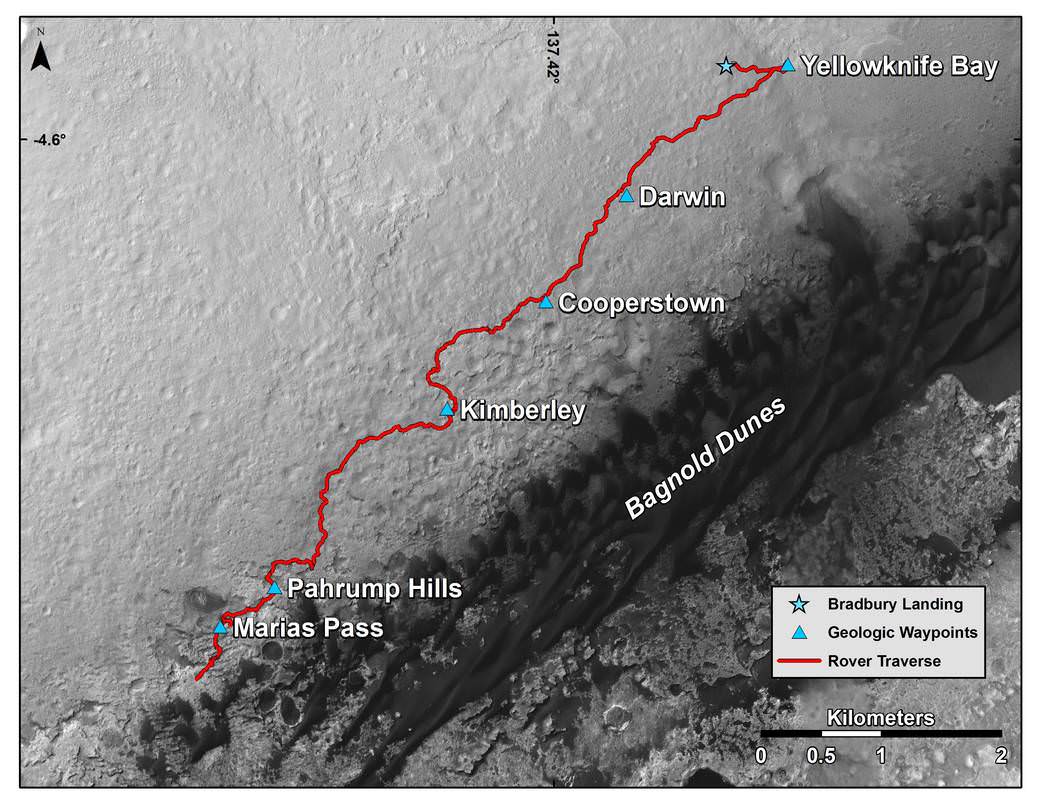
NASA’s Curiosity rover is on the Martian road to soon start the first ever study of currently active sand dunes anywhere beyond Earth. The dunes are located nearby, at the foothills of Mount Sharp, and Curiosity is due to arrive for an up close look in just a few days to start her unique research investigations.
The eerily dark dunes, named the “Bagnold Dunes,” skirt the northwestern flank of Mount Sharp. Ascending and diligently exploring the sedimentary layers of Mount Sharp is the primary goal of the mission.
“The ‘Bagnold Dunes’ are tantalizingly close,” says Ken Herkenhoff, Research Geologist at the USGS Astrogeology Science Center and an MSL science team member, in a mission update on Wednesday, Nov. 18.
The “Bagnold Dunes” have been quite noticeable in numerous striking images taken from Mars orbit, during the vehicles nail biting ‘7 Minutes of Terror’ descent from orbit, as well as in thousands upon thousands of images taken by Curiosity herself as the robot edged ever closer during her over three year long traverse across the floor of the Gale Crater landing site.
Curiosity must safely cross the expansive dune field before climbing Mount Sharp.
Although multiple NASA rovers, including Curiosity, have studied much smaller Martian sand ripples or drifts, none has ever visited and investigated up close these types of large dunes that range in size as tall as a two story building or more and as wide as a football field or more.
