January 31, 2021, will mark 50 years since the launch of Apollo 14. This historic mission was the first to broadcast a color television signal from the surface of the Moon and marked the heroic return to space of America’s first astronaut, Alan Shepard, who famously hit two golf balls off of the lunar regolith. While the significance of Apollo 14 and the Apollo program, in general, can’t be overstated, Shepard spent a mere two days on the lunar surface. The record for the longest human presence on the Moon, held by Eugene Cernan and Harrison Schmitt, is just over three days. All of the Apollo astronauts were exposed to high levels of radiation on the surface of the Moon but with such relatively short stays, the risk was considered to be acceptable.
Continue reading “You’ll Experience 200 Times More Radiation Standing on the Moon than Standing on the Earth”NASA Announces 14 New “Tipping Point” Technologies for its Lunar Exploration
In four years, NASA plans to return astronauts to the Moon as part of Project Artemis. To ensure the success of this endeavor, as well as the creation of a program of sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade, NASA has partnered with multiple entities in the commercial space sector. Recently, they announced that contracts will be awarded to 14 additional companies to develop a range of proposed technologies.
These proposals are part of NASA’s fifth competitive Tipping Point solicitation, one of many private-public partnership programs overseen by NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD). For this latest solicitation, Tipping Point is awarding contracts with a combined value of over $370 million for technology demonstrations that will facilitate future lunar missions and commercial space capabilities.
Continue reading “NASA Announces 14 New “Tipping Point” Technologies for its Lunar Exploration”This is a Landslide… on the Moon

Landslides bringing you down?
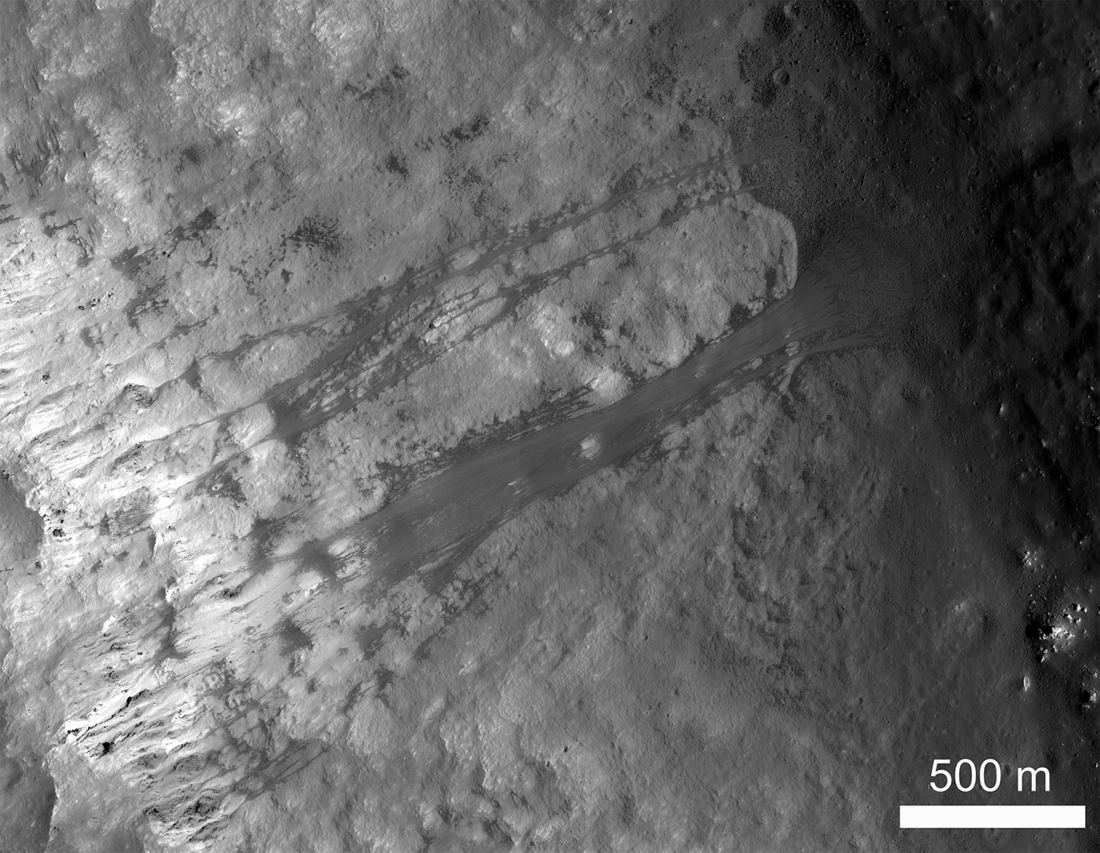
Landslides can be found all across our own planet Earth, on all seven continents plus the ocean floors. Similar large mass movements have been spotted around the Solar System on rocky worlds, including our companion, the Moon.
