[/caption]
The crew of Endeavour said on Wednesday (Jan 20) that construction of new coolant hoses required to connect the new Tranquility module, or Node 3, to the space station is running ahead of schedule and they are optimistic for an on time launch of the STS 130 mission currently set for Feb 7.
Shortly after I attended the rollout to pad 39 A, the launch was thrown into doubt when a set of the 14 ft long external ammonia jumper hoses, which convey coolent critical for temperature control, ruptured during high pressure testing in early January. Tranquility cannot be fully activated until the ammonia lines are installed and functioning properly. Since then, tiger teams of engineers and technicians working at the hose subcontractor and at NASA’s Marshall Spaceflight Center in Huntsville, Ala have worked vigorously to qualify four new replacement hoses. They are also working to modify the original ammonia hoses which will be brought along as a back-up “Plan B” in case problems develop with the new replacement hoses.

During a launch pad press conference with reporters, lead Endeavour spacewalker Robert Behnken said, “We’ve been following these ammonia lines and the story associated with them for 13 months. I think folks paying close attention right now haven’t really heard the entire story. So we’ve been watching them closely for a long time now.”
“Last weekend our crew was at Marshall to see the first line as it was coming together and actually put it on a test rig to make sure it was going to do the job that it was intended. We’re expecting this Saturday to fly up and see all four lines in a pretty good configuration, pretty flight representative. Those lines, after that, will come down here to KSC for processing and installation into the orbiter.”
“Right now, the schedule appears for that set of lines to be a couple of days ahead,” Behnken added. “Our original plan was to do our fit check and our opportunity with them next weekend. But they’re ahead now and we’ll be able to do that this Saturday, which is great news.”
“The program is also pursuing a second set of lines that would allow us to launch at a slightly delayed launch date and still maintain a full capability for Node 3 [Tranquility]. So the program is pursuing two courses. Plan 1 is actually ahead of schedule which allows us to do a fit check a week early. That’s really good news as we move forward to flight”, he concluded.
Tranquility is the primary cargo being lofted in the payload bay of shuttle Endeavour and will be delivered to the International Space Station by the six person crew. During three spacewalks, astronaut teams will attach and activate Tranquility and the Cupola observation module which is joined to Tranquility at one end. The modules were loaded into Endeavour’s payload bay on Wednesday (Jan. 20). See my recent photos of Tranquility and Cupola from inside the Space Station Processing Facility at KSC in earlier reports here and here.
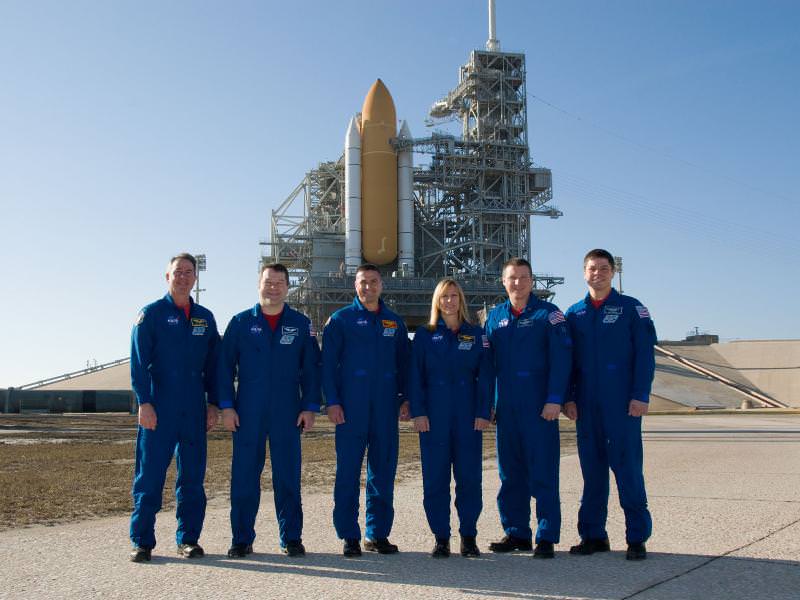
Today (Jan 21), the STS 130 astronauts took part in a mock countdown known as the TCDT, or Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test. While dressed in their orange spacesuits they climbed inside Endeavour at pad 39 A to rehearse all the actual launch procedures right up to the T minus 4 minute point , but not including the point of liftoff. They also practiced emergency evacuation safety procedures in case of a launch pad abort requiring them to rapidly depart the orbiter in a life or death situation and enter the slidewire escape baskets. The crew flies back to Houston on Friday for final pre flight training exercises.
The six person crew comprises of commander George “Zambo” Zamka, pilot Terry Virts, and mission specialists Kathryn Hire, Stephen Robinson, Nicholas Patrick and Robert Behnken.
Senior shuttle managers will meet at KSC on Jan. 27 for an executive-level Flight Readiness Review. They will conduct an in-depth assessment to determine whether the shuttle, crew, payloads and the problematical ammonia lines are fit for launch. Thereafter the team will set an official launch date, which for now is still targeted for Feb 7.
Meanwhile it’s likewise been a busy time up in space for the 5 man crew of Expedition 22 currently in residence aboard the ISS as they conduct essential preparatory work over the next few days which must be completed before Endeavour launches and also to free up the docking port for Tranquility.


Earlier STS 130 article by Ken Kremer from KSC
STS 130 flight pressing forward to launch as NASA resolves coolant hose leak
STS-130 Shuttle flight facing delay due to Payload technical glitch
Shuttle Endeavour Rolled to Pad; Countdown to the Final Five Begins