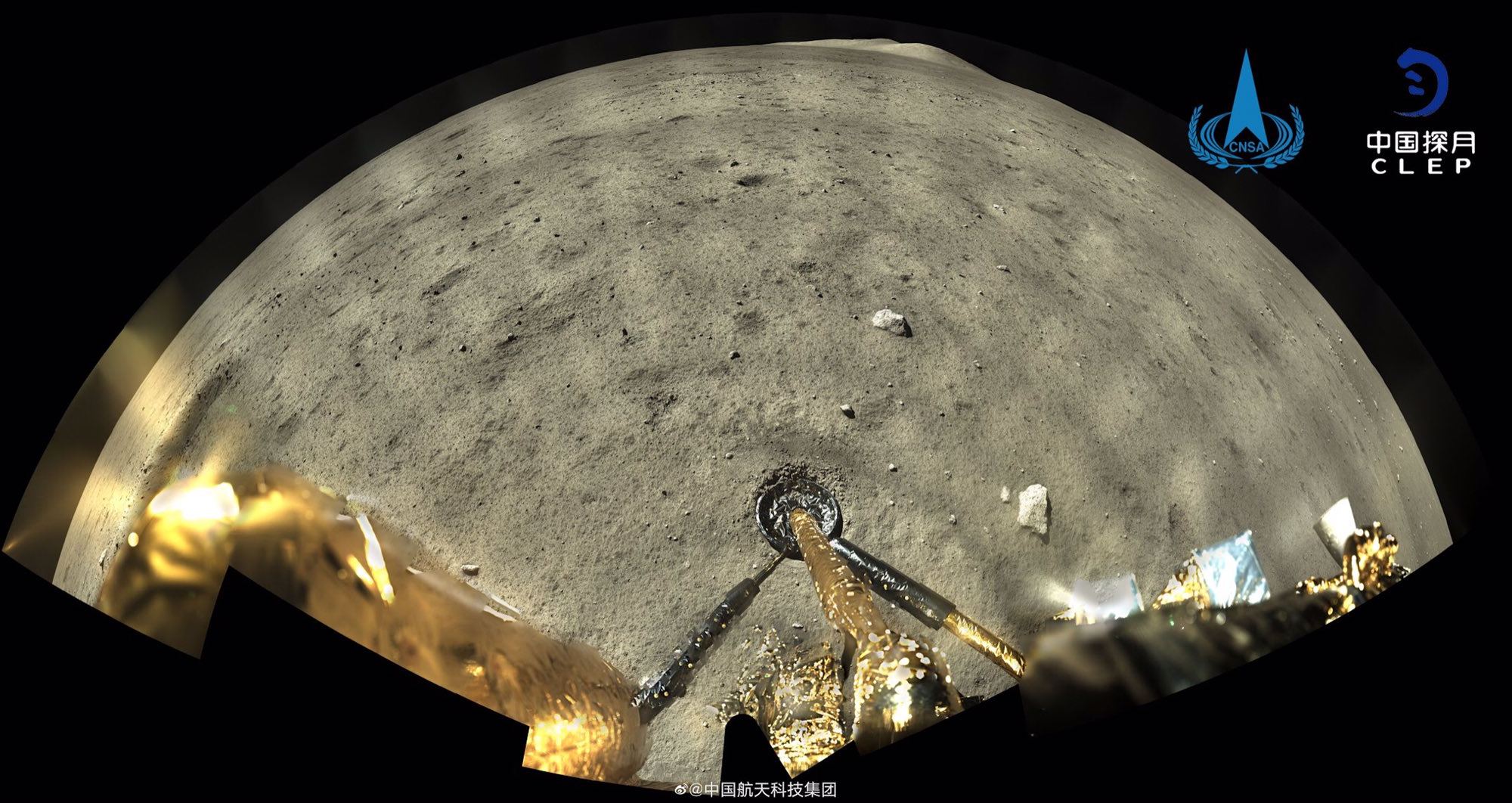
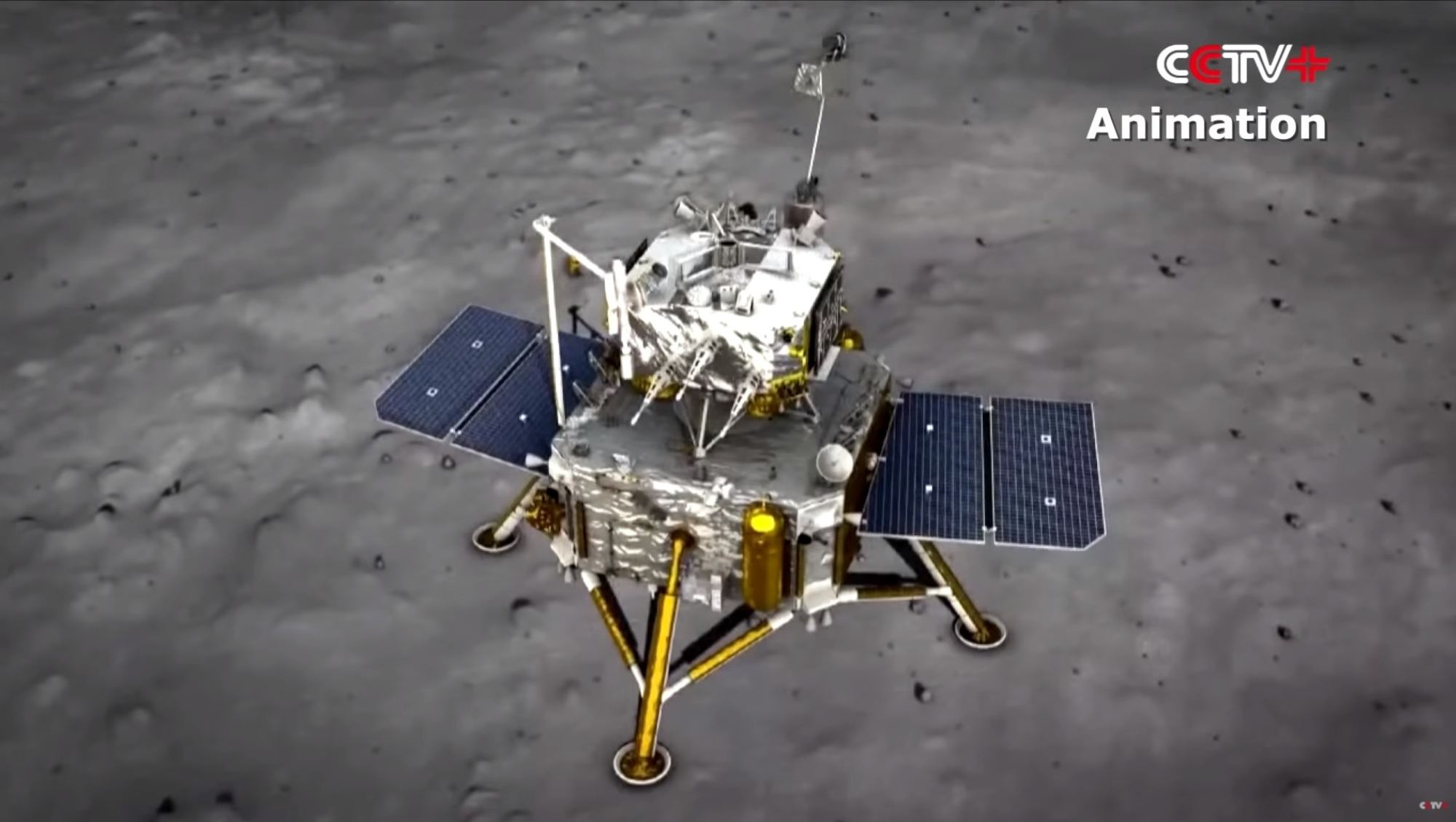
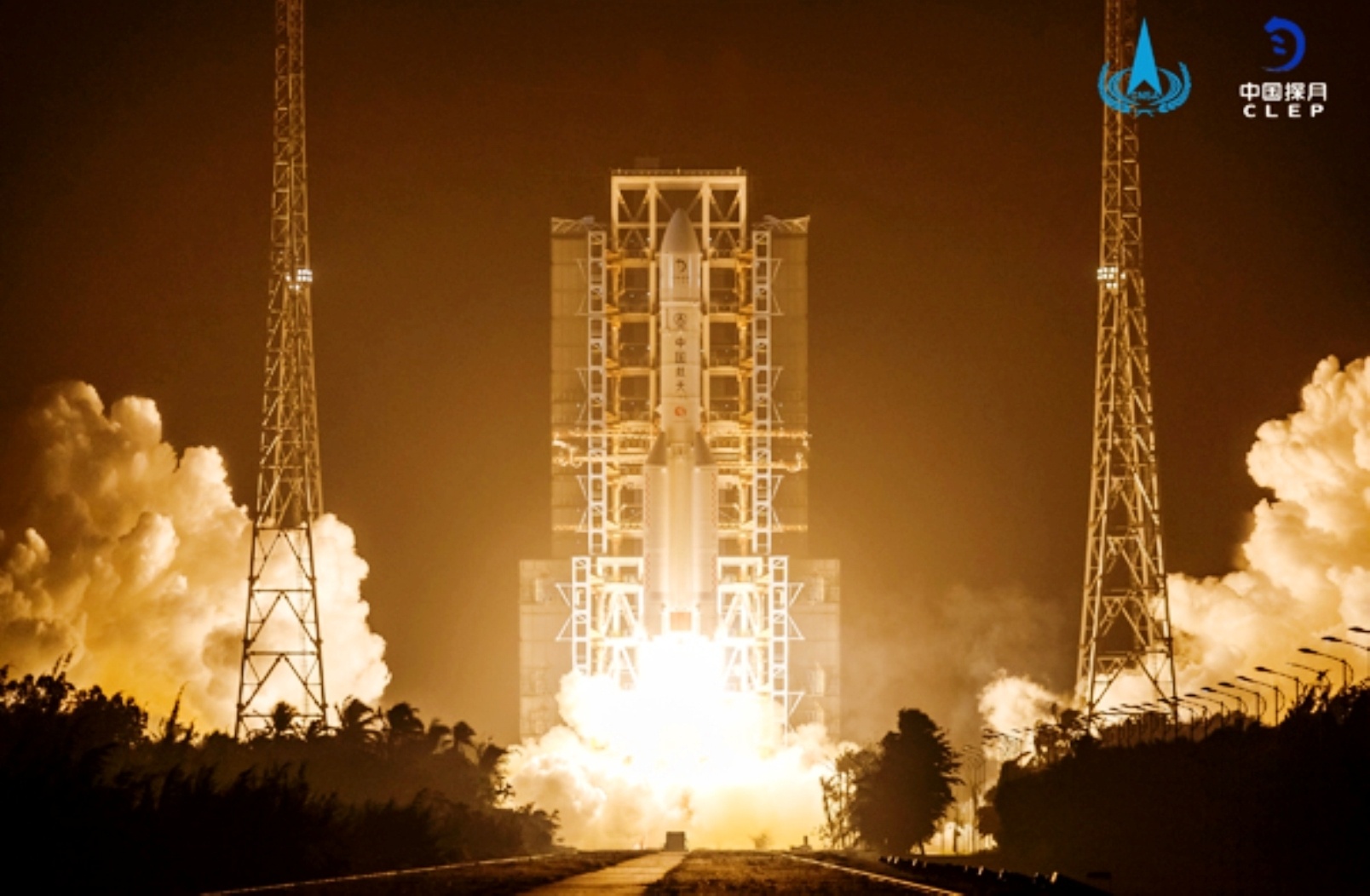
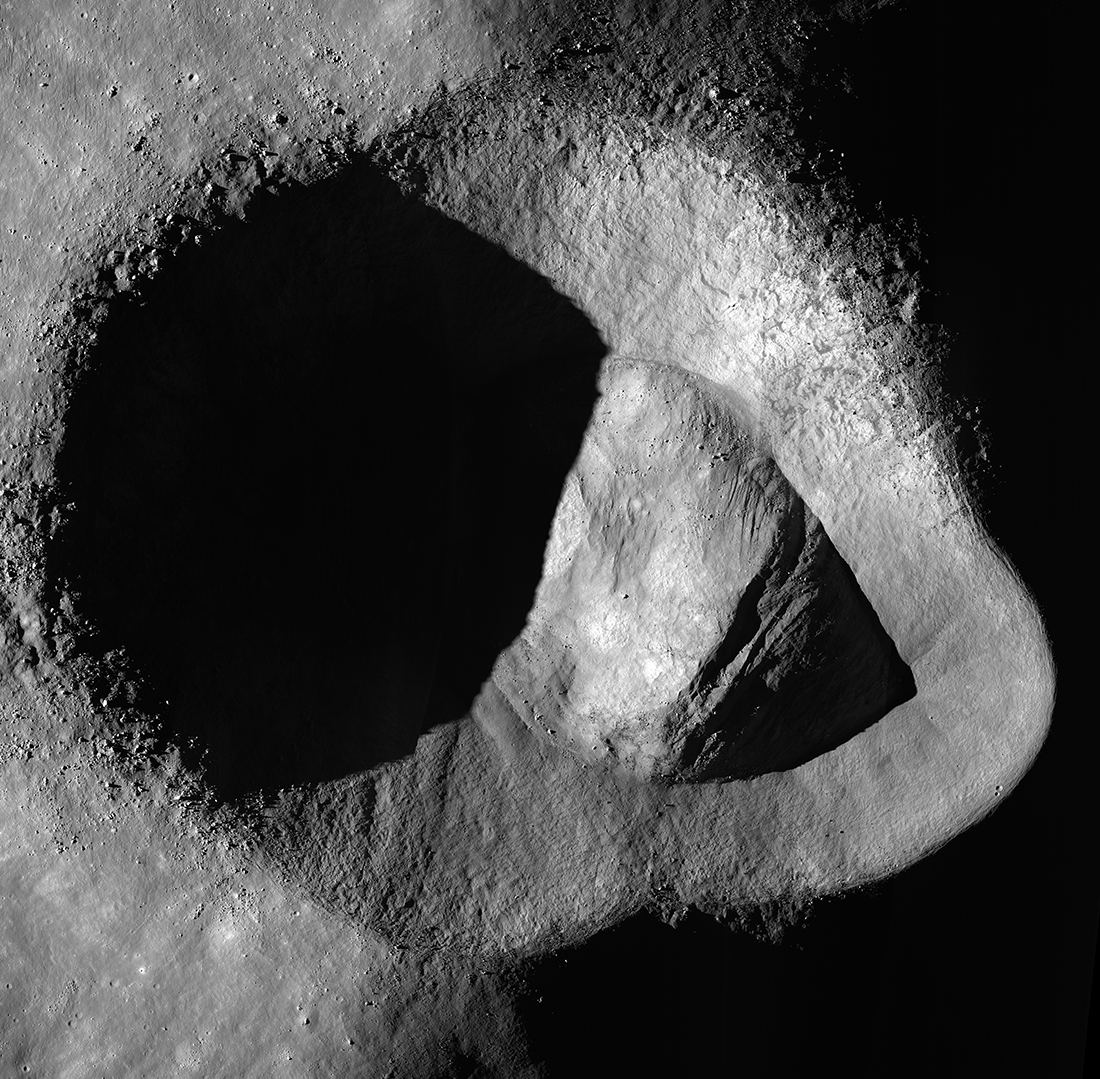
China’s Chang’e-5 robotic moon lander is due to spend only two days collecting samples of lunar rock and soil before it sends its shipment on its way back to Earth, but it’s making the most of the time.
Just hours after landing on December 1st, the probe started using its robotic scoop and drill to dig up material at Mons Rümker, a lava dome in a region called Oceanus Procellarum, or the Ocean of Storms.
It’s also been sending back pictures and video, including this stunning view of the final minutes before touchdown. Watch how the camera tips straight down to focus on the target spot for the lander:
Continue reading “Take a Look at What China’s Chang’e-5 Probe Is Seeing (and Doing) on the Moon”