That ‘amazing astro-shot that isn’t’ is making the rounds of ‘ye ole web again.
You know the one. “See an Amazing Image of an Eclipse… From SPACE!!!” screams the breathless headline, with the all-too-perfect image of totality over the limb of the Earth, with the Milky Way thrown in behind it for good measure.
As the old saying goes, if it looks too good to be true, it probably is. Sure, the pic is a fake, and it’s been debunked many, many times since it was first released into the wild a few years back. But never let reality get in the way of a good viral meme. As eclipse season 2 of 2 gets underway tonight with a total lunar eclipse followed by a partial solar eclipse on October 23rd both visible from North America, the image is once again making its rounds. But there’s a long history of authentic captures of eclipses from space that are just as compelling. We’ve compiled just such a roll call of real images of eclipses seen from space:
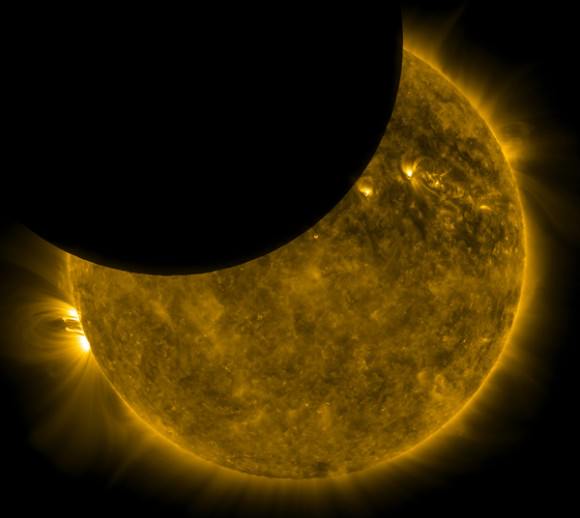

The Solar Dynamics Observatory:
Launched in 2010, The Solar Dynamics Observatory or SDO is NASA’s premier orbiting solar observatory. But unlike Sun-staring satellites based in low Earth orbit, SDO’s geosynchronous orbit assures that it tends to see a cycle of partial solar eclipses twice a year, roughly around the equinoxes. And like many satellites, SDO also passes into the Earth’s shadow as well, offering unique views of a solar eclipse by the limb of the Earth from its vantage point.
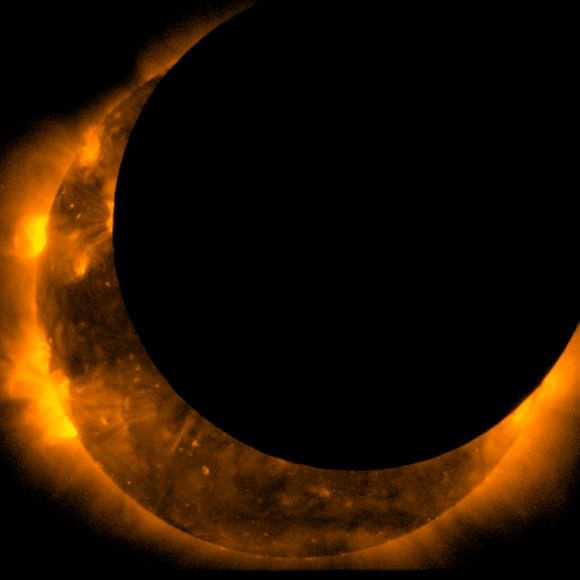

Hinode:
A joint mission between NASA and JAXA (the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency) launched in 2006, Hinode observes the Sun from low Earth orbit. As a consequence, it nearly has a similar vantage point as terrestrial viewers and frequently nabs passages of the Moon as solar eclipses occur. Such events, however, are fleeting; moving at about eight kilometres per second, such eclipses last only seconds in duration!
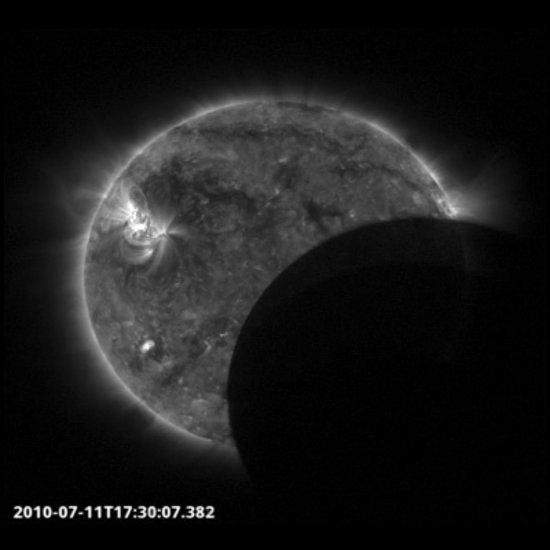

