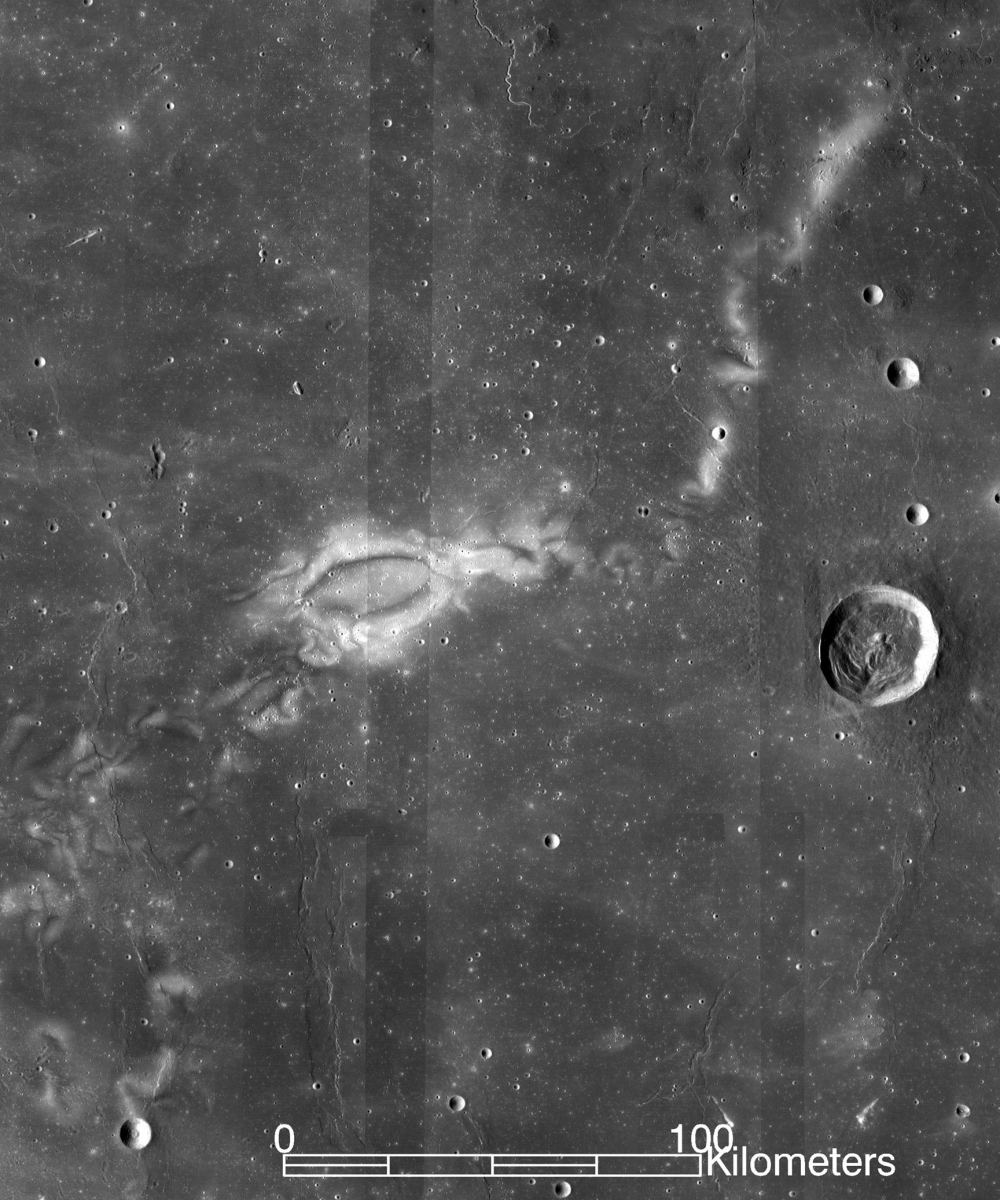
The last place to look for windstorms is on the Moon. Yet, it has swirls on its surface that look like the wind put them there. Since there’s no atmosphere on the Moon, planetary scientists had to look for another cause. It turns out there’s a connection to local magnetic anomalies and an interplay with lunar topography.
Continue reading “There’s No Wind on the Moon, So How Does Dust Shift and Swirl So Quickly?”There’s No Wind on the Moon, So How Does Dust Shift and Swirl So Quickly?