Moreover the Martian dunes are shifting even today.
“Shifting sands lie before me,” Curiosity tweeted. “Off to image, scoop and scuff active dunes on Mars. I’ll be the first craft to visit such dunes beyond Earth!”
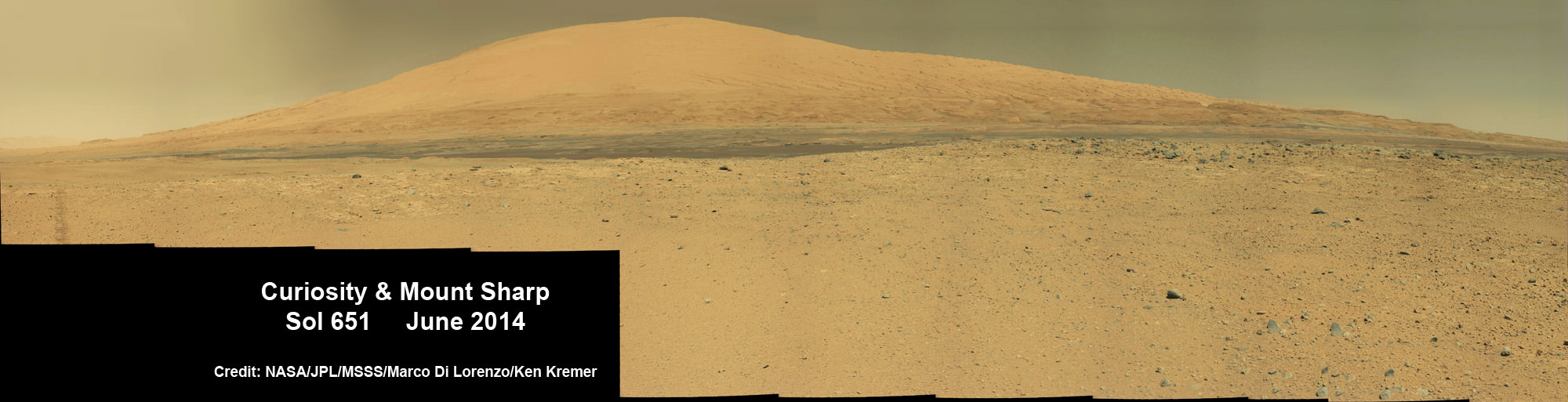

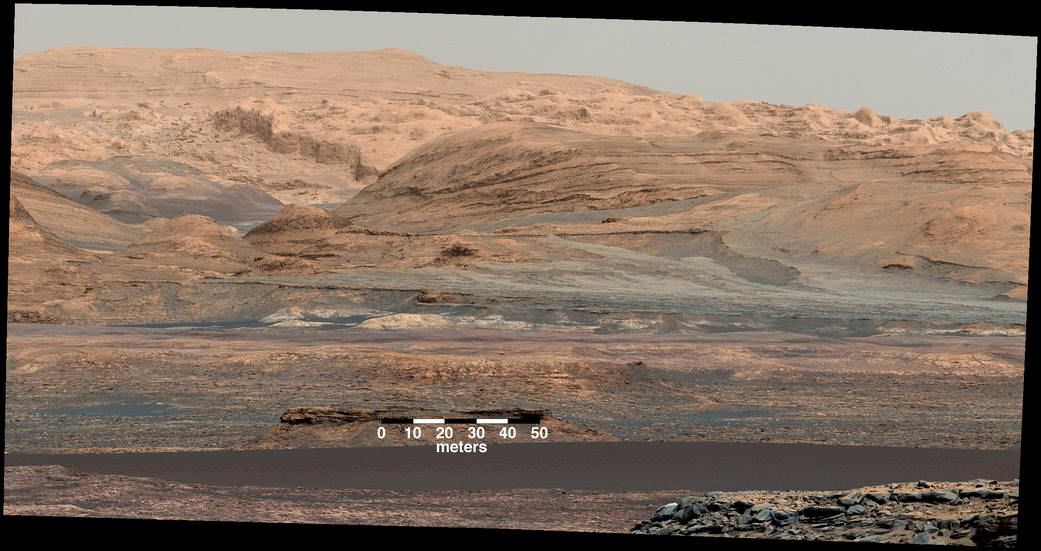
Curiosity rover panorama of Mount Sharp captured on June 6, 2014 (Sol 651) during traverse inside Gale Crater. Note rover wheel tracks at left. She will eventually ascend the mountain at the ‘Murray Buttes’ at right later this year. Assembled from Mastcam color camera raw images and stitched by Marco Di Lorenzo and Ken Kremer. Credit: NASA/JPL/MSSS/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer-kenkremer.com
“The Bagnold Dunes are active: Images from orbit indicate some of them are migrating as much as about 3 feet (1 meter) per Earth year. No active dunes have been visited anywhere in the solar system besides Earth,” notes NASA.