Proba-2:
Like Hinode, Proba-2 is the European Space Agency’s flagship solar observing spacecraft based in low Earth orbit. It also catches sight of the occasional solar eclipse, and these fleeting passages of the Moon in front of the Earth happen in quick multiple cycles. Recent images from Proba-2 are available online.
Eclipses from the ISS:
The International Space Station isn’t equipped to observe the Sun per se, but astronauts and cosmonauts aboard have managed to catch views of solar eclipses in an unusual way, as the umbra of the Moon crosses the surface of the Earth. Such a view also takes the motion of the ISS in low Earth orbit into account. Cosmonauts aboard the late Mir space station also caught sight of the August 11th, 1999, total solar eclipse over Europe.
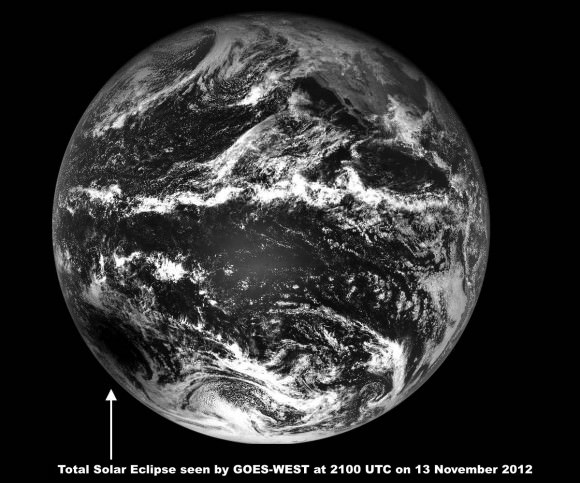
NASA-GOES:
Weather satellites can, and do, occasionally catch sight of the inky black dot of the Moon’s penumbra crossing the disk of the Earth. GOES-West snapped the above image of the November 13th, 2012, solar eclipse. The umbra of the Moon’s shadow races about 1700 kilometres per hour from west to east during an eclipse, and we can expect some interesting images in 2017 when the next total solar eclipse crosses the United States on August 21st, 2017.
Apollo-Soyuz Test Project:
The final mission of Apollo program, the 1975 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, also yielded an unusual and little known effort to observe the Sun. The idea was to use the Apollo command module as a “coronagraph” and have cosmonauts image the Sun from the Soyuz as the Apollo spacecraft blocked it out after undocking. Unfortunately, the Apollo thrusters smeared the exposure, and it became a less than iconic— though unusual — view from the space age.
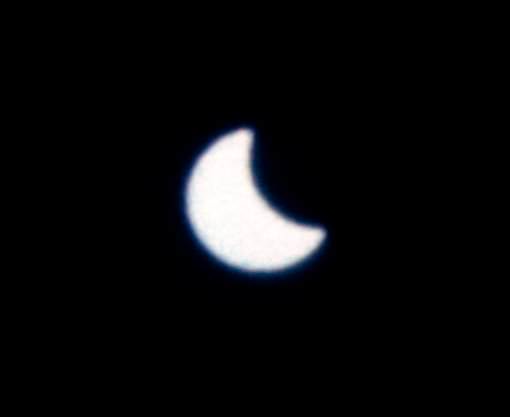

Gemini XII and the first eclipse seen from space:
On November 12th, 1966, a total solar eclipse graced South America. Astronauts James Lovell Jr. and Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin Jr. were also in orbit at the time, and managed to snap the first image of a solar eclipse from space. Gemini XII was the last flight of the program, and the astronauts initially thought they’d missed the eclipse after a short trajectory burn.

