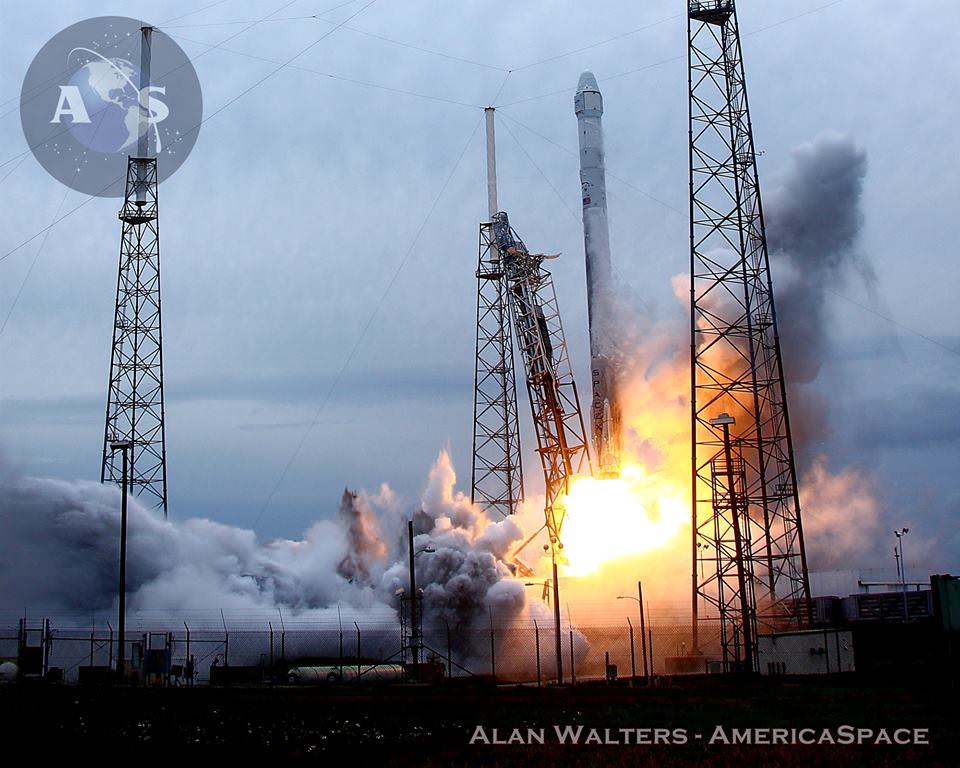
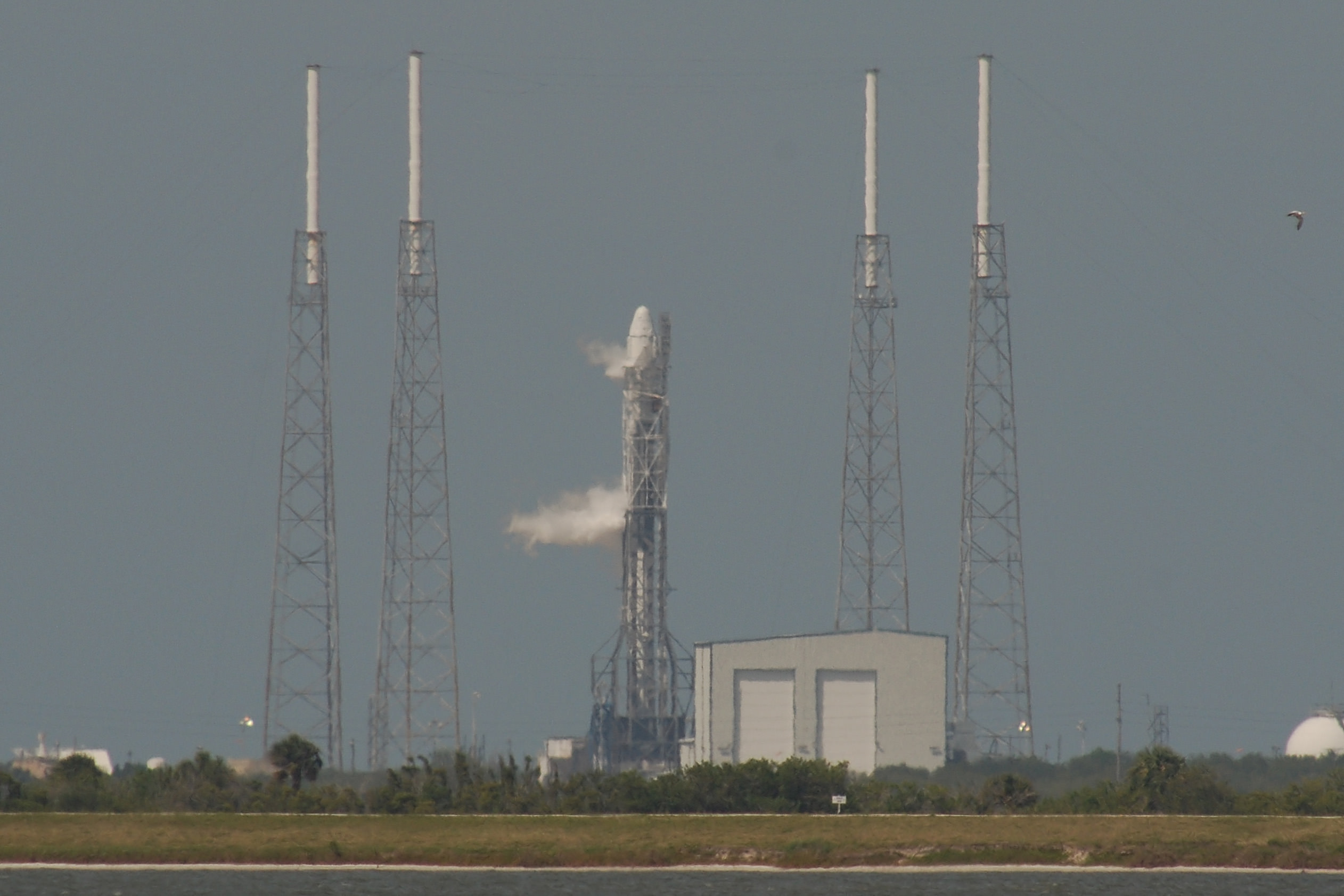
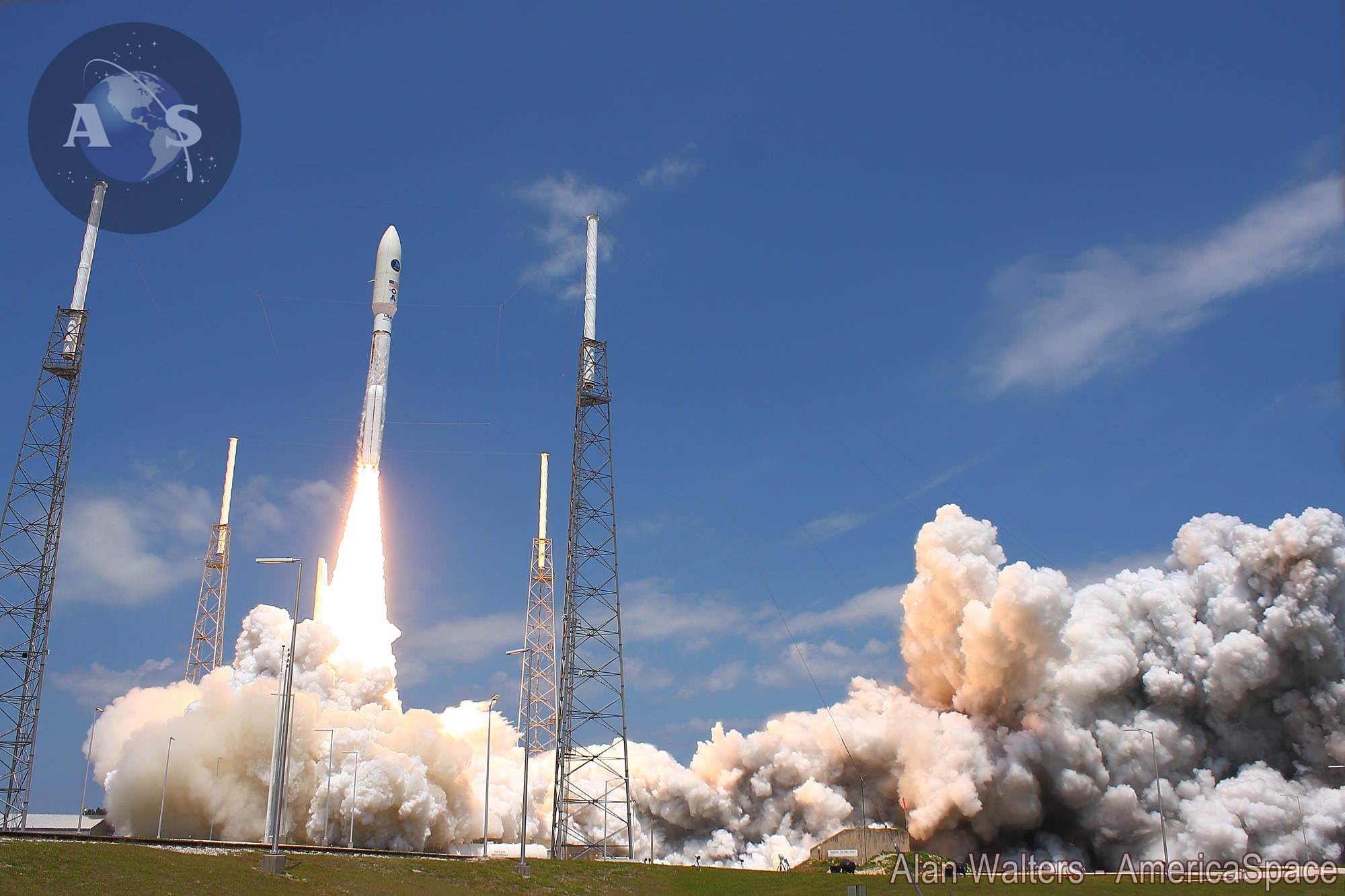
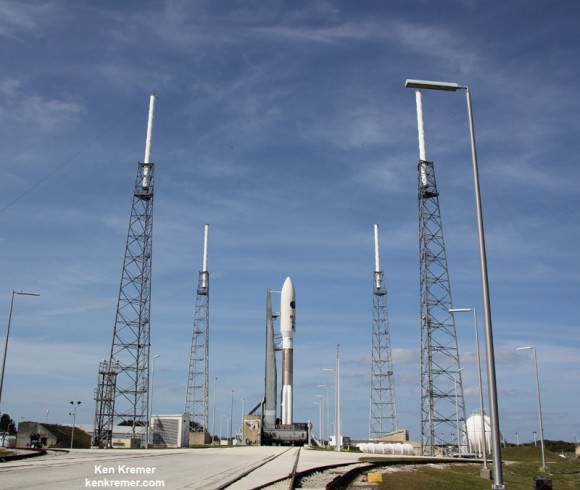
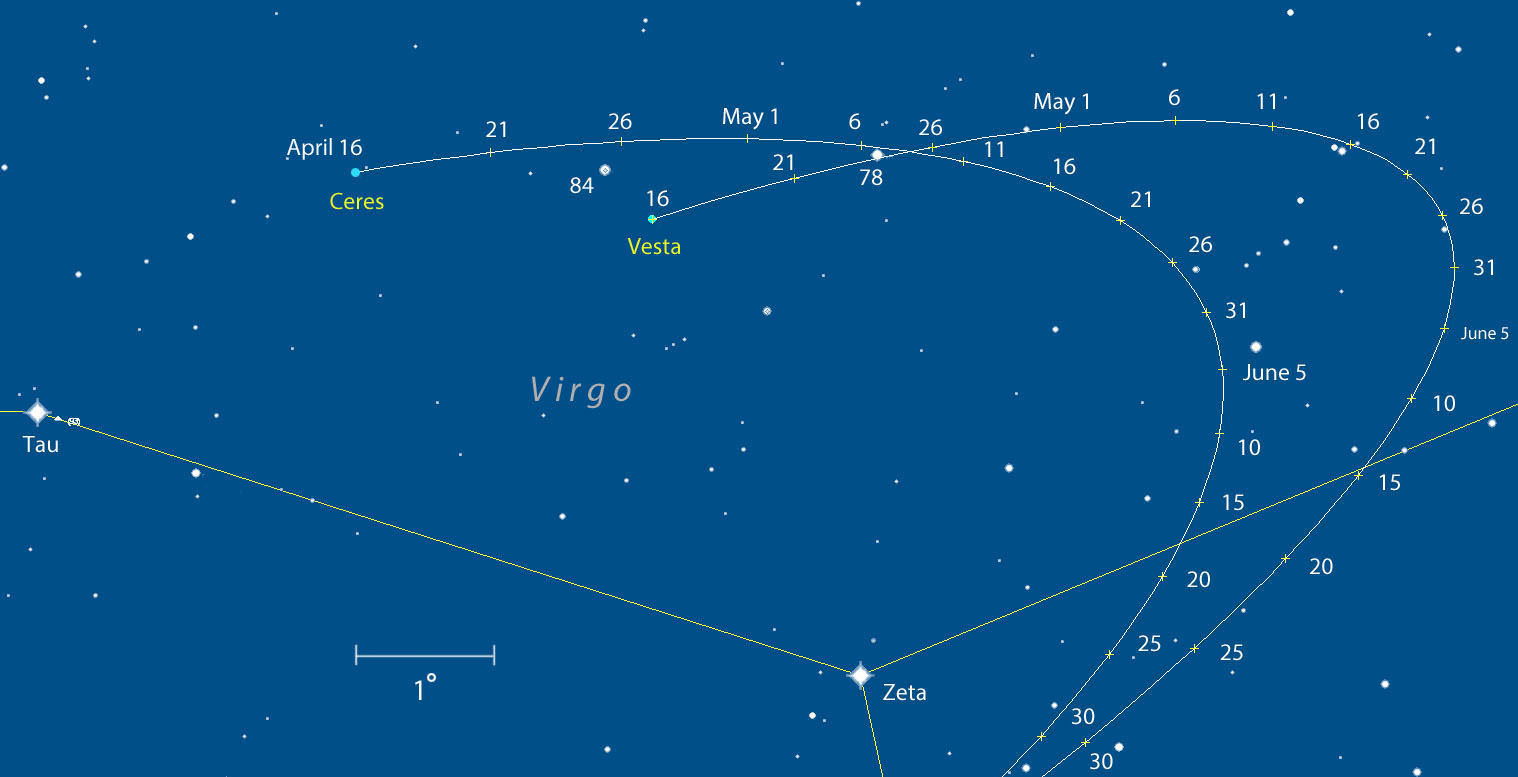
Blastoff of SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on April 18, 2014. Credit: Alan Walters/AmericaSpace
