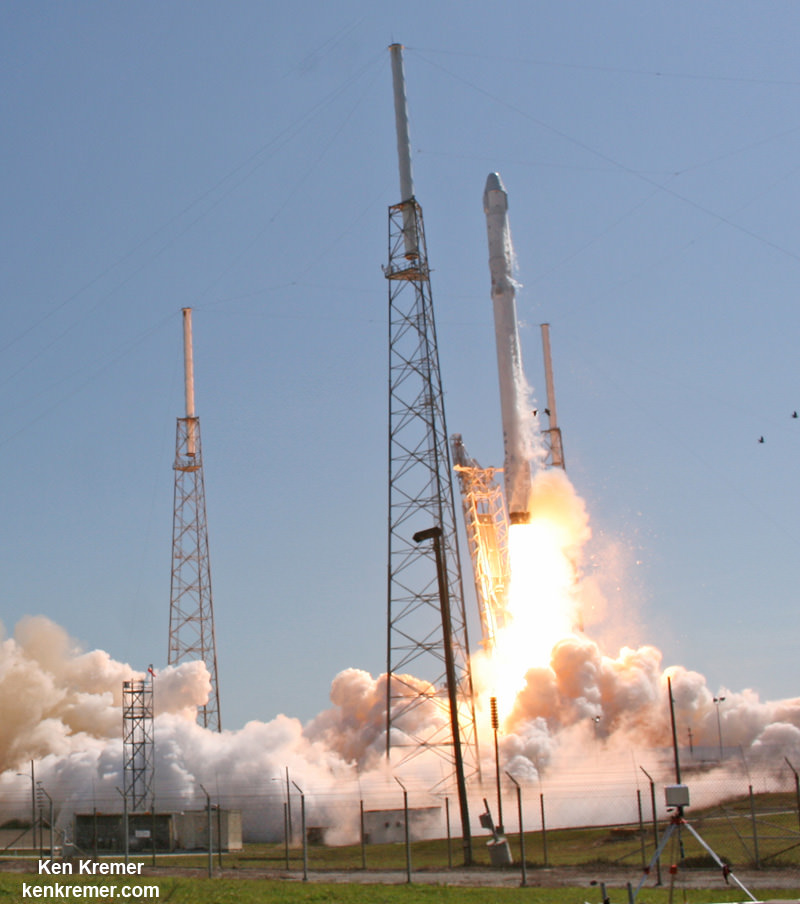
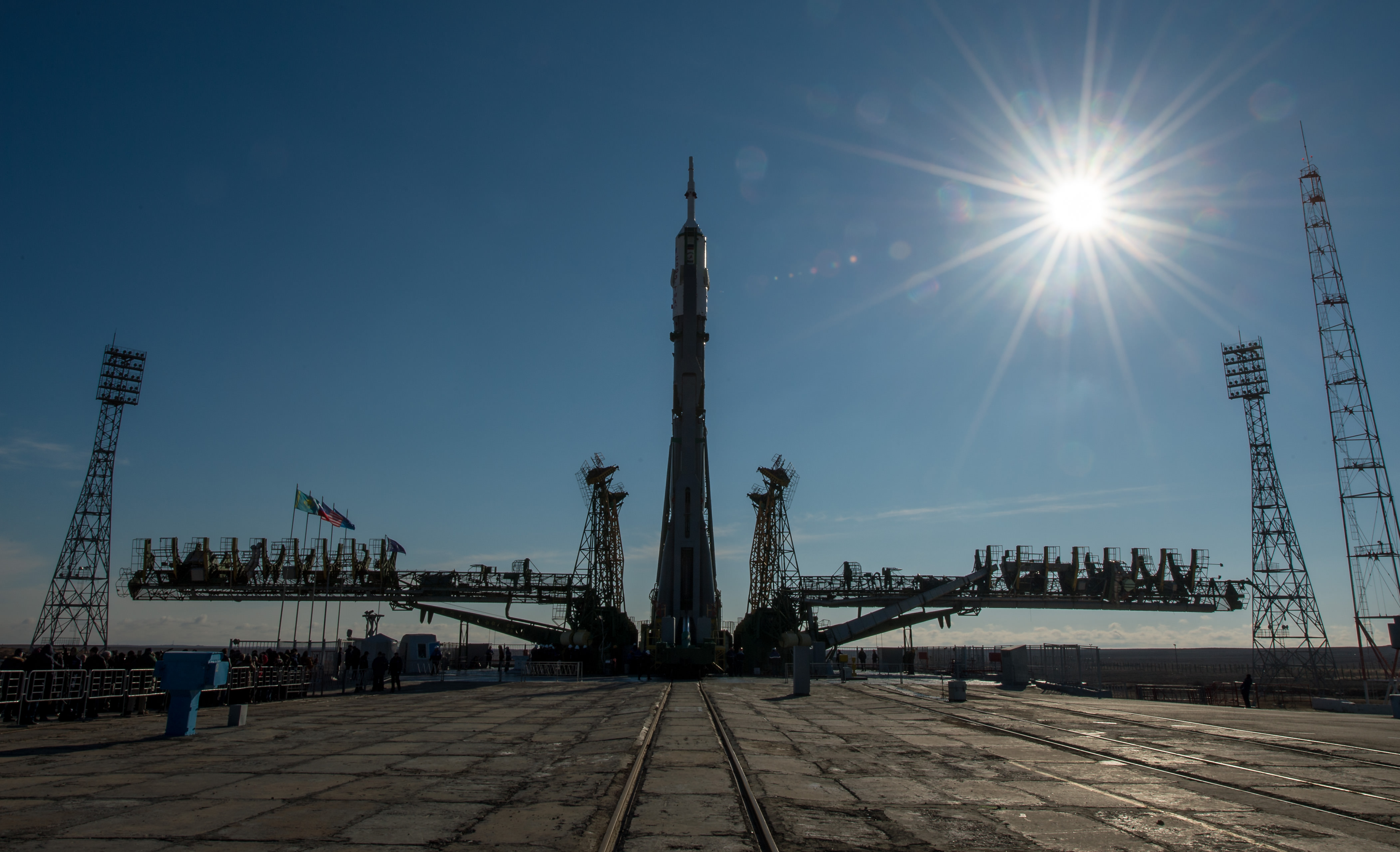
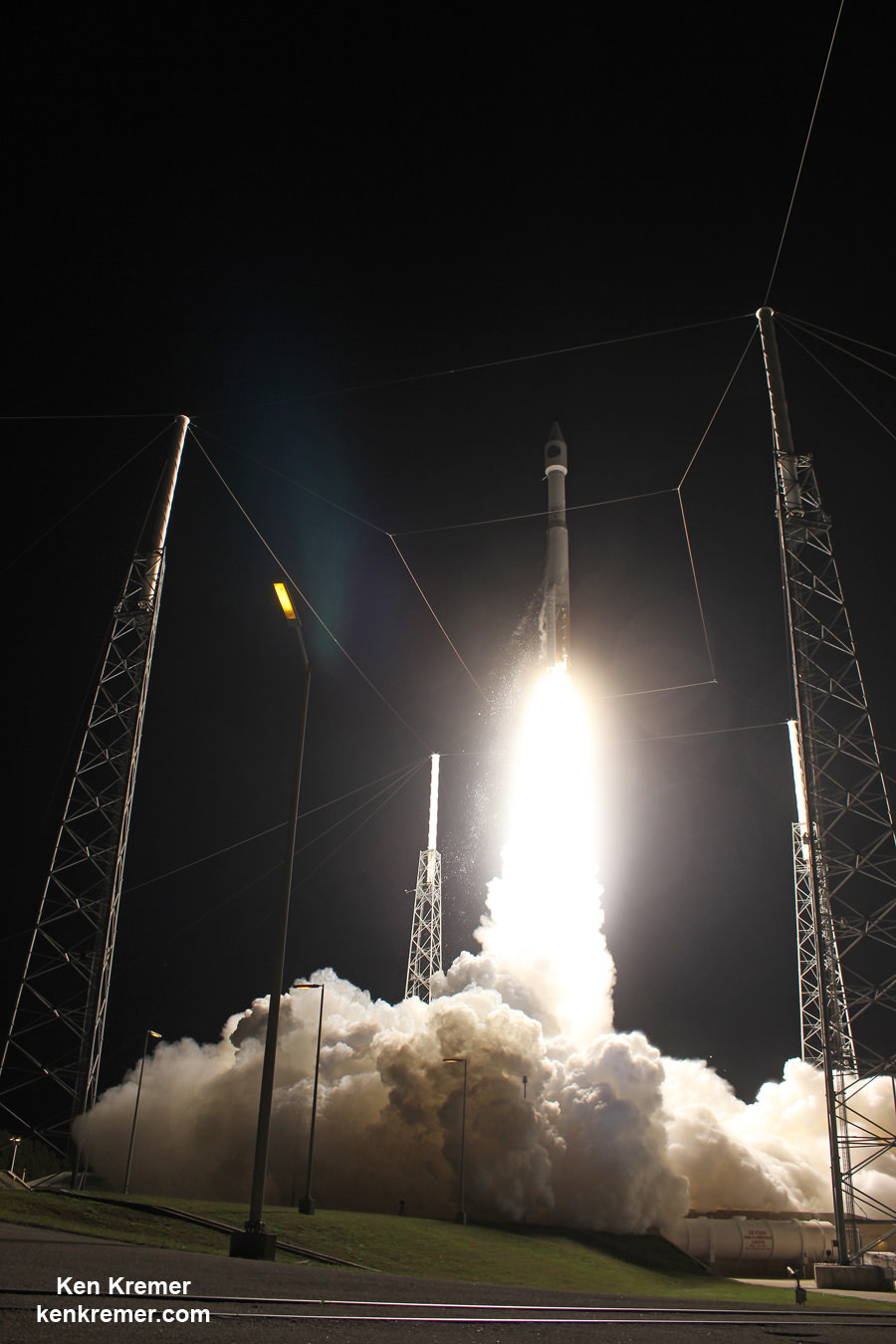
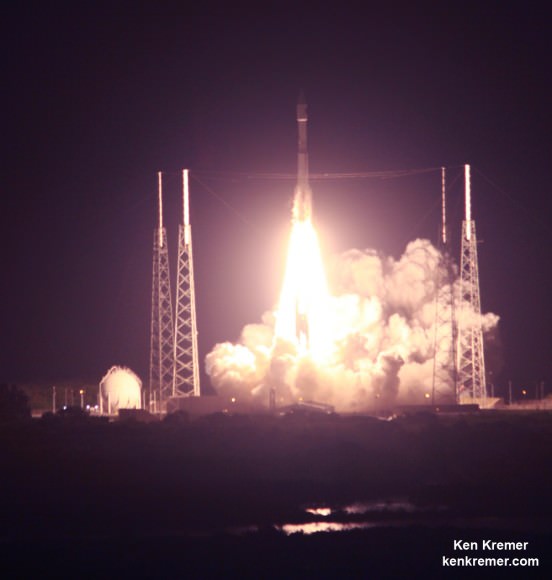
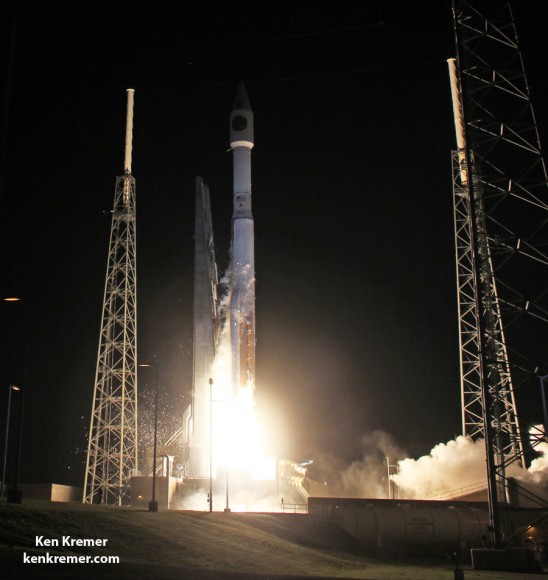
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – After a 24 hour delay due to threatening clouds, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soared spectacularly to orbit from the Florida Space coast today, April 14, carrying a Dragon on a science supply run bound for the the International Space Station that will help pave the way for deep space human missions to the Moon, Asteroids and Mars.
Meanwhile, SpaceX’s bold attempt to land and recover the 14 story tall first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket successfully reached a tiny ocean floating barge in the Atlantic Ocean, but tilted over somewhat over in the final moments of the approach, and tipped over after landing and broke apart. Here’s a Vine video posted on Twitter by Elon Musk:
See the video of the launch, below.