Curiosity is currently only some 200 yards or meters away from the first dune she will investigate, simply named “Dune 1.”
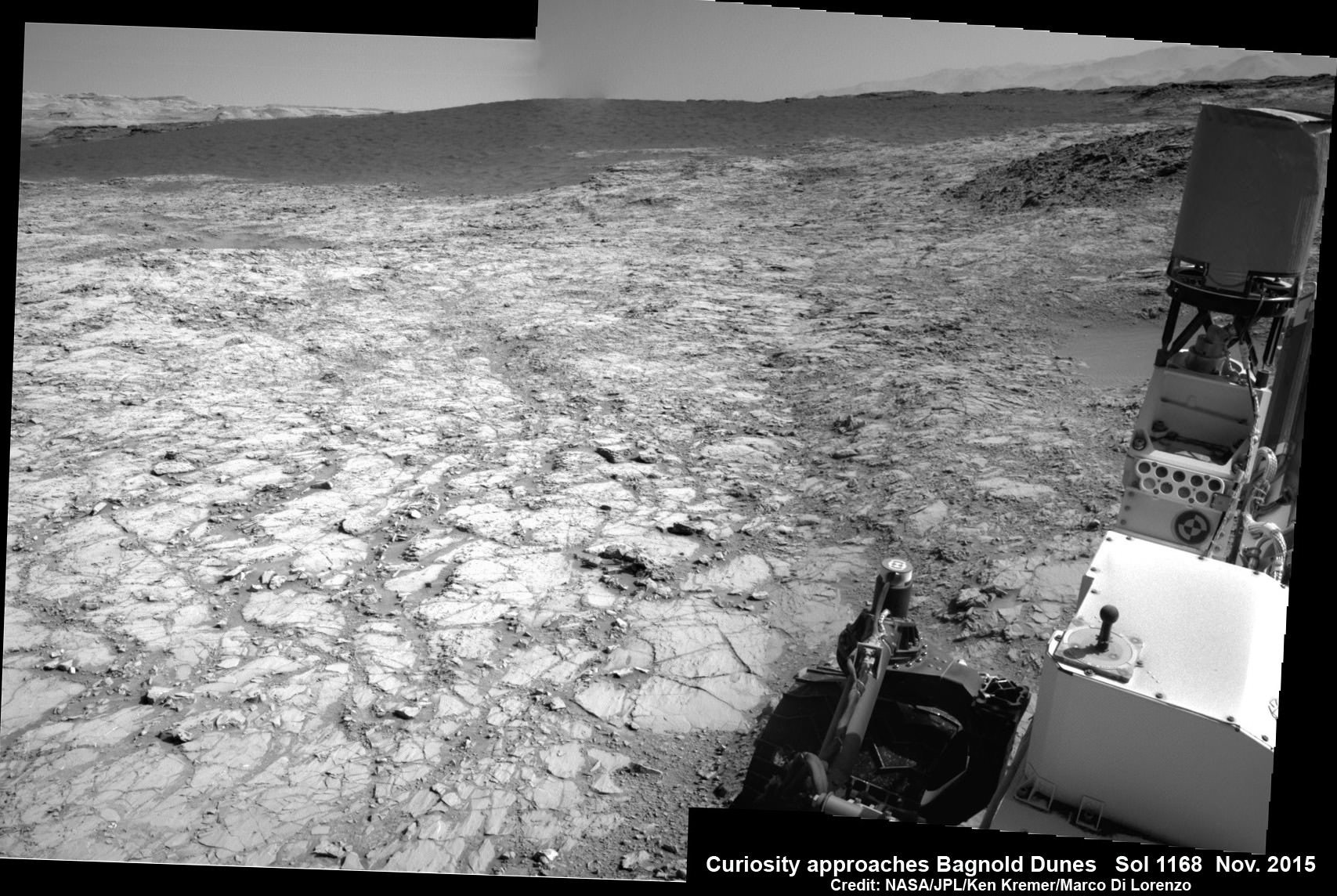

As the rover approaches closer and closer, the dune research campaign is already in progress as she snaps daily high resolution images and gathers measurements of the area’s wind direction and speed.
