Could lava tubes on the Moon and Mars play a role in establishing a human presence on those worlds? Possibly, according to a team of researchers. Their new study shows that lunar and Martian lava tubes might be enormous, and easily large enough to accommodate a base.
Continue reading “Lava Tubes on the Moon and Mars are Really, Really Big. Big Enough to Fit an Entire Planetary Base”China’s Mars Mission Took This Picture of the Earth and Moon
No matter where you are, where you’ve been and where you’re going, it’s always good to see home. And we all love seeing pictures of our home planet, as seen from space.
Continue reading “China’s Mars Mission Took This Picture of the Earth and Moon”Radishes Can Likely Grow in Lunar Regolith
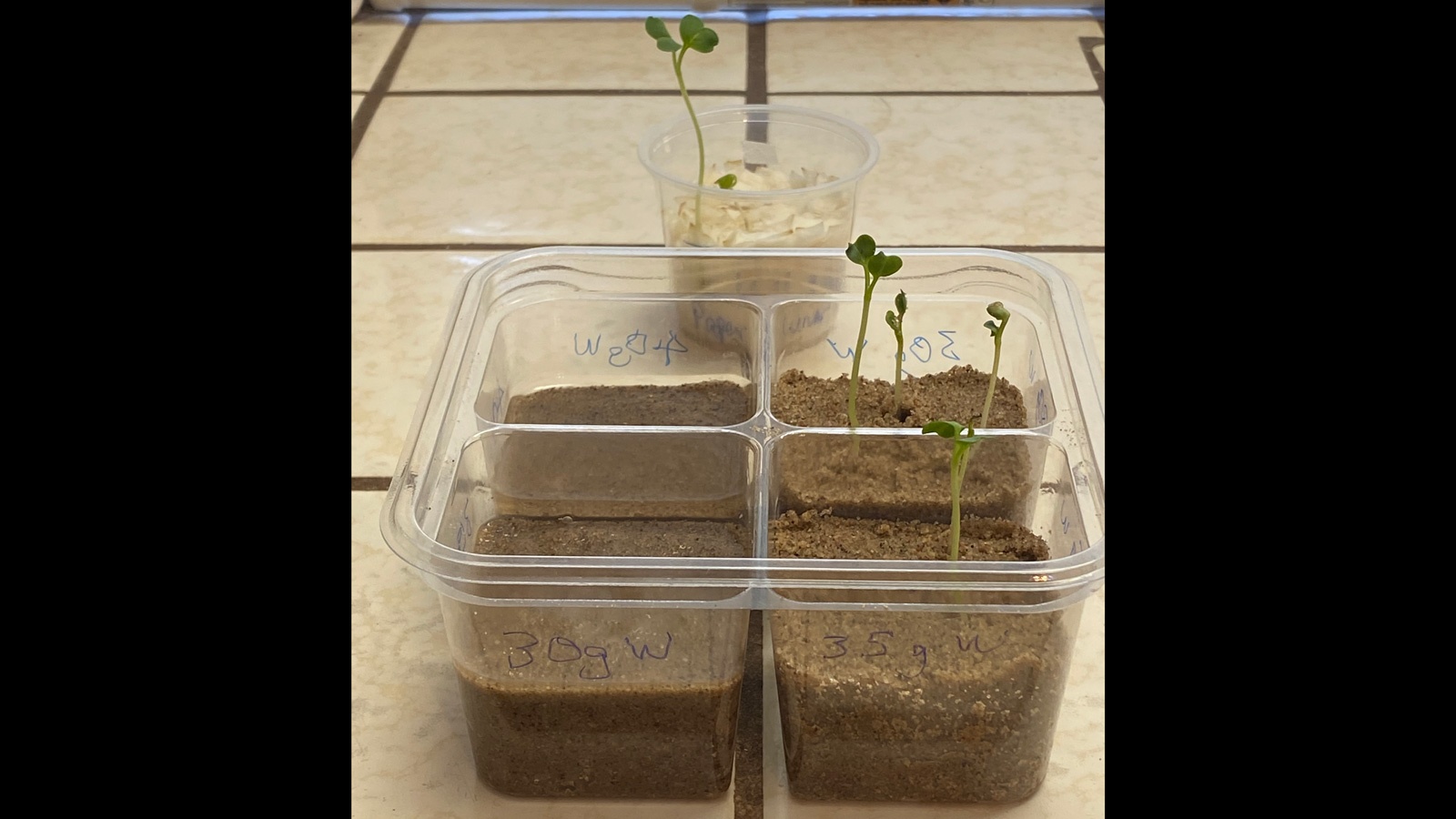

For many of us, gardening has been a therapeutic distraction during this time of pandemic quarantine. But some researchers from the Jet Propulsion Lab have been gardening at home with a specific goal in mind: growing food on the Moon.
