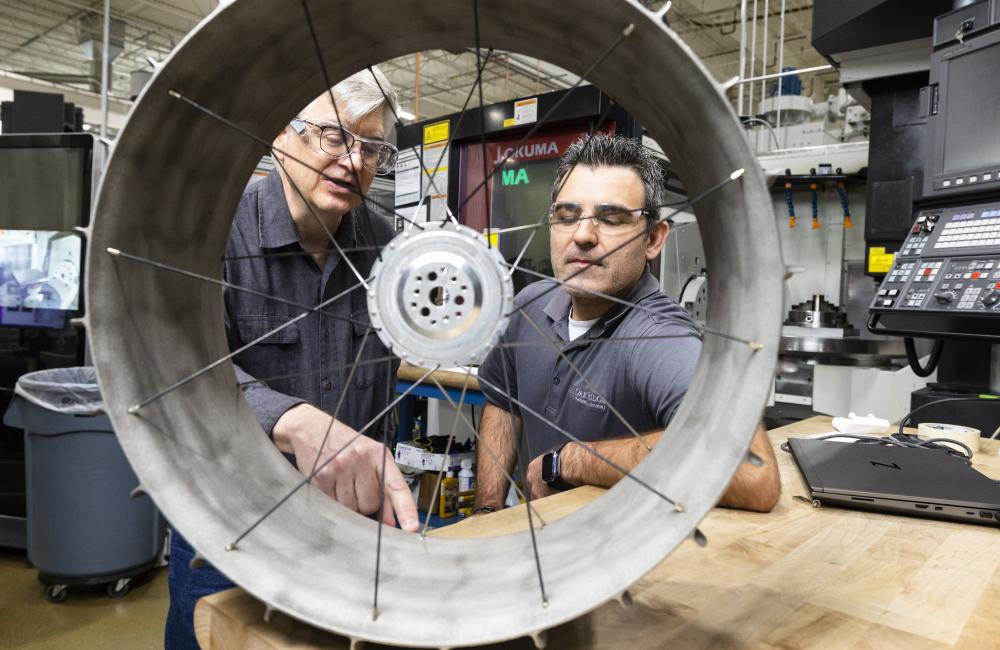
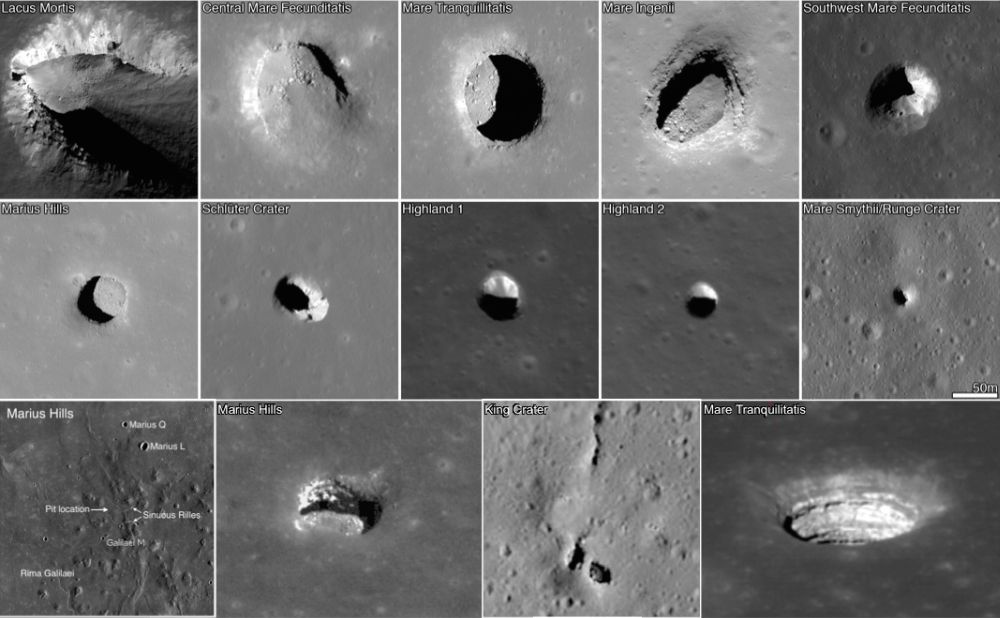
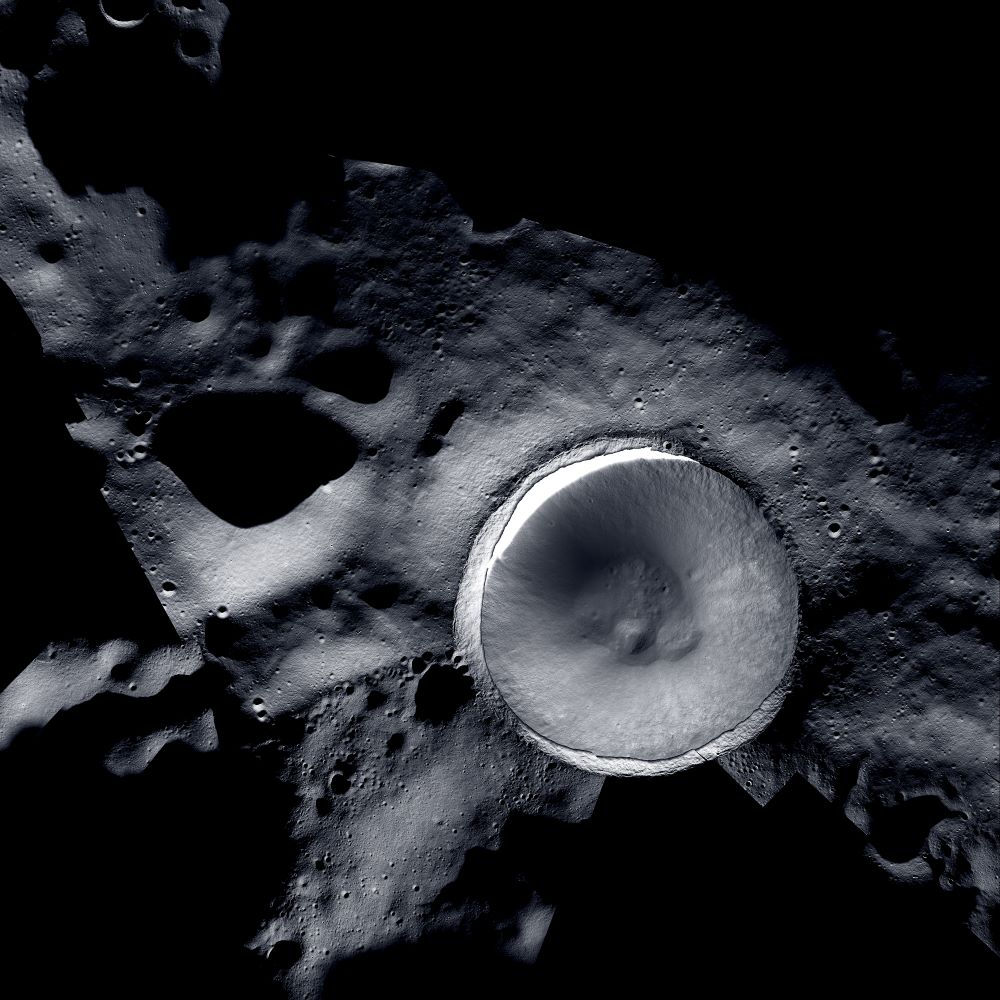
When you think about sending missions to the Moon, every single gram counts on launch day. Therefore, it makes sense to live off the land when you arrive with in-situ resource utilization. For example, what if you could fly a rover without wheels and 3D print them out of lunar regolith when you get there?
It just might happen.
Researchers used a 3D printer to build the same design for a wheel that will be part of the upcoming NASA VIPER rover. It was done using additive manufacturing (another word for 3D printing), melting metal powder and laying down and bonding a large number of successive thin layers of materials into the designed shape.
Continue reading “This Moon Rover Wheel Could be 3D Printed on the Moon”