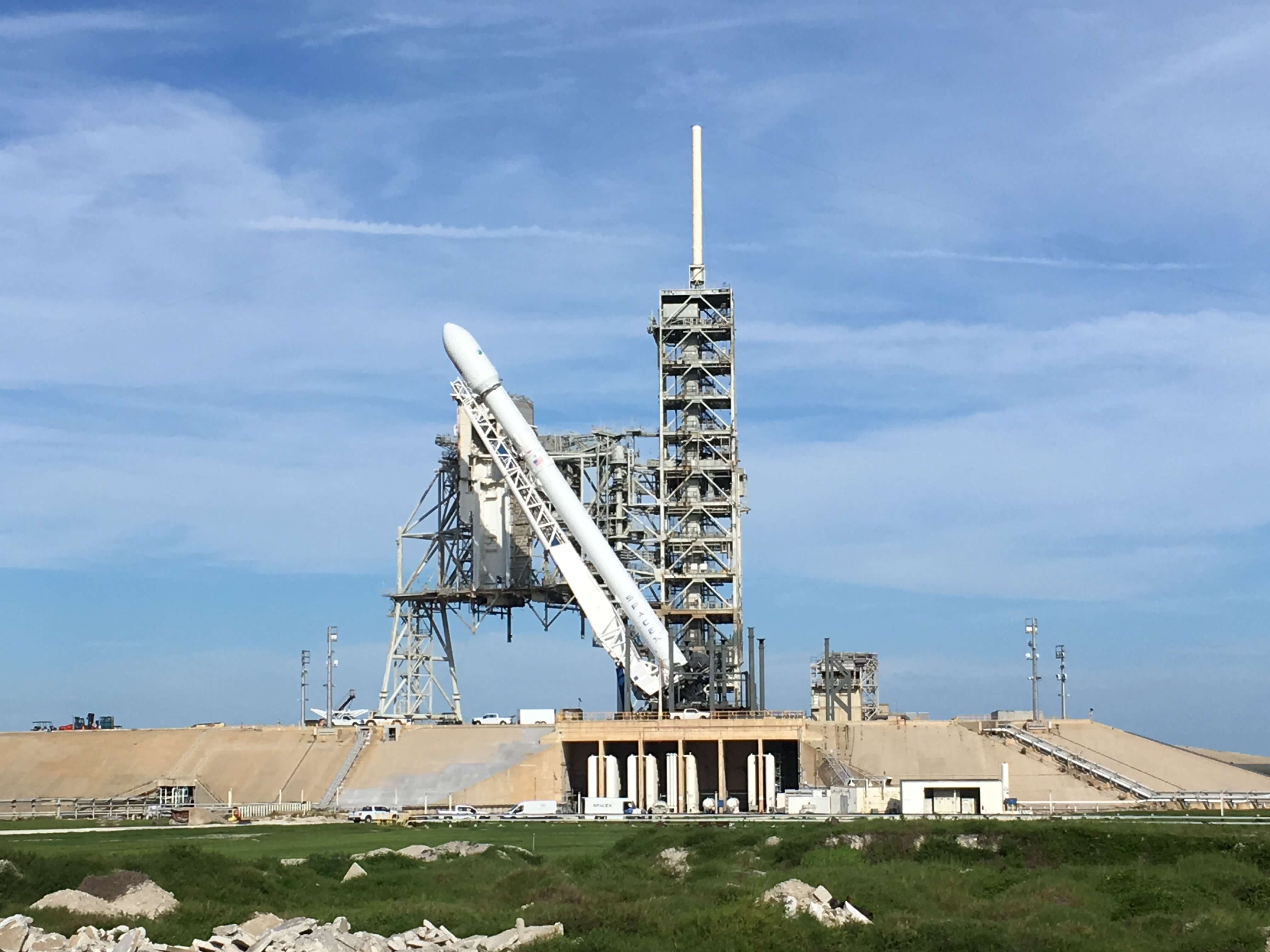
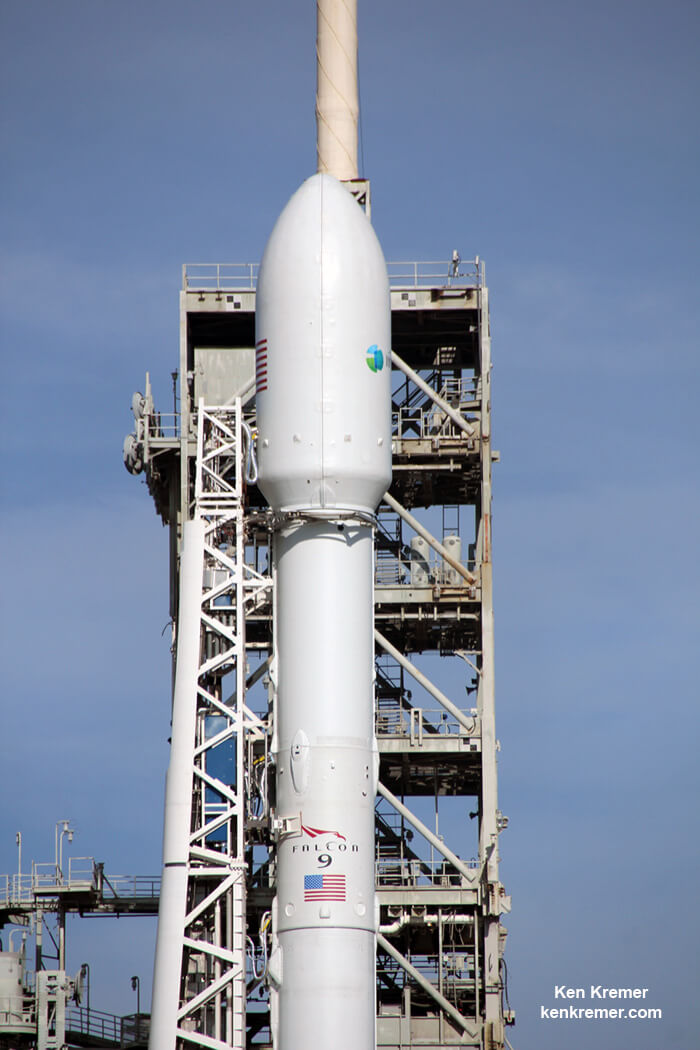
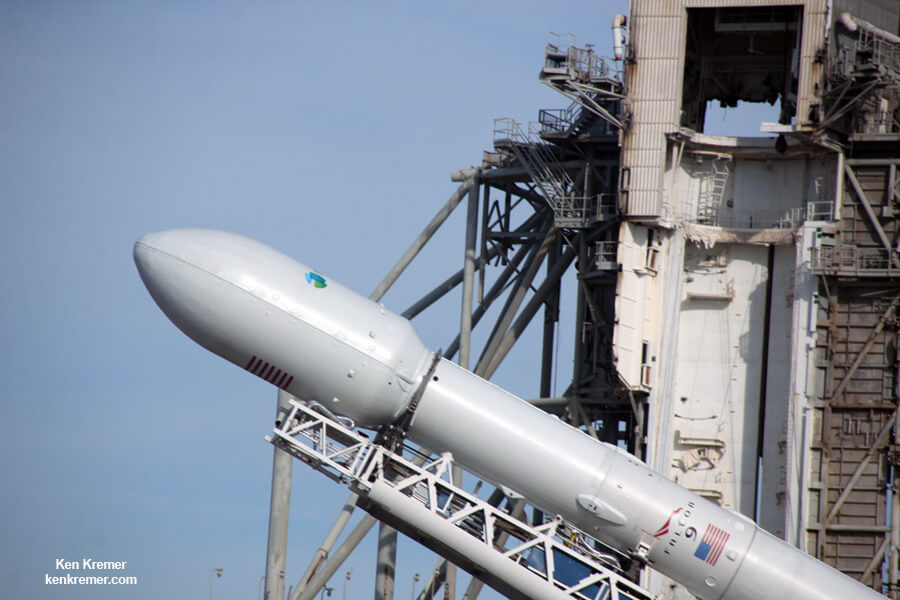
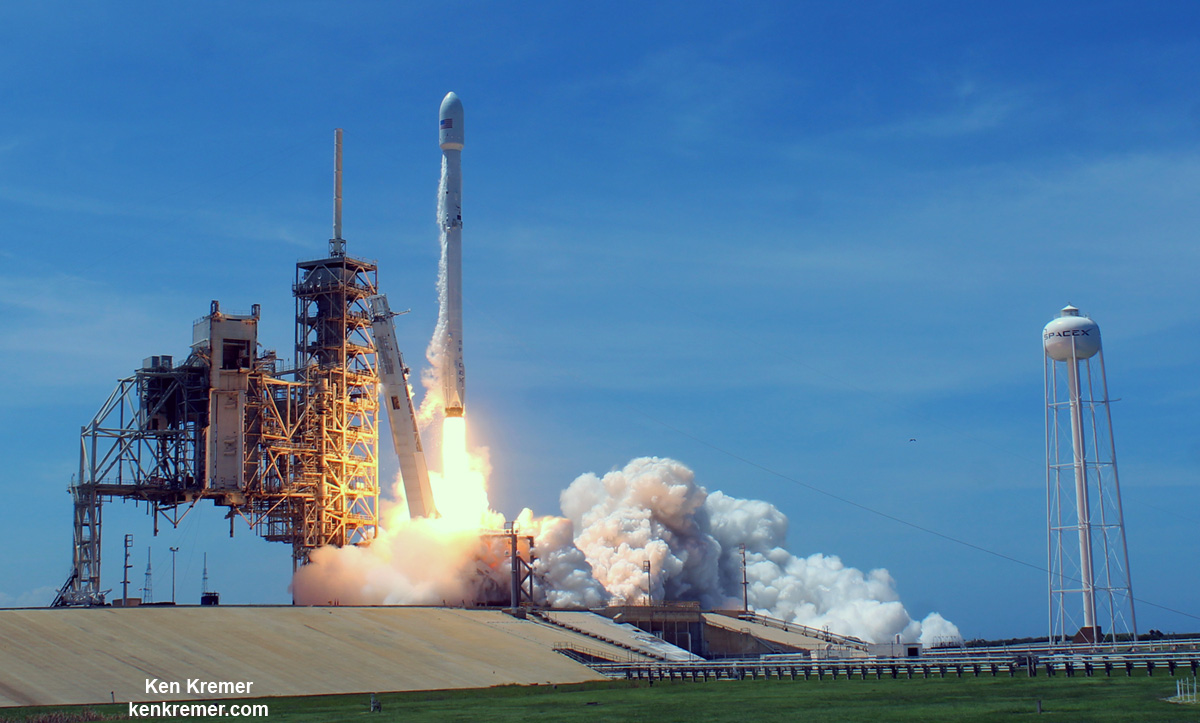
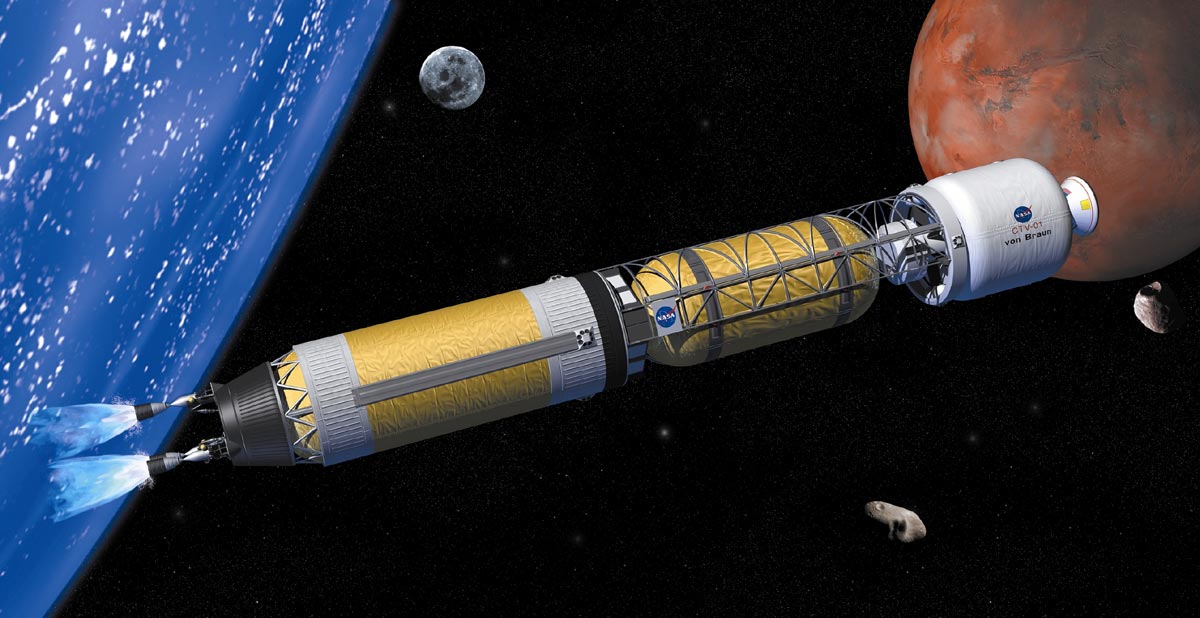
In its pursuit of missions that will take us back to the Moon, to Mars, and beyond, NASA has been exploring a number of next-generation propulsion concepts. Whereas existing concepts have their advantages – chemical rockets have high energy density and ion engines are very fuel-efficient – our hopes for the future hinge on us finding alternatives that combine efficiency and power.
To this end, researchers at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center are once again