“We’ve planned investigations that will not only tell us about modern dune activity on Mars but will also help us interpret the composition of sandstone layers made from dunes that turned into rock long ago,” said Bethany Ehlmann of the California Institute of Technology and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, California, in a statement.
After arriving at the dune, the team will command Curiosity to scoop up samples for analysis by the rover’s pair of miniaturized chemistry instruments inside its belly. It will also scuff the dune with a wheel to examine and compare the surface and interior physical characteristics.

The dark dunes are informally named after British military engineer Ralph Bagnold (1896-1990), who conducted pioneering studies of the effect of wind on motion of individual particles in dunes on Earth. Curiosity will carry out “the first in-place study of dune activity on a planet with lower gravity and less atmosphere.”
Although the huge Bagnold dunes are of great scientific interest, the team will also certainly exercise caution in maneuvering the car sized six wheel robot.
Recall that NASA’s smaller golf cart Spirit Mars rover perished a few years back – albeit over 6 years into her 3 month mission – when the robot became unexpectedly mired in a nearly invisible sand ripple from which she was unable to escape.
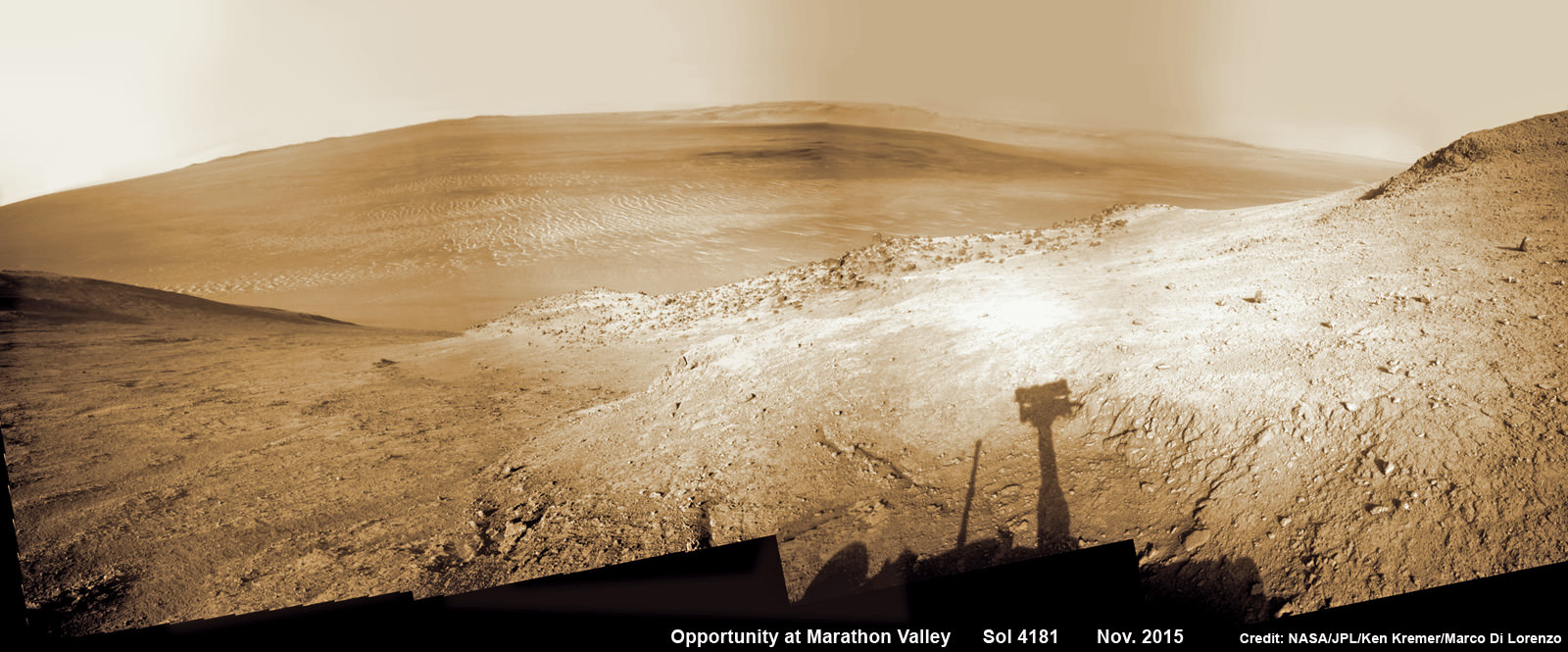
Likewise, sister Opportunity got stuck in a sand ripple earlier in her mission that took the engineering team weeks of painstaking effort to extricate from a spot subsequently named ‘Purgatory’ that resulted in many lessons learned for future operations.
Opportunity is still hard at work – currently exploring Marathon Valley – nearly a dozen years into her planned 3 month mission.
Based on orbital observations by the CRISM and HiRISE instruments aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, the science team has concluded that the Bagnold Dunes are mobile and also have an uneven distribution of minerals, such as olivine.