This image from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) shows an example of lunar landslides, with translational slides of regolith on the walls of Kepler Crater.
Continue reading “This is a Landslide… on the Moon”What the Astronauts Saw as They Orbited the Moon During Apollo 17
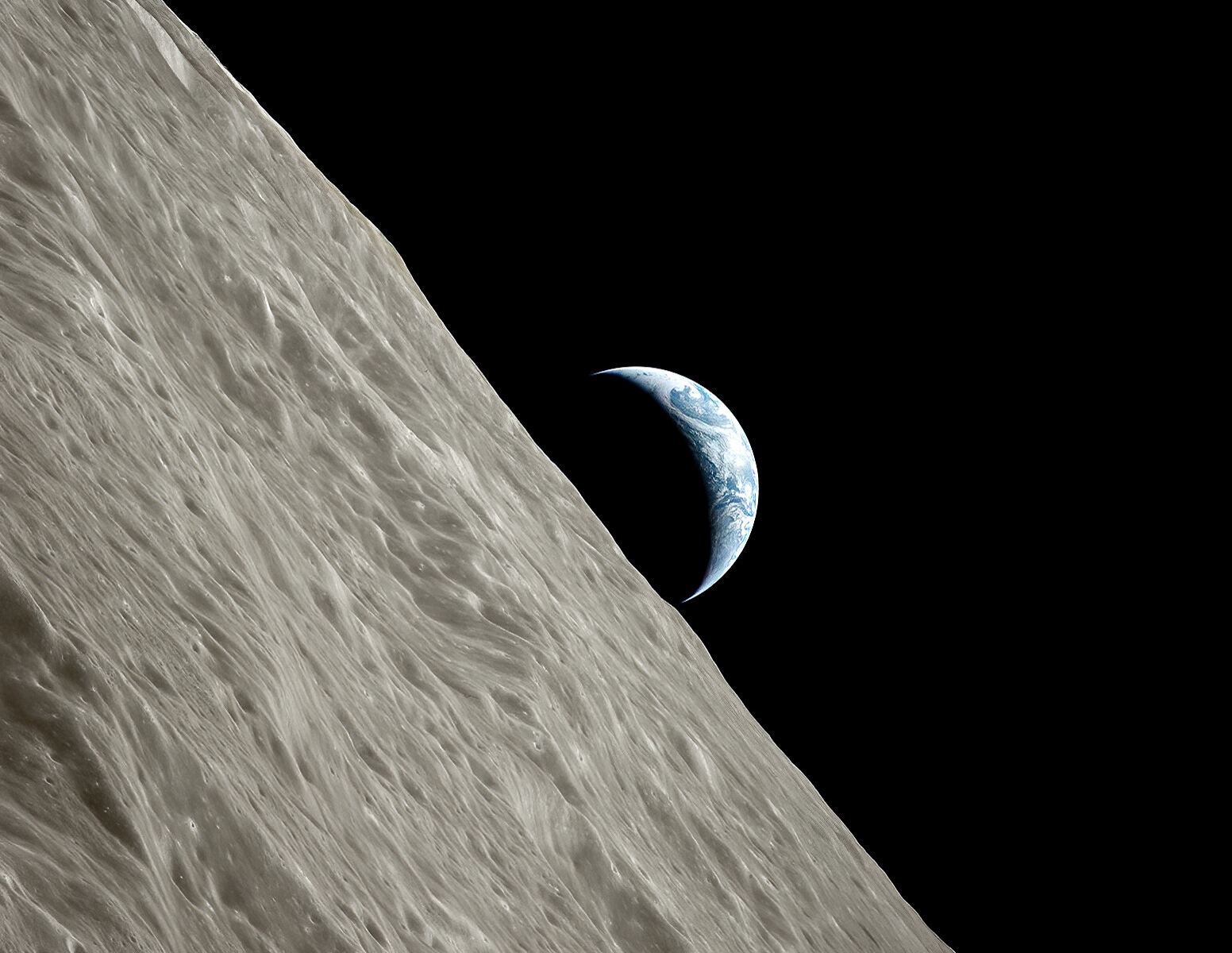

This view always gets me *right there.* But this new version really gets me.