looking to develop nuclear rockets. As part of NASA’s Game Changing Development Program, the Nuclear Thermal Propulsion (NTP) project would see the creation of high-efficiency spacecraft that would be capable of using less fuel to deliver heavy payloads to distant planets, and in a relatively short amount of time.
As Sonny Mitchell, the project of the NTP project at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, said in a recent NASA press statement:
“As we push out into the solar system, nuclear propulsion may offer the only truly viable technology option to extend human reach to the surface of Mars and to worlds beyond. We’re excited to be working on technologies that could open up deep space for human exploration.”

To see this through, NASA has entered into a partnership with BWX Technologies (BWXT), a Virginia-based energy and technology company that is a leading supplier of nuclear components and fuel to the U.S. government. To assist NASA in developing the necessary reactors that would support possible future crewed missions to Mars, the company’s subsidiary (BWXT Nuclear Energy, Inc.) was awarded a three-year contract worth $18.8 million.
During this three years in which they will be working with NASA, BWXT will provide the technical and programmatic data needed to implement NTP technology. This will consist of them manufacturing and testing prototype fuel elements and helping NASA to resolve any nuclear licensing and regulatory requirements. BWXT will also aid NASA planners in addressing the issues of feasibility and affordably with their NTP program.
As Rex D. Geveden, BWXT’s President and Chief Executive Officer, said of the agreement:
“BWXT is extremely pleased to be working with NASA on this exciting nuclear space program in support of the Mars mission. We are uniquely qualified to design, develop and manufacture the reactor and fuel for a nuclear-powered spacecraft. This is an opportune time to pivot our capabilities into the space market where we see long-term growth opportunities in nuclear propulsion and nuclear surface power.”
