After years of hard work by dedicated science and engineering teams, a new pair of Mars orbiter science missions from Earth are in the final stages of prelaunch processing and are nearly set to blast off for the Red Planet in November.
If all goes well, NASA’s MAVEN orbiter and India’s MOM (Mars Orbiter Mission) will “work together” to help solve the mysteries of Mars atmosphere, the chief MAVEN scientist told Universe Today at a NASA briefing today (Oct. 28).
“We plan to collaborate on some overlapping objectives,” Bruce Jakosky told me. Jakosky is MAVEN’s principal Investigator from the University of Colorado at Boulder.
MAVEN and MOM will join Earth’s armada of five operational orbiters and surface rovers currently exploring the Red Planet.
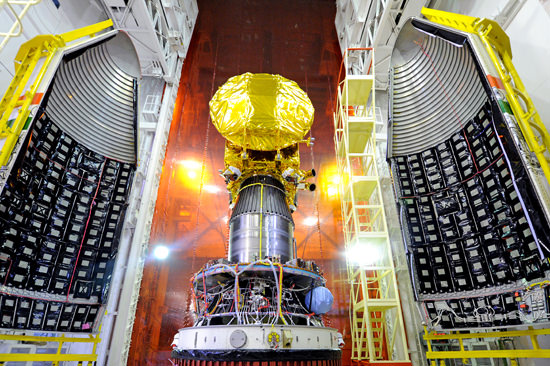
MOM is India’s first mission to Mars. Its also first in line to this year’s Martian on ramp and is slated to lift off in barely one week on Nov. 5 atop the most powerful version of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) rocket from a seaside launch pad in Srihanikota, India.
The 1,350 kilogram (2,980 pound) MOM orbiter, also known as ‘Mangalyaan’, is the brainchild of ISRO, the Indian Space Research Organization.
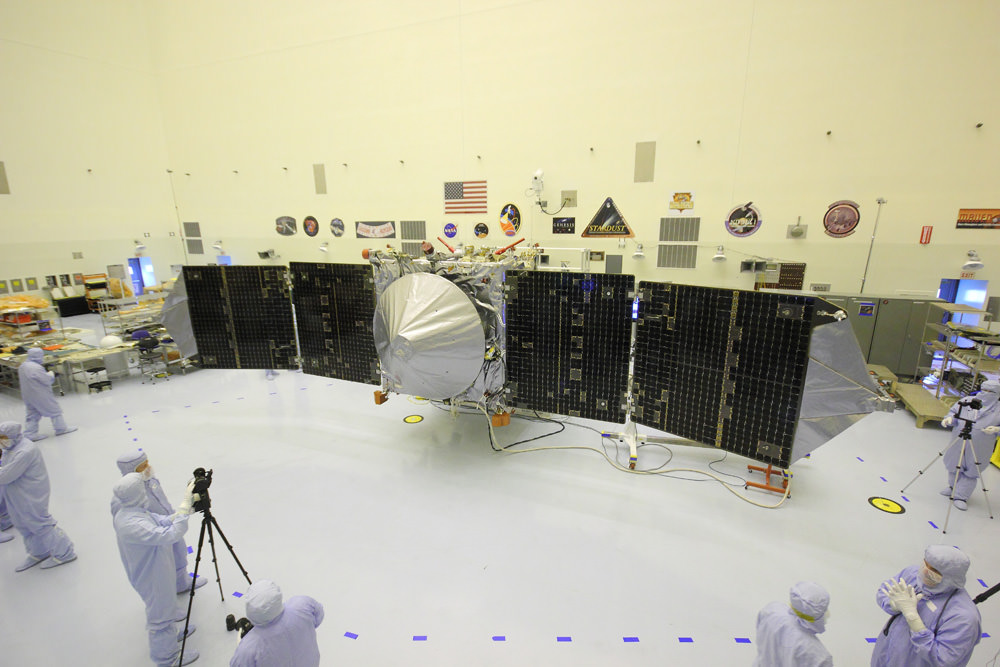
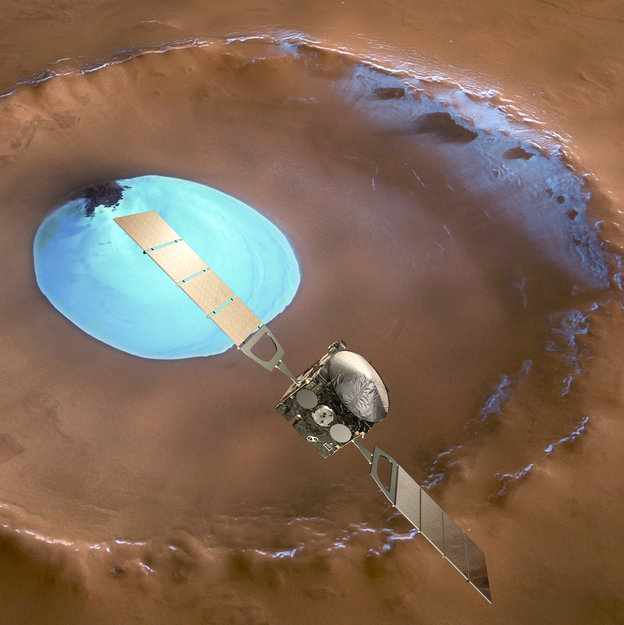
NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN Mission (MAVEN) spacecraft launches in three weeks on Nov. 18 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from a seaside pad on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Both MAVEN and MOM will study the Red Planets atmosphere. Although they are independent and carrying different science payloads the two missions do have some common goals.