Story updated[/caption]
The powerful SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that launched successfully on a cargo delivery run for NASA bound for the Space Station on Friday, April 18, from Cape Canaveral, Fla, also had a key secondary objective for the company aimed at experimenting with eventually recovering the rockets first stage via the use of landing legs and leading to the boosters refurbishment and reuse further down the road.
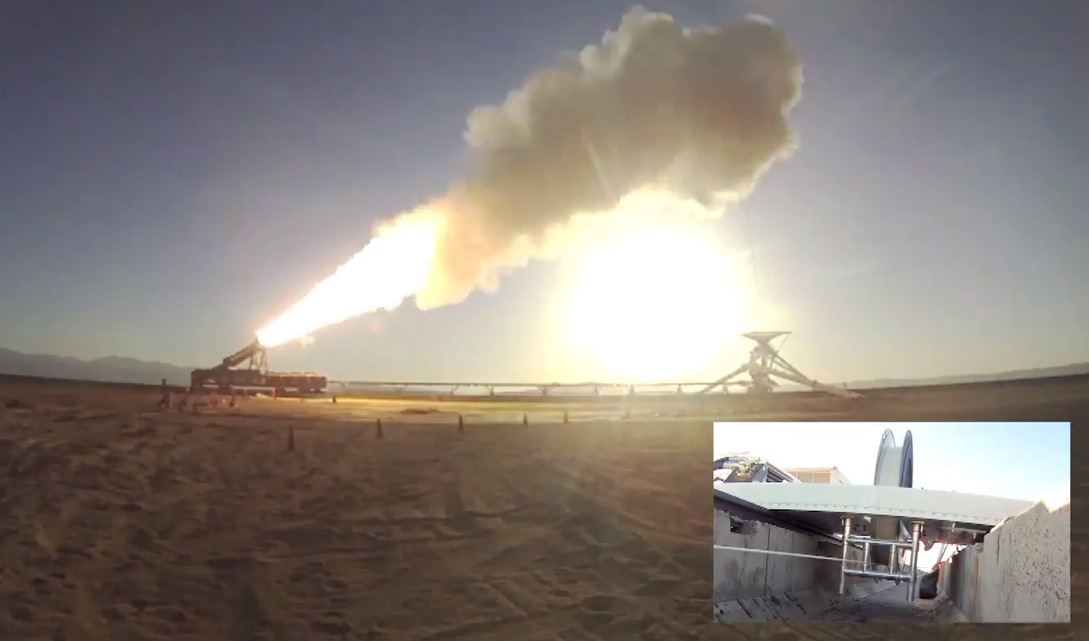
Marking a first of its kind test, this 20 story tall commercial Falcon 9 rocket was equipped with a quartet of landing legs to test controlled soft landing techniques first in the ocean and then back on solid ground at some later date this year or next – by reigniting the 1st stage engines for a guided touchdown.