“We will use Curiosity to learn whether the wind is actually sorting the minerals in the dunes by how the wind transports particles of different grain size,” Ehlmann said.
“If the Bagnold campaign finds that other mineral grains are sorted away from heavier olivine-rich grains by the wind’s effects on dune sands, that could help researchers evaluate to what extent low and high amounts of olivine in some ancient sandstones could be caused by wind-sorting rather than differences in alteration by water,” say researchers.
“These dunes have a different texture from dunes on Earth,” said team member Nathan Bridges, of the Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, Maryland.
“The ripples on them are much larger than ripples on top of dunes on Earth, and we don’t know why. We have models based on the lower air pressure. It takes a higher wind speed to get a particle moving. But now we’ll have the first opportunity to make detailed observations.”
Last month Curiosity conducted her eighth drill campaign for sample chemical analysis at the ‘Big Sky’ site, before moving on to ‘Greenhorn’. Big Sky was an area of cross-bedded sandstone rock in the Stimson geological unit on the lower slopes of Mount Sharp.

Curiosity has already accomplished her primary objective of discovering a habitable zone on the Red Planet – at the Yellowknife Bay area – that contains the minerals necessary to support microbial life in the ancient past when Mars was far wetter and warmer billions of years ago.
As of today, Sol 1168, November 19, 2015, she has driven over 6.9 miles (11.1 kilometers) kilometers and taken over 282,100 amazing images.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about Orbital ATK Cygnus, ISS, ULA Atlas rocket, SpaceX, Boeing, Space Taxis, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Dec 1 to 3: “Orbital ATK Atlas/Cygnus launch to the ISS, ULA, SpaceX, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings
Dec 8: “America’s Human Path Back to Space and Mars with Orion, Starliner and Dragon.” Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton, AAAP, Princeton University, Ivy Lane, Astrophysics Dept, Princeton, NJ; 7:30 PM.