NASA has actively joined the hunt for the missing Malaysian Airline flight MH-370 that mysteriously disappeared without a trace more than two weeks ago on March 8, 2014.
Sensors aboard at least two of NASA’s unmanned Earth orbiting global observation satellites as well as others flying on the manned International Space Station (ISS) are looking for signs of the jetliner that could aid the investigators from a multitude of nations and provide some small measure of comfort to the grieving families and loved ones of the passengers aboard.
“Obviously NASA isn’t a lead agency in this effort. But we’re trying to support the search, if possible,” Allard Beutel, NASA Headquarters, Office of Communications director, told Universe Today this evening.
NASA’s airplane search assistance comes in two forms; mining existing space satellite observing data and retargeting space based assets for new data gathering since the incident.
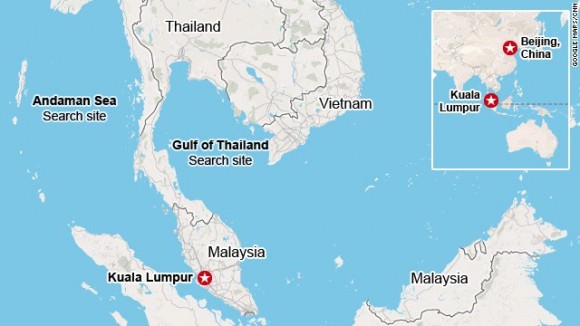
The Malaysian Airline Boeing 777-2H6ER jetliner went missing on March 8 while cruising en route from Kuala Lampur, Malaysia to Beijing, China. See cockpit photo below.
Accurate facts on why MH-370 vanished with 239 passengers aboard have sadly been few and far between.
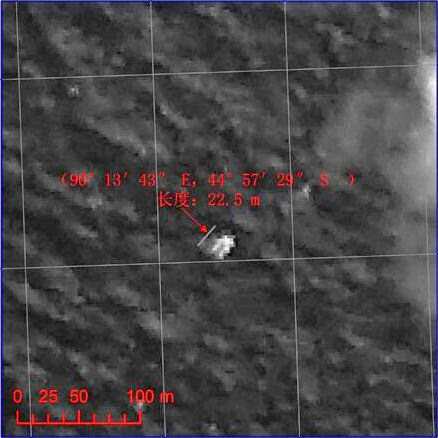

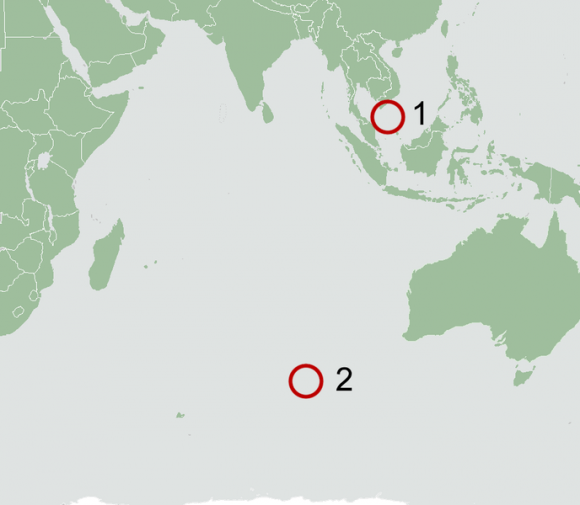
Last week, the search area shifted to a wide swath in the southern Indian Ocean when potential aircraft debris was spotted in a new series of separate satellite images from Australia and China government officials.
A prior set of official Chinese government satellite images at a different location yielded absolutely nothing.
The area is now focused 2,500 km (1,600 mi) south west of Perth, a city on the western coast of Australia.
NASA’s search support was triggered upon activation of the International Charter on Space and Major Disasters.
Available data from NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites has already been transmitted to the U.S. Geological Survey and new data are now being collected in the search area.
“In response to activation of the International Charter on Space and Major Disasters last week regarding the missing Malaysia Airlines jetliner, NASA sent relevant space-based data to the U.S. Geological Survey’s Earth Resources Observations and Science Hazard Data Distribution System that facilitates the distribution of data for Charter activations,” according to a NASA statement.
And it’s important to note that NASA satellites and space-based cameras are designed for long-term scientific data gathering and Earth observation.
“They’re really not meant to look for a missing aircraft,” Beutel stated.
“The archive of global Earth-observing satellite data is being mined for relevant images. These include broad-area views from the MODIS [instrument] on NASA’s Terra and Aqua satellites,” Beutel informed me.
The next step was to retarget both satellites and another high resolution camera aboard the ISS.
“In addition, two NASA high-resolution assets have been targeted to take images of designated search areas: the Earth Observing-1 satellite and the ISERV camera on the International Space Station,” Beutel explained.

Aqua and Terra were already gathering new observations with the MODIS instrument in the search area off Australia last week. MODIS measures changes in Earth’s cloud cover.
Here are the satellite observation times and capabilities:
• MODIS on the Aqua satellite observed at about 1:30 p.m. local time as it passes overhead from pole-to-pole
• MODIS on the Terra satellite observed at about 10:30 a.m. local time
• The width (field of view) of a MODIS observation is 2,300 kilometers
• One pixel of a MODIS image – the limit of how small a feature it can see – is about 1 kilometer.
A new set of high resolution Earth imaging cameras are being sent to the ISS and are loaded aboard the SpaceX CRS-3 Dragon resupply capsule now slated for blastoff on March 30.
The newly launched NASA/JAXA GPM precipitation monitoring satellite which will cover this ocean area in the future is still in the midst of science instrument checkout.

Ships and planes from at least 26 countries have been being dispatched to the new based on the new satellite imagery to search for debris and the black boxes recording all the critical engineering data and cockpit voices of the pilot and copilot and aid investigators as to what happened.
No one knows at this time why the Malaysia Airlines flight mysteriously disappeared.