Continue reading “Radishes Can Likely Grow in Lunar Regolith”The Moon is an Ideal Spot for a Gravitational Wave Observatory
In the coming years, multiple space agencies will be sending missions (including astronauts) to the Moon’s southern polar region to conduct vital research. In addition to scouting resources in the area (in preparation for the construction of a lunar base) these missions will also investigate the possibility of conducting various scientific investigations on the far side of the Moon.
However, two prominent scientists (Dr. Karan Jani and Prof. Abraham Loeb) recently published a paper where they argue that another kind of astronomy could be conducted on the far side of the Moon – Gravitational Wave astronomy! As part of NASA’s Project Artemis, they explain how a Gravitational-wave Lunar Observatory for Cosmology (GLOC) would be ideal for exploring GW in the richest and most challenging frequencies.
Continue reading “The Moon is an Ideal Spot for a Gravitational Wave Observatory”800 Million Years Ago, it Was Raining Asteroids on the Earth and Moon
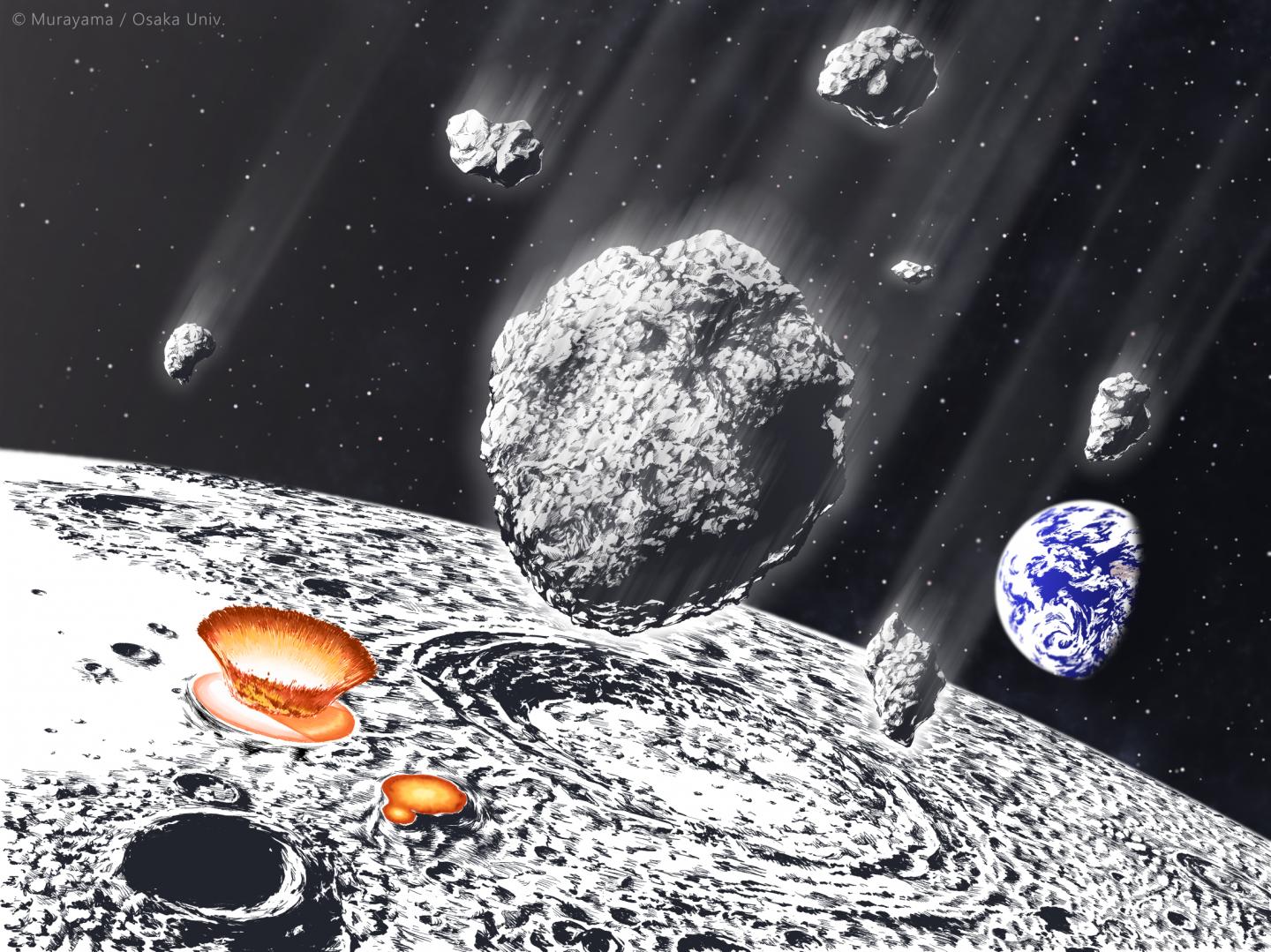

Natural processes here on Earth continually re-shape the planet’s surface. Craters from ancient asteroid strikes are erased in a short period of time, in geological terms. So how can researchers understand Earth’s history, and how thoroughly it may have been pummeled by asteroid strikes?
Scientists can turn their attention to our ancient companion, the Moon.
Continue reading “800 Million Years Ago, it Was Raining Asteroids on the Earth and Moon”The Moon Might Have Formed a Little Later than Originally Believed
According to the Giant Impact Hypothesis, the Moon formed when a Mars-sized object (named Theia) collided with Earth billion years ago, at a time when the Earth was still a ball of magma. This event not only led to the Earth-Moon system we recognize today, it is also beleived to have led to the differentiation of the Earth’s core region into an molten Outer Core and a solid Inner Core.