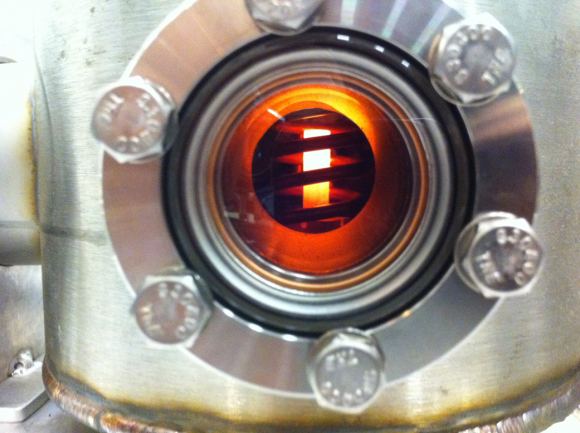
In an NTP rocket, uranium or deuterium reactions are used to heat liquid hydrogen inside a reactor, turning it into ionized hydrogen gas (plasma), which is then channeled through a rocket nozzle to generate thrust. A second possible method, known as Nuclear Electric Propulsion (NEC), involves the same basic reactor converted its heat and energy into electrical energy which then powers an electrical engine.

In both cases, the rocket relies on nuclear fission to generates propulsion rather than chemical propellants, which has been the mainstay of NASA and all other space agencies to date. Compared to this traditional form of propulsion, both types of nuclear engines offers a number of advantages. The first and most obvious is the virtually unlimited energy density it offers compared to rocket fuel.
This would cut the total amount of propellant needed, thus cutting launch weight and the cost of individual missions. A more powerful nuclear engine would mean reduced trip times. Already, NASA has estimated that an NTP system could make the voyage to Mars to four months instead of six, which would reduce the amount of radiation the astronauts would be exposed to in the course of their journey.
To be fair, the concept of using nuclear rockets to explore the Universe is not new. In fact, NASA has explored the possibility of nuclear propulsion extensively under the Space Nuclear Propulsion Office. In fact, between 1959 and 1972, the SNPO conducted 23 reactor tests at the Nuclear Rocket Development Station at AEC’s Nevada Test Site, in Jackass Flats, Nevada.
In 1963, the SNPO also created the Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Applications (NERVA) program to develop nuclear-thermal propulsion for long-range crewed mission to the Moon and interplanetary space. This led to the creation of the NRX/XE, a nuclear-thermal engine which the SNPO certified as having met the requirements for a crewed mission to Mars.

The Soviet Union conducted similar studies during the 1960s, hoping to use them on the upper stages of of their N-1 rocket. Despite these efforts, no nuclear rockets ever entered service, owing to a combination of budget cuts, loss of public interest, and a general winding down of the Space Race after the Apollo program was complete.
But given the current interest in space exploration, and ambitious mission proposed to Mars and beyond, it seems that nuclear rockets may finally see service. One popular idea that is being considered is a multistage rocket that would rely on both a nuclear engine and conventional thrusters – a concept known as a “bimodal spacecraft”. A major proponent of this idea is Dr. Michael G. Houts of the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center.
In 2014, Dr. Houts conducted a presentation outlining how bimodal rockets (and other nuclear concepts) represented “game-changing technologies for space exploration”. As an example, he explained how the Space Launch System (SLS) – a key technology in NASA’s proposed crewed mission to Mars – could be equipped with chemical rocket in the lower stage and a nuclear-thermal engine on the upper stage.
In this setup, the nuclear engine would remain “cold” until the rocket had achieved orbit, at which point the upper stage would be deployed and the reactor would be activated to generate thrust. Other examples cited in the report include long-range satellites that could explore the Outer Solar System and Kuiper Belt and fast, efficient transportation for manned missions throughout the Solar System.
The company’s new contract is expected to run through Sept. 30th, 2019. At that time, the Nuclear Thermal Propulsion project will determine the feasibility of using low-enriched uranium fuel. After that, the project then will spend a year testing and refining its ability to manufacture the necessary fuel elements. If all goes well, we can expect that NASA’s “Journey to Mars” might just incorporate some nuclear engines!