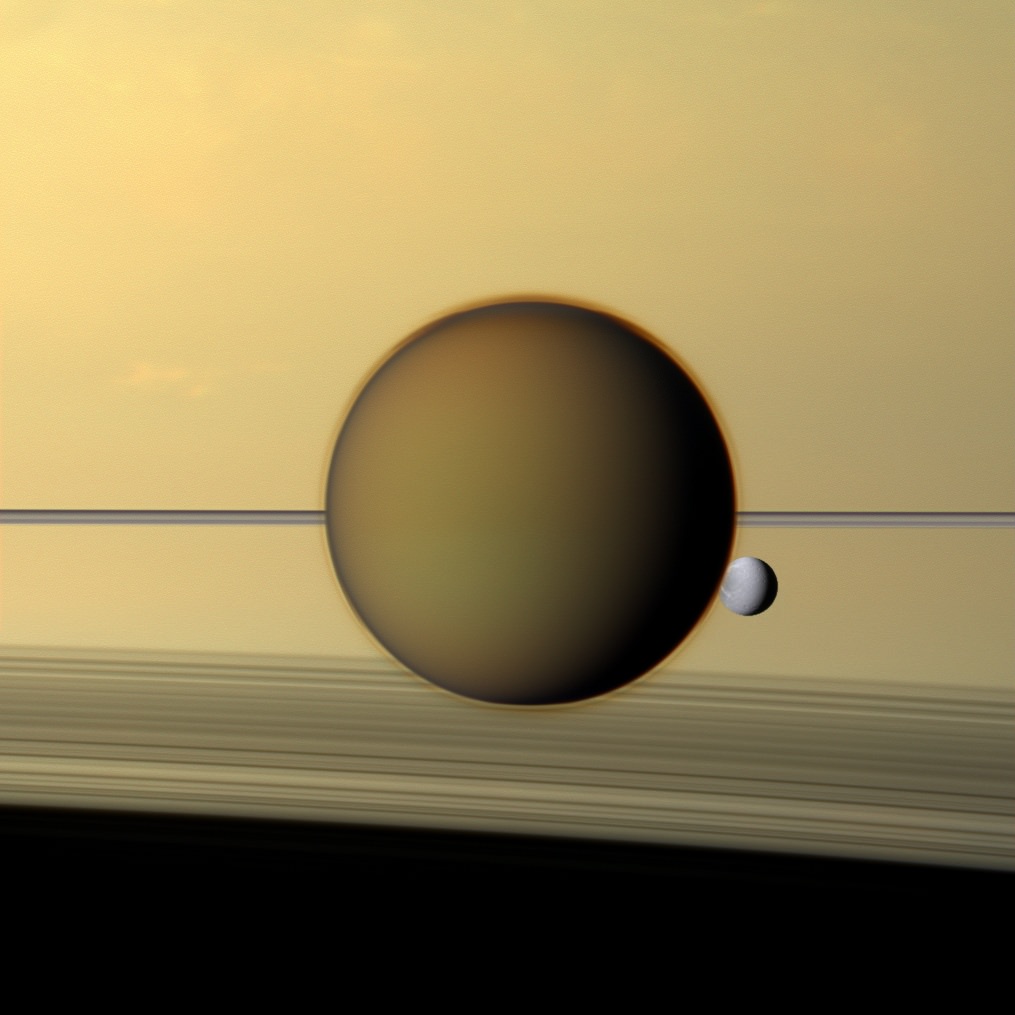
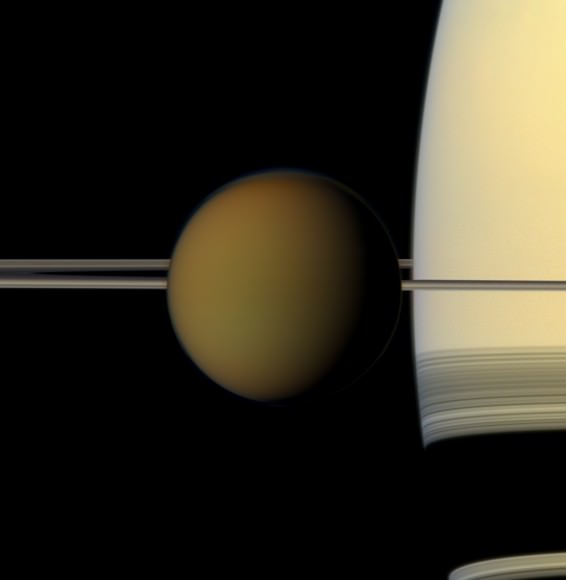
The colorful globe of Saturn's largest moon, Titan, passes in front of the planet and its rings in this true color snapshot from NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute

This past year Ken was incredibly fortunate to witness the ongoing efforts of many of these magnificent endeavors.