The 12 foot diameter Falcon 9 rocket would sprout the legs just prior to water impact for the controlled soft landing in the Atlantic Ocean, guided by SpaceX engineers.

Prior to the launch SpaceX managers were careful not to raise expectations.
“The entire recovery of the first stage is completely experimental,” said Hans Koenigsmann, SpaceX vice president of mission assurance. “It has nothing to do with the primary mission.”
He estimated the odds of successfully retrieving an intact booster at merely 30 or 40 percent.
Following Friday’s blastoff, SpaceX reported they made significant strides towards that goal of a 1st stage recovery.

SpaceX engineers had preprogrammed the spent first stage to relight several Merlin 1 D engines after completing the boost phase and stage seperation to stabilize it, reduce its roll rate and then gradually lower its altitude back down to the Atlantic Ocean’s surface for a soft landing attempt and later possible recovery by retrieval ships.
All these critical steps seemed to go fairly well in initial reports that are subject to change.
SpaceX CEO and founder Elon Musk reported at a post launch briefing and later tweeted further updates that the Falcon 9 first stage actually made a good water landing despite rough seas, with waves swelling at least six feet.
“Roll rate close to zero (v important!).”
“Data upload from tracking plane shows landing in Atlantic was good! Several boats enroute through heavy seas,” Musk tweeted.
Furthermore he reported that the 1st stage survived the ocean touchdown.
“Flight computers continued transmitting for 8 seconds after reaching the water. Stopped when booster went horizontal.”
Because of the high waves, the recovery boats had difficulty reaching the booster in the recovery area located some two hundred miles off shore from Cape Canaveral.
Several previous attempts by SpaceX to recover the first stage via parachutes and thrusters were not successful. So SpaceX adopted this new approach with the landing legs and 1st stage Merlin 1 D engines.
Further details will be proved when they become available.

The attachment of the 25 foot long 1st stage landing legs to SpaceX’s next-generation Falcon 9 rocket for ocean recovery counts as a major step towards the firm’s future goal of building a fully reusable rocket and dramatically lowering launch costs compared to expendable boosters.
The eventual goal is to accomplish a successful first stage touchdown by the landing legs on solid ground back somewhere near on Cape Canaveral, Florida.
Musk said that SpaceX is still working out the details on finding a suitable landing location with NASA and the US Air Force.

Extensive work and testing remains to develop and refine the technology before a land landing will be attempted by the company, says Musk.
It will be left to future missions to accomplish a successful first stage touchdown by the landing legs back on solid ground back through a series of ramped up rocket tests at Cape Canaveral, Florida.
“Even though we probably won’t get the stage back, I think we’re really starting to connect the dots of what’s needed,” Musk said at the briefing.
“There are only a few more dots that need to be there to have it all work. I think we’ve got a decent chance of bringing a stage back this year, which would be wonderful.”
Overall Musk was very pleased with the performance of the rocket and the landing leg test.
“I would consider it a success in the sense that we were able to control the boost stage to a zero roll rate, which is previously what has destroyed the stage, an uncontrolled roll, where the on-board nitrogen thrusters weren’t able to control the aerodynamic torque and spun up.”
“This time, with more powerful thrusters and more nitrogen propellant, we were able to null the roll rates.”
“I’m feeling pretty excited,” Musk stated. “This is a happy day. Most important of all is that we did a good job for NASA.”
This extra powerful new version of the Falcon 9 dubbed v1.1 is powered by a cluster of nine of SpaceX’s new Merlin 1D engines that are about 50% more powerful compared to the standard Merlin 1C engines. The nine Merlin 1D engines 1.3 million pounds of thrust at sea level rises to 1.5 million pounds as the rocket climbs to orbit.
Therefore the upgraded Falcon 9 can boost a much heavier cargo load to the ISS, low Earth orbit, geostationary orbit and beyond.
Indeed Dragon is loaded with nearly 5000 pounds of cargo, about double the weight carried previously.
If all goes well, Dragon will reach the ISS early on Easter Sunday morning after a two day orbital chase.
Station crew members Rick Mastracchio and Steven Swanson will grapple the Dragon cargo freighter with the 57 foot long Canadarm2 on Easter Sunday at about 7:14 a.m. and then berth it at the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module.
NASA TV coverage of the Easter Sunday grappling process will begin at 5:45 a.m. with berthing coverage beginning at 9:30 a.m. : http://www.nasa.gov/ntv
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, commercial space, Orion, Chang’e-3, LADEE, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more planetary and human spaceflight news.
Ken Kremer