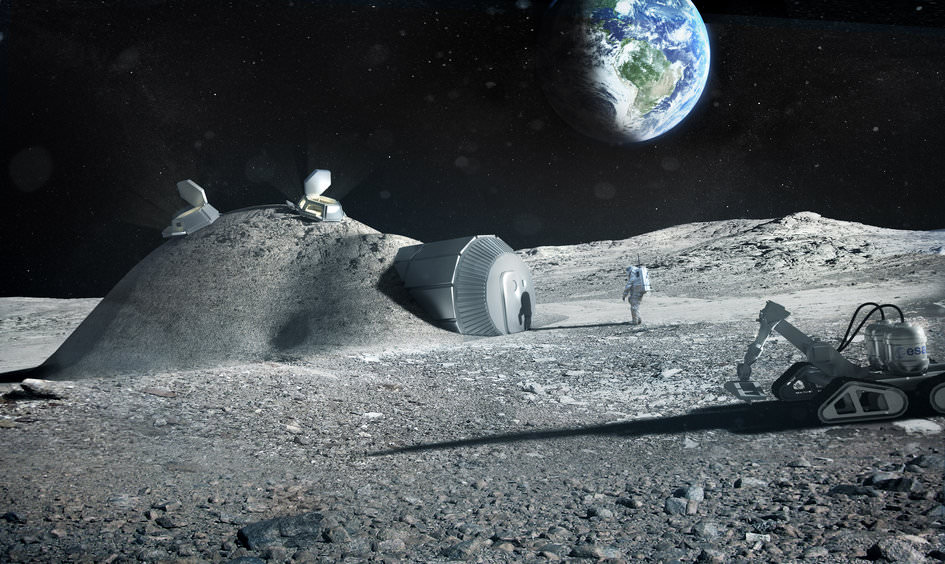
In the next few decades, NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), China, and Russia all plan to create outposts on the lunar surface that will allow for a permanent human presence. These proposals seek to leverage advances in additive manufacturing (aka. 3-D printing) with In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) to address the particular challenges of living and working on the Moon.
For the sake of their International Moon Village, the ESA has been experimenting with “lunacrete” – lunar regolith combined with a bonding agent to create a building material. But recently, a team of researchers conducted a study (in cooperation with the ESA) that found that lunacrete works even better if you add a special ingredient that the astronauts make all by themselves – urine!
Continue reading “Astronaut Pee Will Help Build Bases on the Moon”