ISS Astronauts catch a transit of Venus:
We were fortunate that the International Space Station had its very own amateur astronomer in residence in 2012 to witness the historic transit of Venus from space. NASA astronaut Don Pettit knew that the transit would occur during his rotation, and packed a full-aperture white light solar filter for the occasion. Of course, a planetary transit meets the very loosest definition of a partial eclipse, but it’s a unique capture nonetheless.
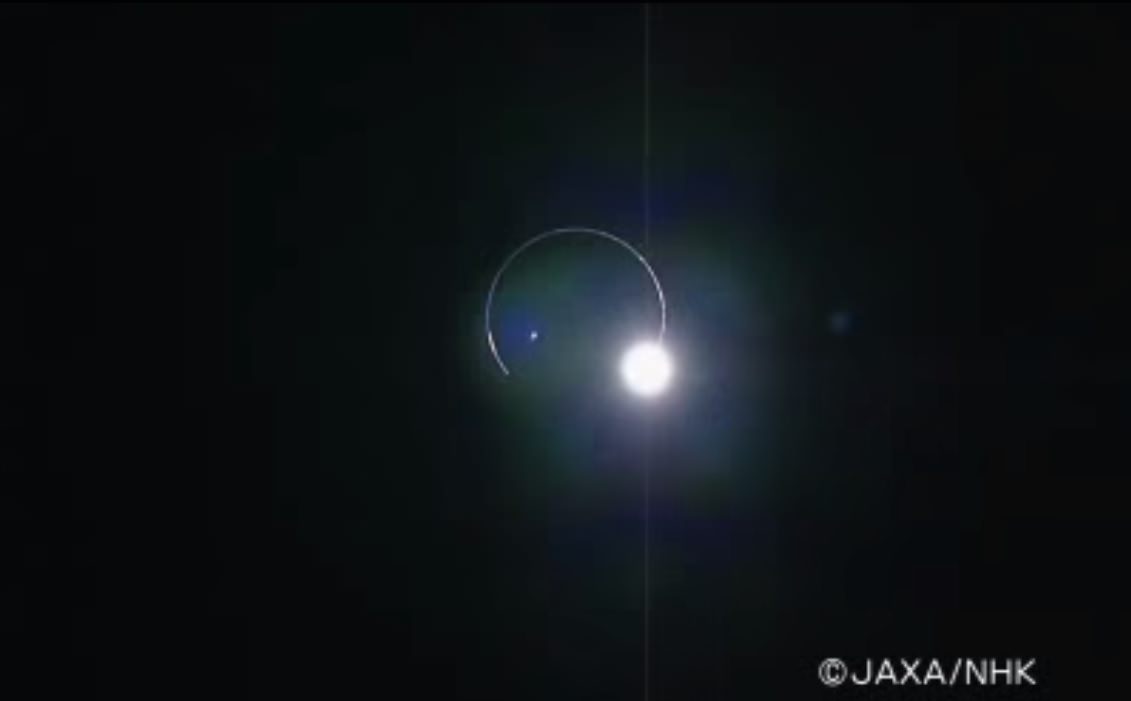
Kaguya:
Japan’s SELENE-Kaguya spacecraft entered orbit around the Moon in 2007 and provided some outstanding imagery of our solitary natural neighbor. On February 10th, 2009, it also managed to catch a high definition view of the Earth eclipsing the Sun as seen from lunar orbit. A rare catch, such an event occurs during every lunar eclipse as seen from the Earth.

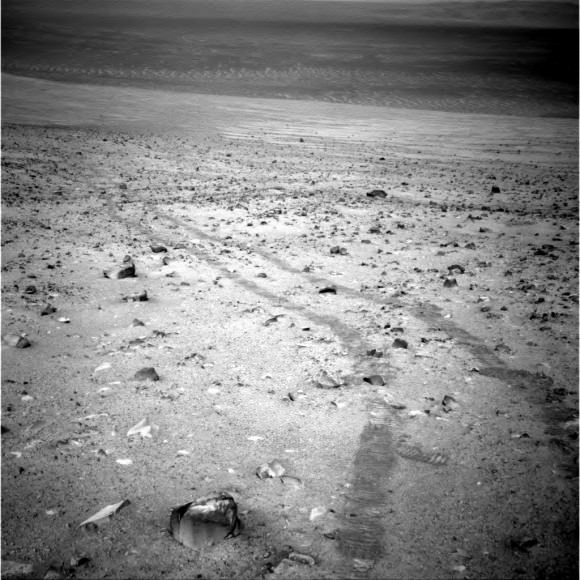
An unusual eclipse… seen from Mars:
We’re fortunate to live in an epoch in time and space where total solar eclipses can occur as seen from the Earth. But bizarre eclipses and transits can also be seen from Mars. The Spirit and Opportunity rovers have witnessed brief transits of the Martian moons Phobos and Deimos across the face of the Sun, and in 2010, the Curiosity rover recorded the passage of Phobos in front of the Sun in a bizarre-potato shaped “annular eclipse”. But beyond just the “coolness” factor, the event also helped researchers refine our understanding of orbital path of the Martian moon.
The future: It’s also interesting to think of what sort of astronomical wonders await travelers as we venture out across the solar system. For example, no human has yet to stand on the Moon and witness a solar eclipse. Or how about a ring plane passage through Saturn’s rings, thus far only witnessed via the robotic eyes of Cassini? Of course, for the best views of Saturn’s rings, we recommend a vacation stay on Iapetus, the only major Saturnian moon whose orbit is inclined to the ring plane. And stick around ‘til November 10th, 2084, and you can witness a transit of Earth, the Moon and Phobos as seen from the slopes of Elysium Mons on Mars:
Hopefully, they’ll have perfected that whole Futurama “head-in-a-jar” thing by then…
-Looking for eclipses in science fiction? Check out the author’s tales Exeligmos and Shadowfall.