“There are some overlapping objectives between MAVEN and MOM,” Jakosky said.
“We have had some discussions with the MOM science team.”

Both orbiters are due to arrive at Mars in September 2014 after 10 month interplanetary cruises and will enter different elliptical orbits after main engine braking burns.
MAVEN is the first spacecraft from Earth devoted to investigating and understanding the upper atmosphere of Mars.
The purpose is to study specific processes and determine how and why Mars lost virtually all of its atmosphere billions of years ago and what effect that had on the history of climate change and habitability.
“The major questions about the history of Mars center on the history of its climate and atmosphere and how that’s influenced the surface, geology and the possibility for life,” said Jakosky.
“MAVEN will focus on understanding the history of the atmosphere, how the climate has changed through time, and how that influenced the evolution of the surface and the potential for habitability by microbes on Mars.”
“We don’t know the driver of the change.”
“Where did the water go and where did the carbon dioxide go from the early atmosphere? What were the mechanisms?”
“That’s what driving our exploration of Mars with MAVEN,” said Jakosky.
One of the significant differences between MOM and MAVEN regards methane detection – which is a potential marker for Martian life. Some 90% of Earth’s atmospheric methane derives from living organisms.
MOM has a methane sensor but not MAVEN.
“We just had to leave that one off to stay focused and to stay within the available resources ,” Jakosky told me.
MAVEN carries nine sensors in three instrument suites.
The Particles and Fields Package, provided by the University of California at Berkeley with support from CU/LASP and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., contains six instruments to characterize the solar wind and the ionosphere of Mars. The Remote Sensing Package, built by CU/LASP, will determine global characteristics of the upper atmosphere and ionosphere. The Neutral Gas and Ion Mass Spectrometer, built by Goddard, will measure the composition of Mars’ upper atmosphere.
MOM’s science complement comprises the tri color Mars Color Camera to image the planet and its two moons, Phobos and Deimos; the Lyman Alpha Photometer to measure the abundance of hydrogen and deuterium and understand the planets water loss process; a Thermal Imaging Spectrometer to map surface composition and mineralogy, the MENCA mass spectrometer to analyze atmospheric composition, and the Methane Sensor for Mars to measure traces of potential atmospheric methane down to the ppm level.

“At the point where we [MAVEN and MOM] are both in orbit collecting data we do plan to collaborate and work together with the data jointly,” Jakosky told me.
“We agreed on the value of collaboration and will hold real discussions at a later time,” he noted.
NASA is providing key communications and navigation support to ISRO and MOM through the agency’s trio of huge tracking antennas in the Deep Space Network (DSN).
Over the course of its one-Earth-year primary mission, MAVEN will observe all of Mars’ latitudes at altitudes ranging from 93 miles to more than 3,800 miles.
MAVEN will execute five deep dip maneuvers during the first year, descending to an altitude of 78 miles. This marks the lower boundary of the planet’s upper atmosphere.
MAVEN has sufficient fuel reserves on board to continue observations for more than a decade.
The spacecraft will function as an indispensible orbital relay by transmitting surface science data through the “Electra” from NASA’s ongoing Curiosity and Opportunity rovers as well as the planned 2020 rover.
Stay tuned here for continuing MAVEN and MOM news and my launch reports from on site at the Kennedy Space Center press center.
…………….
Learn more about MAVEN, Mars rovers, Orion and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Nov 15-19: “MAVEN Mars Launch and Curiosity Explores Mars, Orion and NASA’s Future”, Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, 8 PM