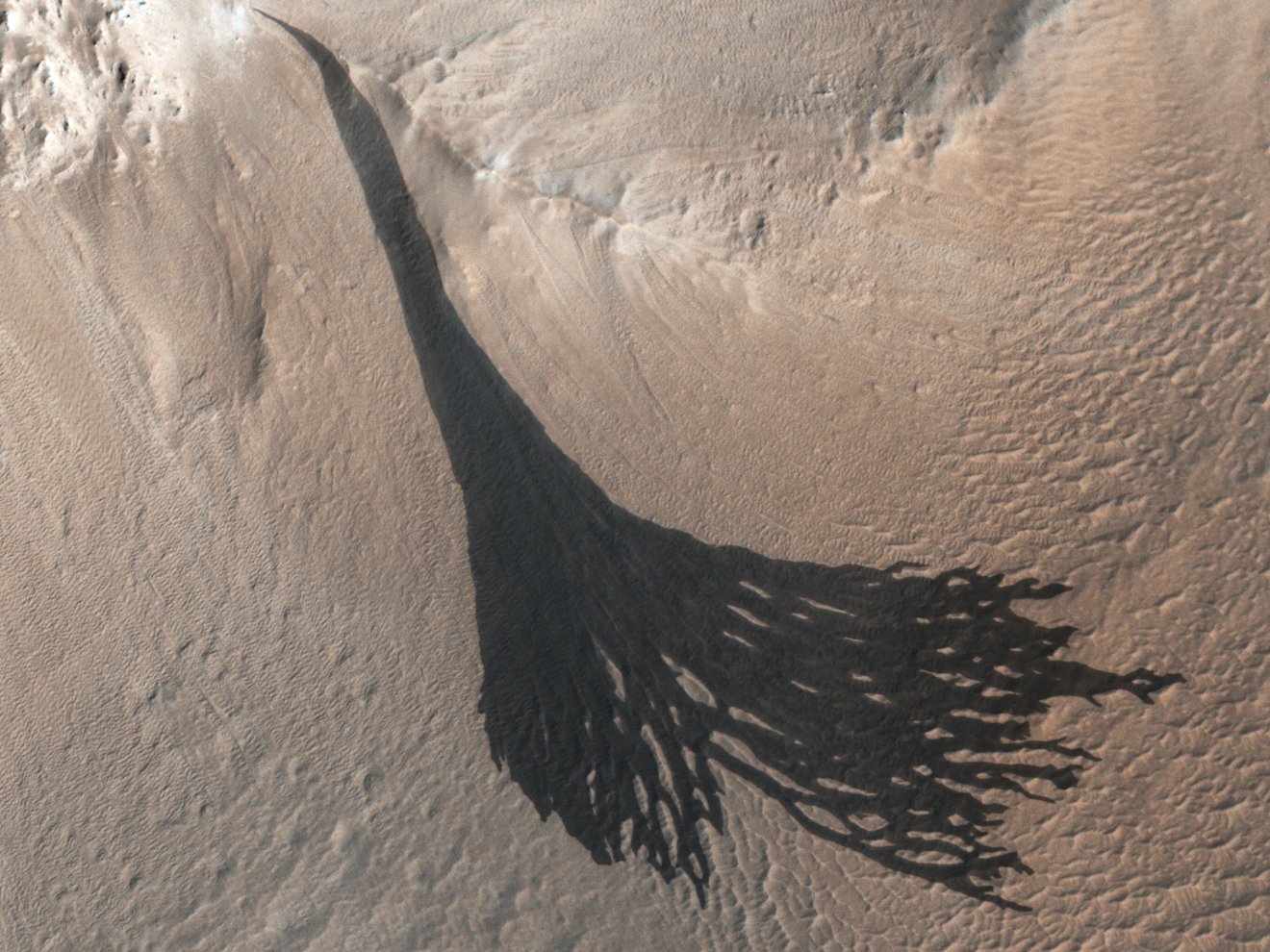
For decades, scientists have observed dark landslides called slope streaks on Mars. First seen by the Viking orbiters in the 1970s, every orbiter mission since has observed them, but the mechanism behind the slope streaks has been hotly debated: could they be caused by water activity on the Red Planet, or are they the result of some sort of dry mechanics?
Turns out, the leading candidate is “dry.” But scientists with the Mars Odyssey mission have verified an additional culprit behind the slope streaks: carbon dioxide frost.
Continue reading “This is a Dust Avalanche on Mars”