However, there has been an ongoing debate as to the timing of this impact and how long the subsequent formation of the Moon took place. According to a new study by a team of German researchers, the Moon formed from a magma ocean that took up to 200 million years to solidify. This means that the Moon finished forming about 4.425 billion years ago, or 100 million years later than previously thought.
Continue reading “The Moon Might Have Formed a Little Later than Originally Believed”NASA Chooses 10 Projects that Will Help it Live Off the Land… on the Moon
Before this decade is out, NASA plans to send astronauts to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era and establish a sustainable program of lunar exploration. In order to ensure that future lunar missions are cost-effective and not entirely dependent on Earth for resupply, NASA is looking for ways to leverage lunar resources – everything from water ice to oxygen-rich regolith – to meet their astronauts’ needs.
This process, known as In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU), is a major part of NASA’s plans to explore the Moon in the coming years, as well their long-term plans to send astronauts to Mars. To help them meet this challenge, NASA recently selected 10 proposals through its Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) program to developed ISRU-related technologies.
Continue reading “NASA Chooses 10 Projects that Will Help it Live Off the Land… on the Moon”NASA and HeroX are Looking to Light Up the Moon!
NASA is busy preparing to land astronauts around the Moon’s South Pole-Aitken Basin by 2024, which will be the first time astronauts have walked on lunar soil since the Apollo Era. By 2028, they plan to establish the Lunar Gateway and Lunar Base Camp, which will facilitate long-term lunar exploration and also missions to Mars. Naturally, a lot of things need to be figured out beforehand, like seeing to the astronauts’ needs.