This is what Apollo 17 astronauts saw in December of 1972 as they came around the farside of the Moon: the blue and white crescent Earth rising above the stark lunar horizon. And now image editing guru Kevin Gill has sharpened the image, giving it more texture, color and contrast. I can imagine this sharp, spectacular view must be close to what the astronauts saw with their own eyes.
“There I was, and there you are, the Earth – dynamic, overwhelming…” said Apollo 17 astronaut Gene Cernan.
Continue reading “What the Astronauts Saw as They Orbited the Moon During Apollo 17”NASA Has a New Challenge to Bring Frozen Samples of the Moon Back to Earth
When astronauts return to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era, they will be tasked with conducting some very lucrative science operations. Like their predecessors, this will include a sample-return mission, where they bring back lunar rocks and regolith for study. There have also been proposals that renewed missions to the Moon bring back samples of lunar ice so scientists can determine where the Moon’s water came from.
And it appears NASA was listening and would like some public input on this! To this end, the NASA Tournament Lab and TechConnect Ventures (a n open-innovation platform) have come together to launch the NASA Lunar Deep Freeze Challenge. Basically, NASA is looking for ideas on how cold samples collected in the lunar polar region could be preserved and kept frozen for the return trip to Earth.
Continue reading “NASA Has a New Challenge to Bring Frozen Samples of the Moon Back to Earth”We Might Have a New Mini-Moon Soon
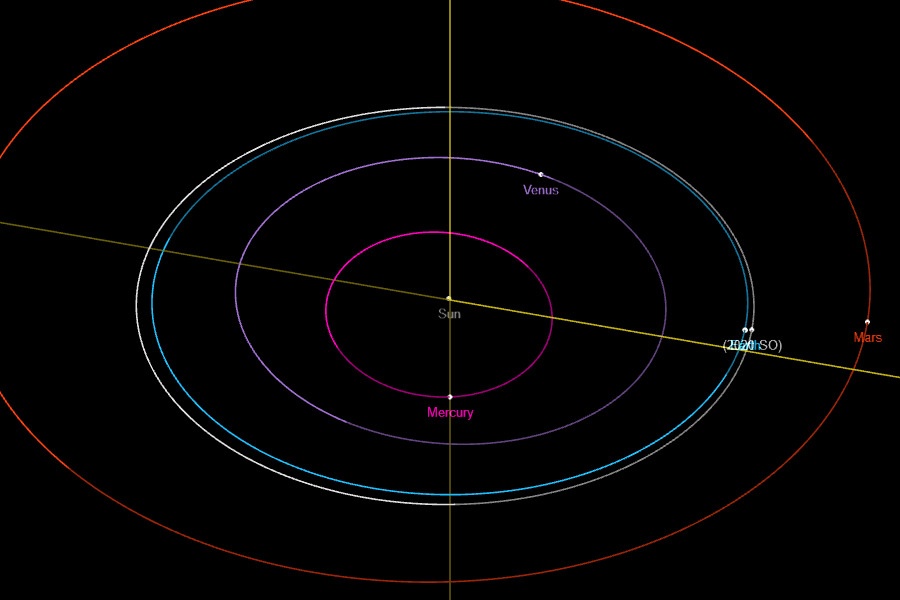
Is it a new asteroid mini–moon or a human-made mini-moon? That’s the question about a small object approaching Earth, called 2020 SO. NASA’s Small Body Database predicts the object will captured by Earth’s gravity in October 2020 and temporarily be trapped in orbit.
Continue reading “We Might Have a New Mini-Moon Soon”Artemis Missions Should Bring Ice Home From the Moon Too

During the Apollo Era, astronauts conducted vital science operations on the Moon, which included bringing samples of lunar rocks back to Earth for study. Thanks to the examination of these rocks, scientists were able to learn a great deal about the formation and evolution of the Moon and even found evidence of lunar water. In the coming years, when NASA sends astronauts back as part of Project Artemis, more samples will be returned.
