Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs) have a long history of service in space exploration. Since the first was tested in space in 1961, RTGs have gone on to be used by 31 NASA missions, including the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Packages (ALSEPs) delivered by the Apollo astronauts to the lunar surface. RTGs have also powered the Viking 1 and 2 missions to Mars, the Ulysses mission to the Sun, Galileo mission to Jupiter, and the Pioneer, Voyager, and New Horizons missions to the outer Solar System – which are currently in (or well on their way to) interstellar space.
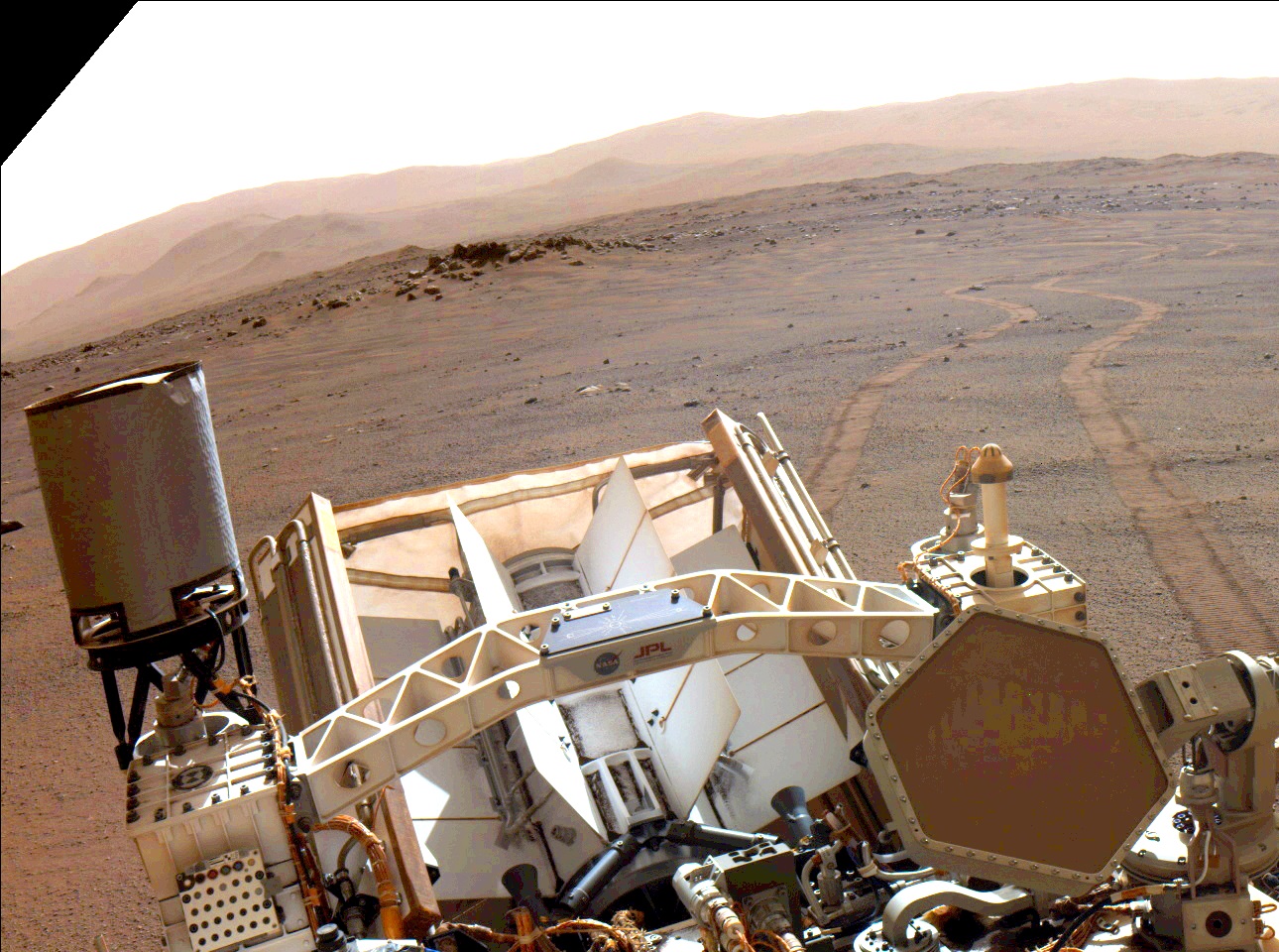
In recent years, RTGs have allowed the Curiosity and Perseverance rovers to continue the search for evidence of past (and maybe present) life on Mars. In the coming years, these nuclear batteries will power more astrobiology missions, like the Dragonfly mission that will explore Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. In recent years, there has been concern that NASA was running low on Plutonium-238, the key component for RTGs. Luckily, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) recently delivered a large shipment of plutonium oxide, putting it on track to realize its goal of regular production of the radioisotopic material.
Continue reading “NASA is Getting the Plutonium it Needs for Future Missions”