This includes shelter from the elements, food, and water, but also electricity. To meet that demand, the NASA Centennial Challenges Program has once again launched an incentive challenge through HeroX to inspire solutions. It’s called the Watts on the Moon Challenge, and in exchange for a prize purse of up to $5 million, NASA is looking for solutions on how to provide a reliable supply of energy for lunar missions.
Continue reading “NASA and HeroX are Looking to Light Up the Moon!”Why Lava Tubes Should be Our Top Exploration Priority on Other Worlds

When magma comes out of the Earth onto the surface, it flows as lava. Those lava flows are fascinating to watch, and they leave behind some unique landforms and rocks. But a lot of what’s fascinating about these flows can be hidden underground, as lava tubes.
These lava tubes are turning out to be a very desirable target for exploration on other worlds, just as they are here on Earth.
Continue reading “Why Lava Tubes Should be Our Top Exploration Priority on Other Worlds”That Strange Gel-Like Material Discovered by China’s Lunar Rover? It’s Just Rock
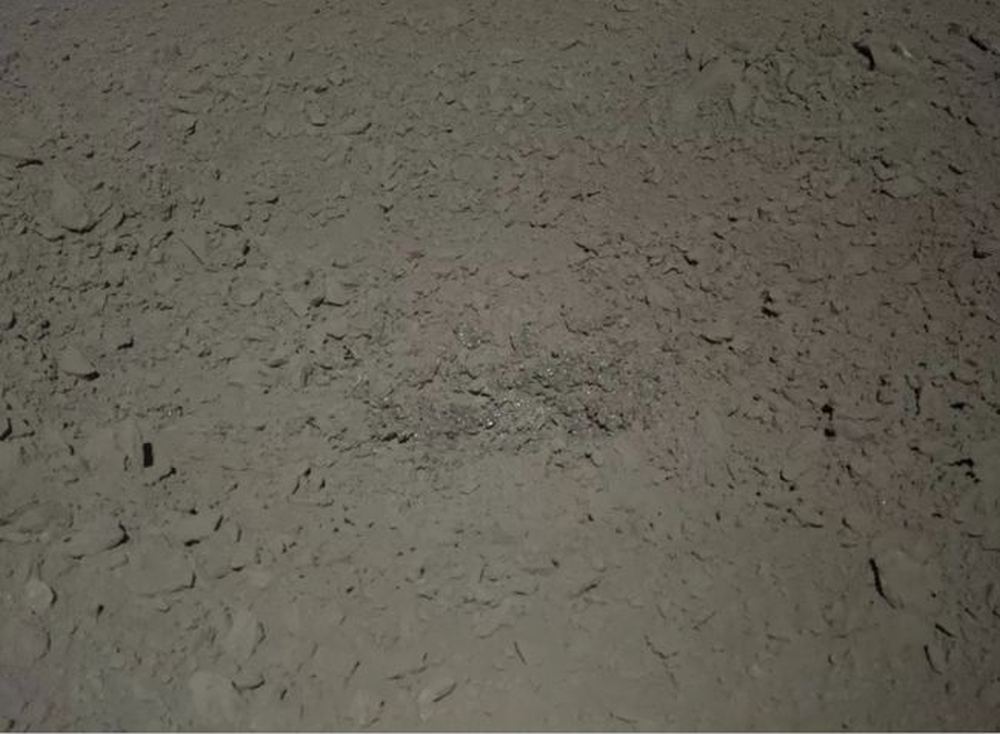

In January 2019, China landed its Chang’e 4 mission on the Moon’s far side. The Yutu-2 rover got busy exploring its surroundings. It’s still going, even though the rover’s nominal operating mission was only three months.
Among the mission’s findings was a strange material described as “gel-like.” Now an analysis of the material has revealed that it’s just rock: impact melt breccia.
Continue reading “That Strange Gel-Like Material Discovered by China’s Lunar Rover? It’s Just Rock”