Recently, NASA put out the call for science white papers to help them design a framework for the kind of science operations the Artemis astronauts will conduct. According to one proposal, the Artemis astronauts should not only bring back samples of lunar regolith or rocks but lunar ice as well. By examining them here on Earth, scientists may finally be able to resolve the mystery of where the Moon’s water came from.
Continue reading “Artemis Missions Should Bring Ice Home From the Moon Too”NASA Will Pay You to Retrieve Regolith and Rocks from the Moon

As part of Project Artemis, NASA intends to send the first woman and the next man to the Moon by 2024, in what will be the first crewed mission to the lunar since the Apollo Era. By the end of the decade, NASA also hopes to have all the infrastructure in place to create a program for “sustainable lunar exploration,” which will include the Lunar Gateway (a habitat in orbit) and the Artemis Base Camp (a habitat on the surface).
Part of this commitment entails the recovery and use of resources that are harvested locally, including regolith to create building materials and ice to create everything from drinking water to rocket fuel. To this end, NASA has asked its commercial partners to collect samples of lunar soil or rocks as part of a proof-of-concept demonstration of how they will scout and harvest natural resources and conduct commercial operations on the Moon.
Continue reading “NASA Will Pay You to Retrieve Regolith and Rocks from the Moon”Earth’s Oxygen Could be Making the Moon Rust
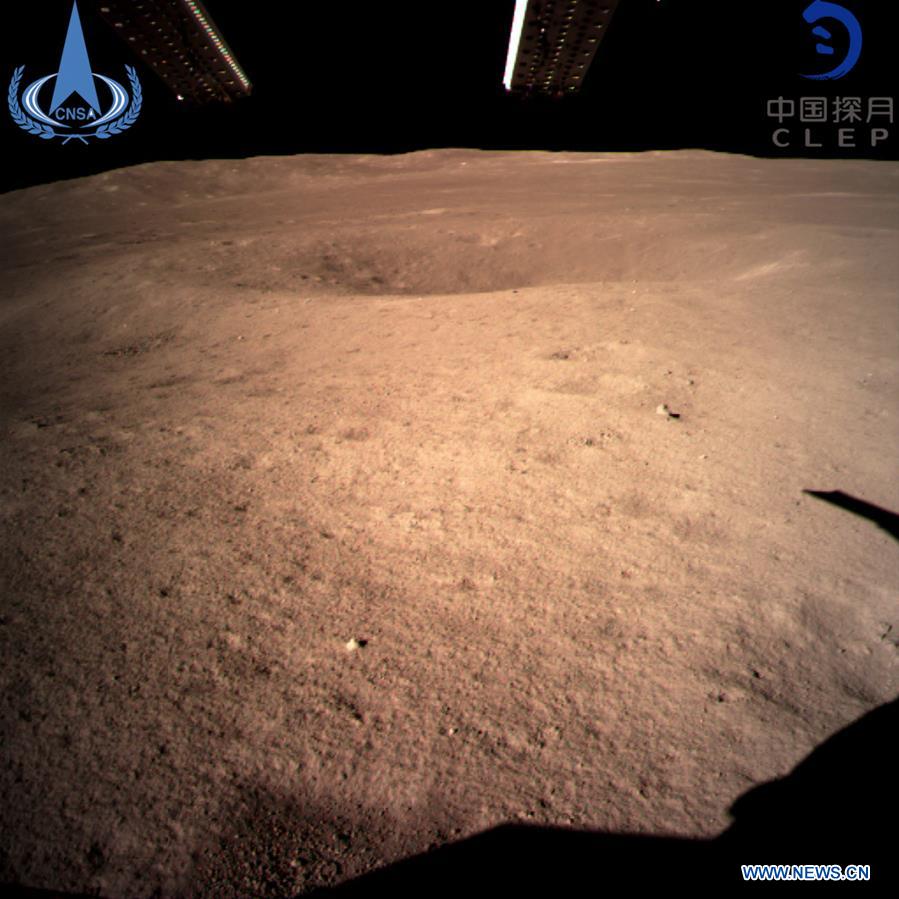
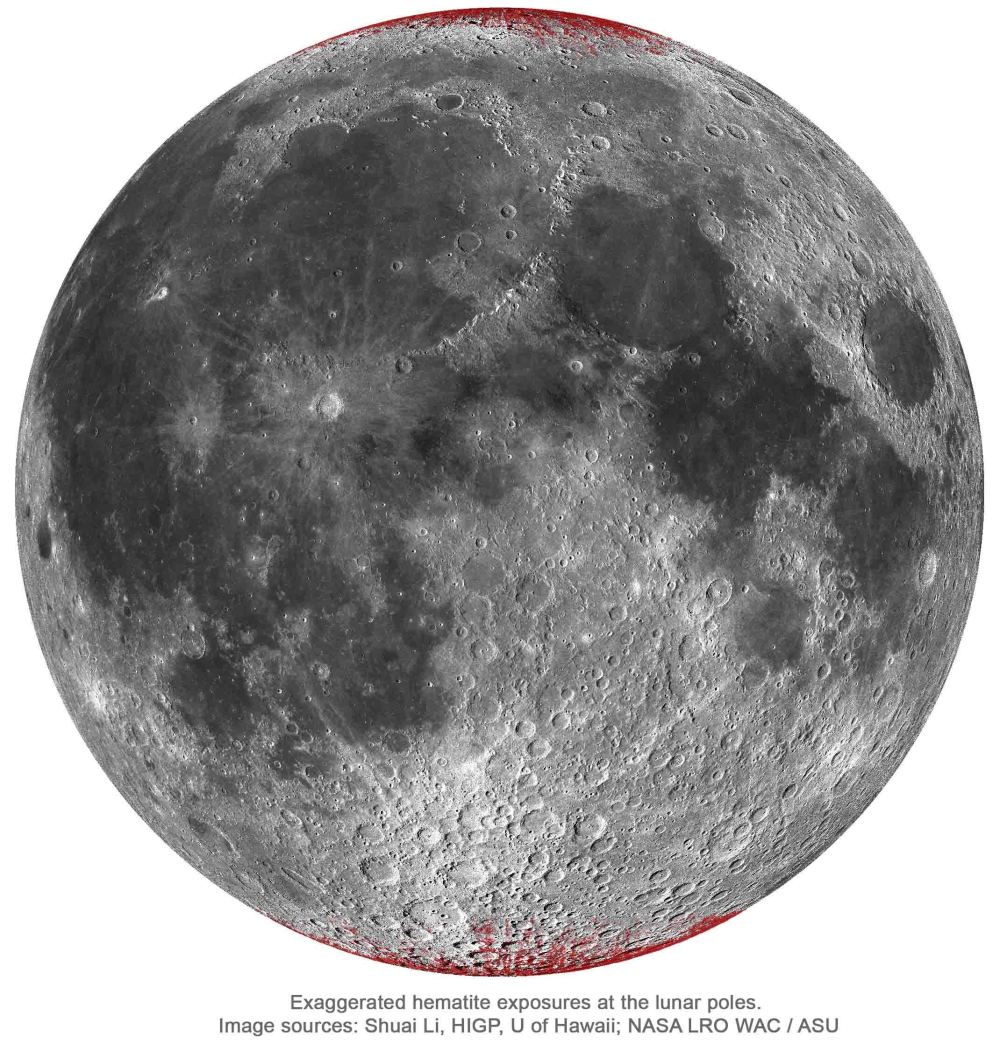
It takes oxygen to make iron rust. So when scientists discovered hematite spread widely through lunar high latitudes, they were surprised. How did that happen?
A new study suggests that oxygen from Earth could be playing a role in rusting the Moon.
Continue reading “Earth’s Oxygen Could be Making the Moon Rust”Lunar Landings Will Make it Harder to Study the Moon’s Ice Deposits
When astronauts return to the Moon in the next few years (as part of Project Artemis) they will be scouting locations and resources around the South Pole-Aitken Basin that will eventually help them to stay there. In this cratered, permanently-shadowed region, water ice has been found in abundance, which could one-day be harvested for drinking water, irrigation, and the creation of oxygen gas and rocket fuels.
A critical aspect to planning for all or this is to consider how future missions may affect the local environment. Based on new research from a team of planetary scientists and engineers, a major risk comes in the form of contamination by lunar landers. In short, exhaust from these vehicles could spread around the Moon and contaminate the very ices the astronauts hope to study.
Continue reading “Lunar Landings Will Make it Harder to Study the Moon’s Ice Deposits”



