In an expected move, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) has announced a mission extension for their Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Hayabusa2 will be sent to rendezvous with another asteroid in a few years time.
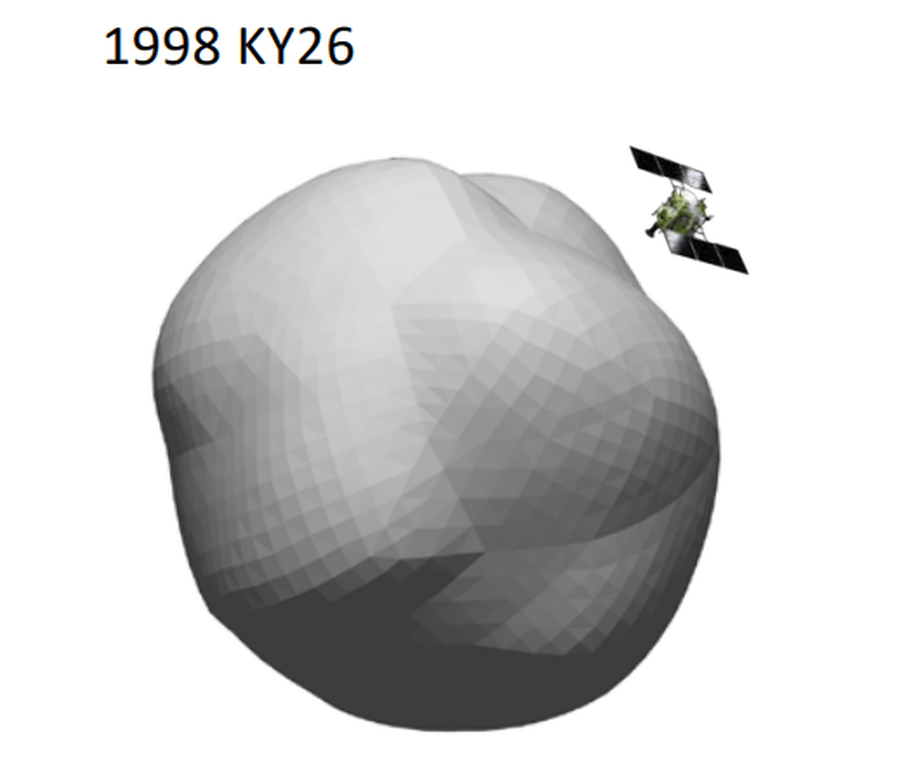
It’s target is 1998 KY26, a near-Earth object (NEO) less than a kilometer in diameter. But it’ll take a while and some maneuvering around other objects in the Solar System to reach its goal. JAXA says the spacecraft will arrive at the asteroid in July 2031.
Continue reading “Hayabusa2’s Mission isn’t Over. It has a New Asteroid Target to Visit: 1998 KY26”