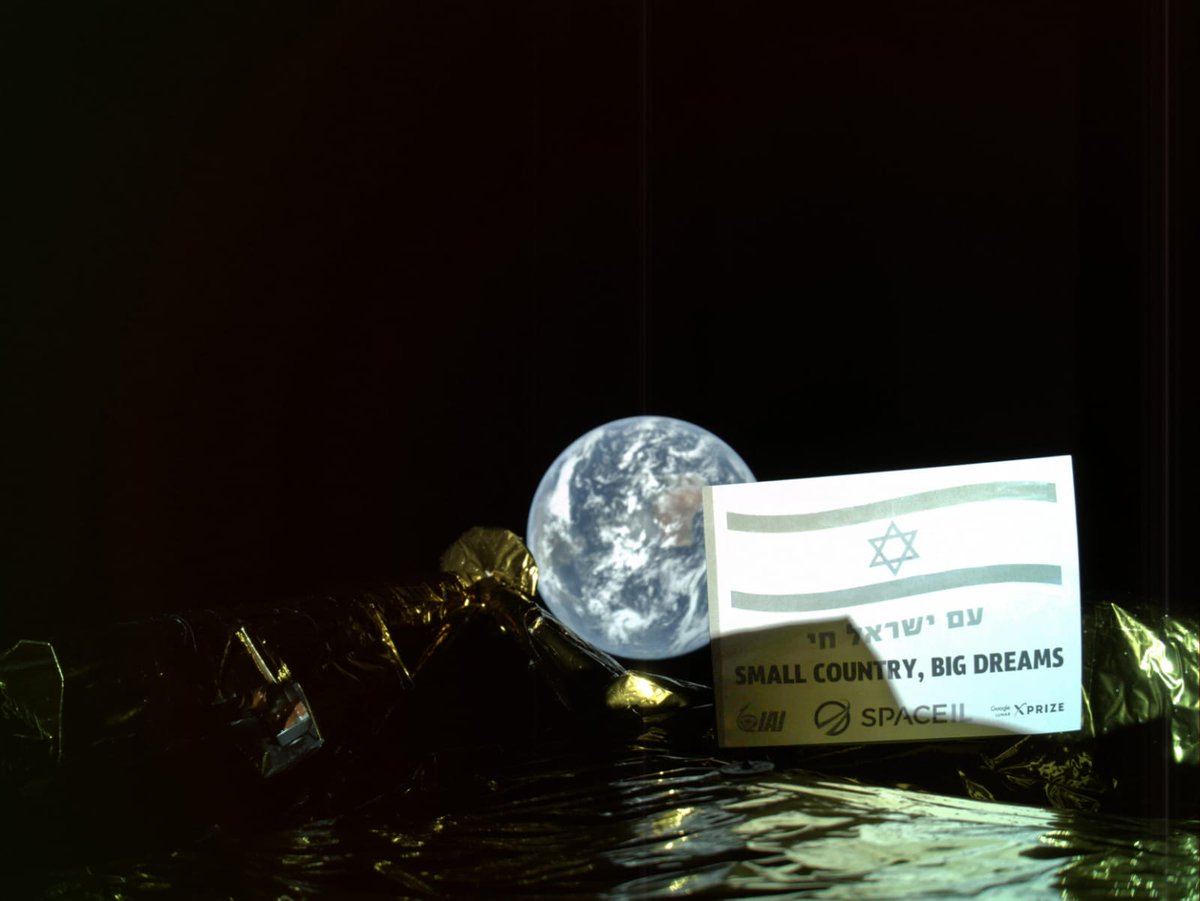
Israel’s space program doesn’t get a lot of headlines. Israel itself is in the news a lot, but usually for other reasons. But they do have a space program, and right now they have a lander, called Beresheet, on the way to the Moon.
Continue reading “You’re in This Picture. It’s a Selfie Taken by SpaceIL’s Beresheet Lunar Lander on its Way to the Moon”You’re in This Picture. It’s a Selfie Taken by SpaceIL’s Beresheet Lunar Lander on its Way to the Moon