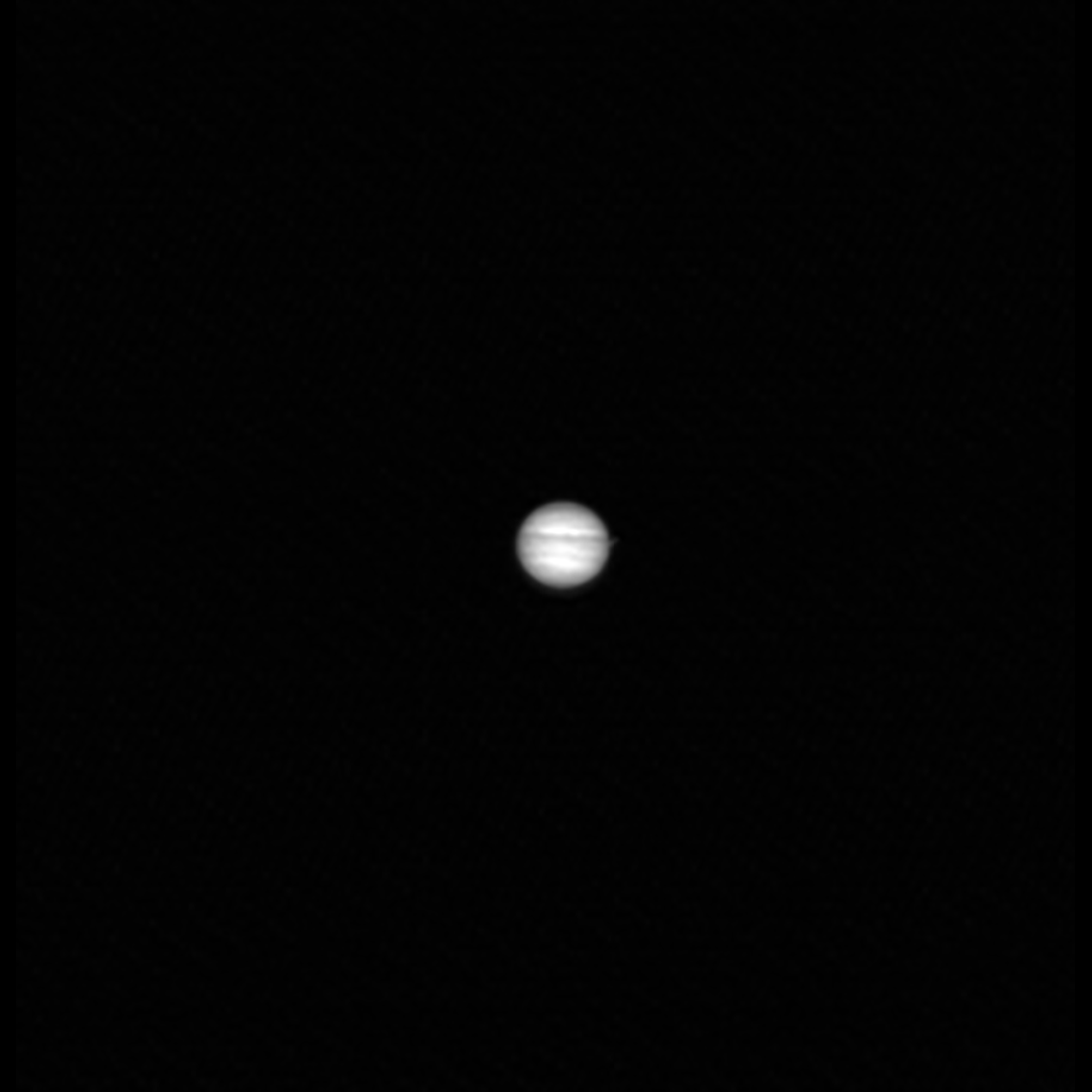
You know the feeling …. seeing Jupiter through your own telescope. If it gives you the chills — like it does for me — then you’ll know how the team for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter felt when they turned their spacecraft around – yes, the orbiter that’s been faithfully circling and looking down at the Moon since 2008 – and saw the giant planet Jupiter with their camera. If you zoom in on the picture, you can even see Jupiter’s Galilean moons.
Continue reading “NASA Spacecraft Takes a Picture of Jupiter … From the Moon”NASA Spacecraft Takes a Picture of Jupiter … From the Moon