We’ve written extensively about the orbital debris problem here on Universe Today. In a nutshell, just about every time we launch something from Earth there are bits and pieces that are left behind. Screws. Paint flecks. Sometimes bigger pieces from rocket stages, or at worst, dysfunctional satellites.
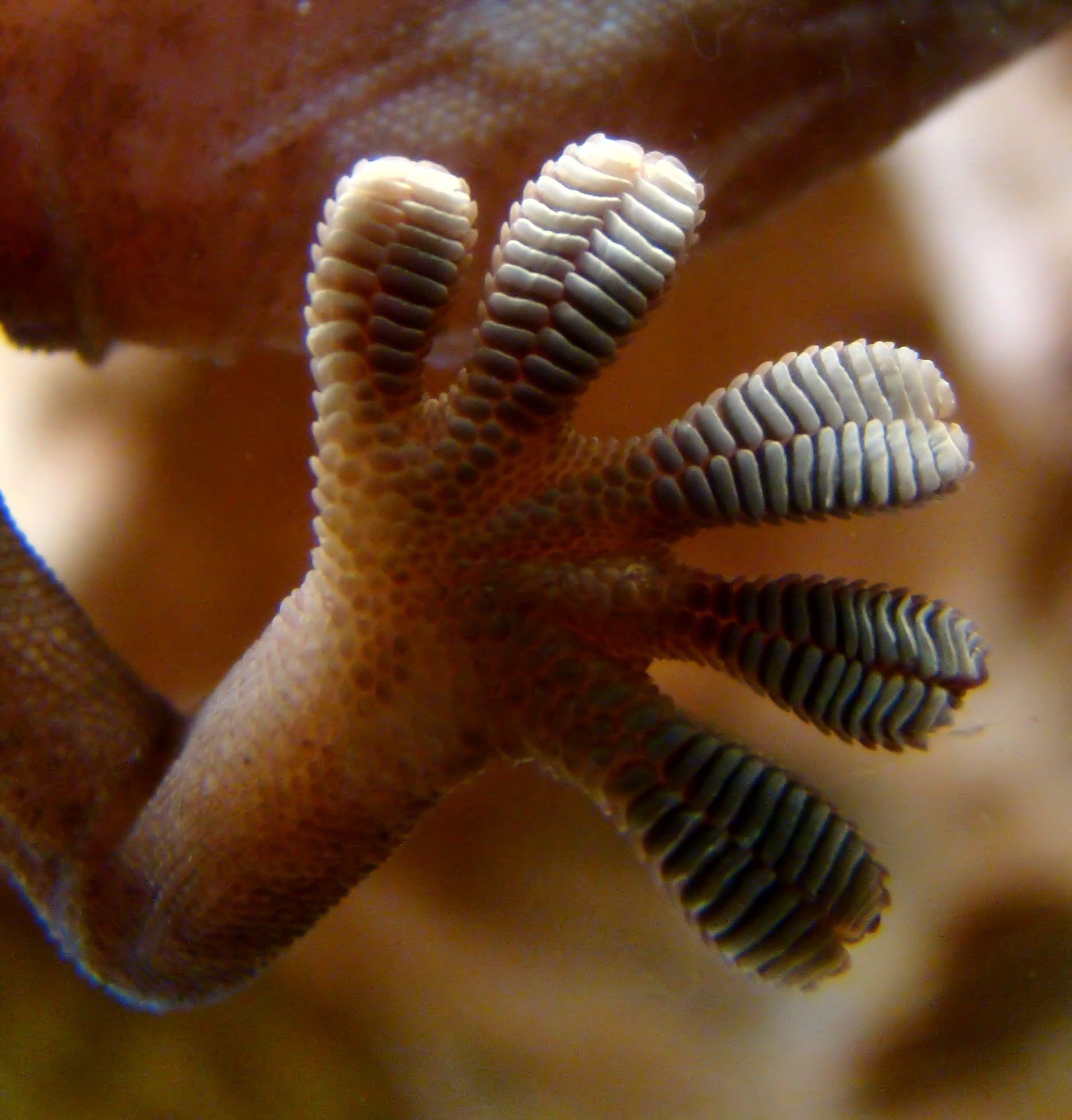
Added to the list of lasers, magnets, robot hands and other ideas to get space junk out of orbit is a new one from NASA — gecko grippers. Yes, lizard hands. The idea is by using techniques from these animal appendages, we might be able to efficiently snag dead satellites or other debris at low cost.
Space debris is all whizzing above us and puts us at risk for devastating crashes that can create a sort of prison of debris for any spacecraft hoping to fly above the atmosphere. We’ve already had to move the shuttle and International Space Station due to threats, and the fear is as more satellites reach space, the problem will get worse.
Here’s what NASA has to say about the idea, which is led by Aaron Parness, a robotics researcher at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory:
The gripping system … was inspired by geckos, lizards that cling to walls with ease. Geckos’ feet have branching arrays of tiny hairs, the smallest of which are hundreds of times thinner than a human hair. This system of hairs can conform to a rough surface without a lot of force. Although researchers cannot make a perfect replica of the gecko foot, they have put “hair” structures on the adhesive pads of the grippers.
The grippers were put through their paces in a simulated microgravity test in August (recently highlighted on NASA’s website). On a plane that flew parabolas with brief “weightless” periods, the grippers managed to grab on to a 20-pound cube and a 250-pound researcher-plus-spacecraft-material-panels combination.
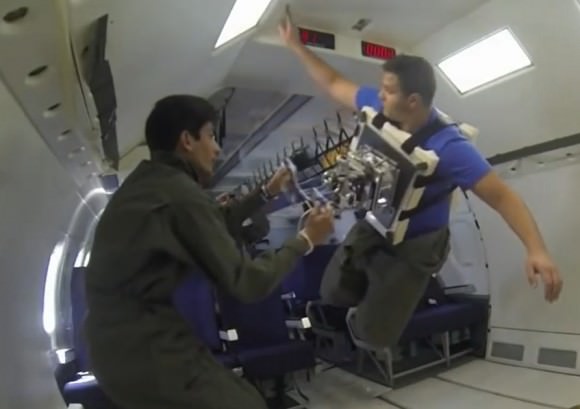

The key limitation was researchers actually held on to their invention themselves, but eventually they hope to use a robotic leg or arm to achieve the same purpose. Meanwhile, on the ground, the grippers have been used on dozens of spacecraft surfaces in a vacuum and in temperatures simulating what you’d find in orbit.
There’s no guarantee that the system itself will make it to space, as it’s still in the early stages of testing. But in a statement, Parness said he thinks it’s possible that “our system might one day contribute to a solution.” NASA also said these could be used for small satellites to attach to the space station, but development would need to move quickly in that case. The station is only guaranteed to be in use until 2020, with possible extension to 2024.
Source: Jet Propulsion Laboratory