SpaceX will continue with attempt to soft land and recover the rocket on upcoming launches, which was a secondary goal of the company. SpaceX released some imagery and video with a few hours of the landing attempt.
“Looks like Falcon landed fine, but excess lateral velocity caused it to tip over post landing,” tweeted SpaceX CEO Elon Musk.

The Falcon 9 first stage was outfitted with four landing legs and grid fins to enable the landing attempt, which is a secondary objective of SpaceX.
The top priority was to safely launch the Falcon 9 and deliver critical supplies to the station with the Dragon cargo vessel.
“Five years ago this week, President Obama toured the same SpaceX launch pad used today to send supplies, research and technology development to the ISS,” said NASA Administrator Charles Bolden.
“Back then, SpaceX hadn’t even made its first orbital flight. Today, it’s making regular flights to the space station and is one of two American companies, along with The Boeing Company, that will return the ability to launch NASA astronauts to the ISS from U.S. soil and land then back in the United States. That’s a lot of progress in the last five years, with even more to come in the next five.”
“Looks like Falcon landed fine, but excess lateral velocity caused it to tip over post landing,” tweeted SpaceX CEO Elon Musk.
A chase plane captured dramatic footage of the landing on the ocean going platform known as the ‘autonomous spaceport drone ship’ (ASDS).
It was pre-positioned some 200 to 250 miles offshore of the Carolina coast in the Atlantic Ocean along the rockets flight path flying along the US Northeast coast to match that of the ISS.
The ASDS measures only 300 by 100 feet, with wings that extend its width to 170 feet.
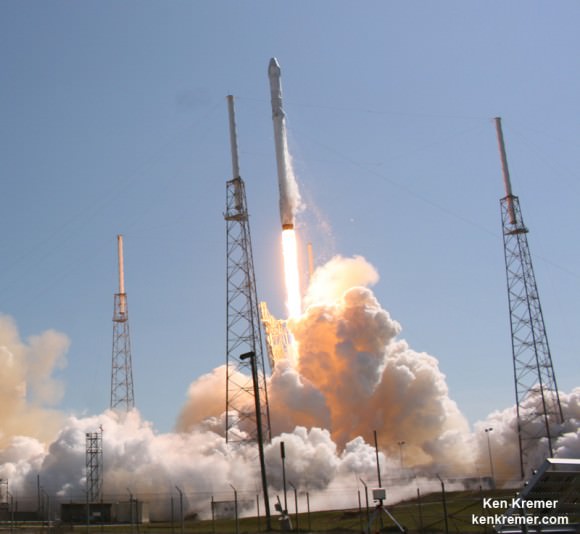

Overall CRS-6 is the sixth SpaceX commercial resupply services mission and the seventh trip by a Dragon spacecraft to the station since 2012.
CRS-6 marks the company’s sixth operational resupply mission to the ISS under a $1.6 Billion contract with NASA to deliver 20,000 kg (44,000 pounds) of cargo to the station during a dozen Dragon cargo spacecraft flights through 2016 under NASA’s original Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract.

Dragon is packed with more than 4,300 pounds (1915 kilograms) of scientific experiments, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, spare parts, food, water, clothing and assorted research gear for the six person Expedition 43 and 44 crews serving aboard the ISS.
After a three day orbital chase, the Dragon spacecraft with rendezvous with the million post Earth orbiting outpost Friday morning April 17.
After SpaceX engineers on the ground maneuver the Dragon close enough to the station, European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti will use the station’s 57.7-foot-long (17-meter-long) robotic arm to reach out and capture Dragon at approximately 7 a.m. EDT on April 17.
Cristoforetti will be assisted by fellow Expedition 43 crew member and NASA astronaut
Terry Virts, as they work inside the stations seven windowed domed cupola to berth Dragon at the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module.

Watch for Ken’s continuing onsite coverage of the CRS-6 launch from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about SpaceX, Mars rovers, Orion, Antares, MMS, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Apr 18/19: “Curiosity explores Mars” and “NASA Human Spaceflight programs” – NEAF (NorthEast Astronomy Forum), 9 AM to 5 PM, Suffern, NY, Rockland Community College and Rockland Astronomy Club