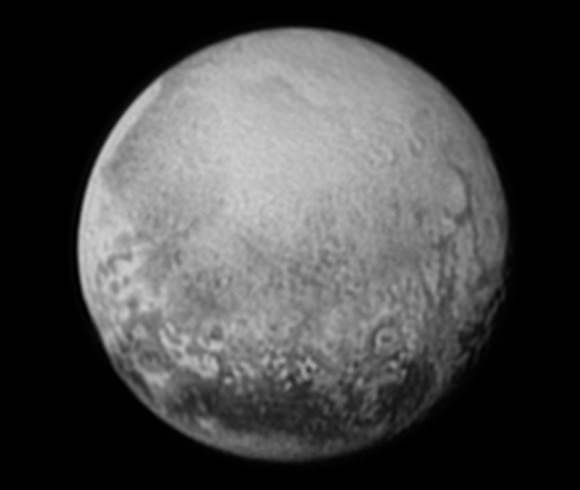
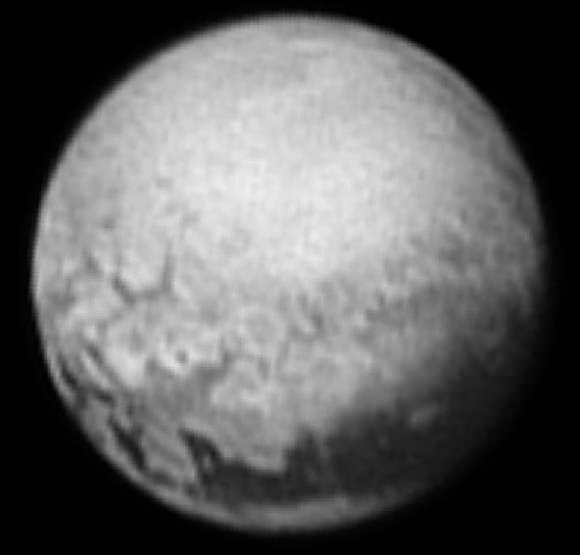
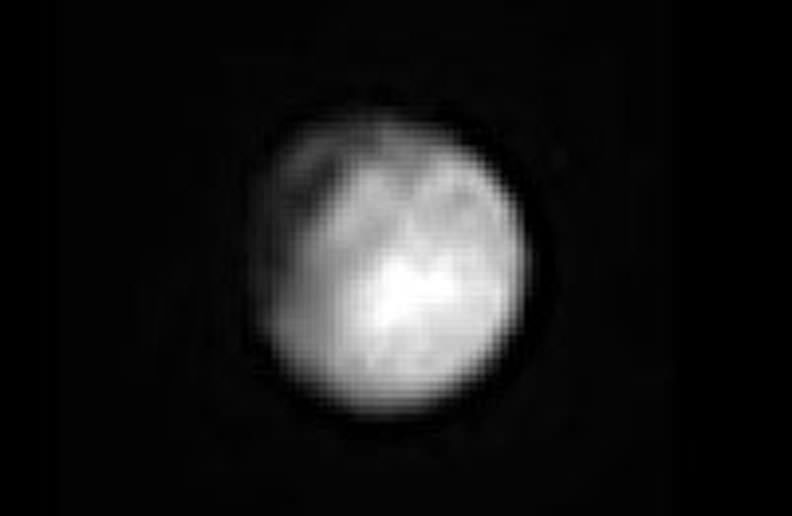
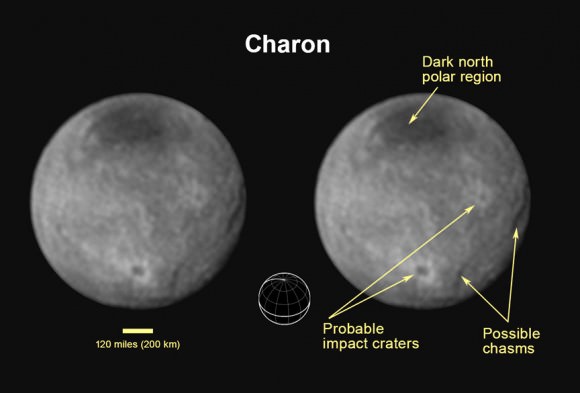
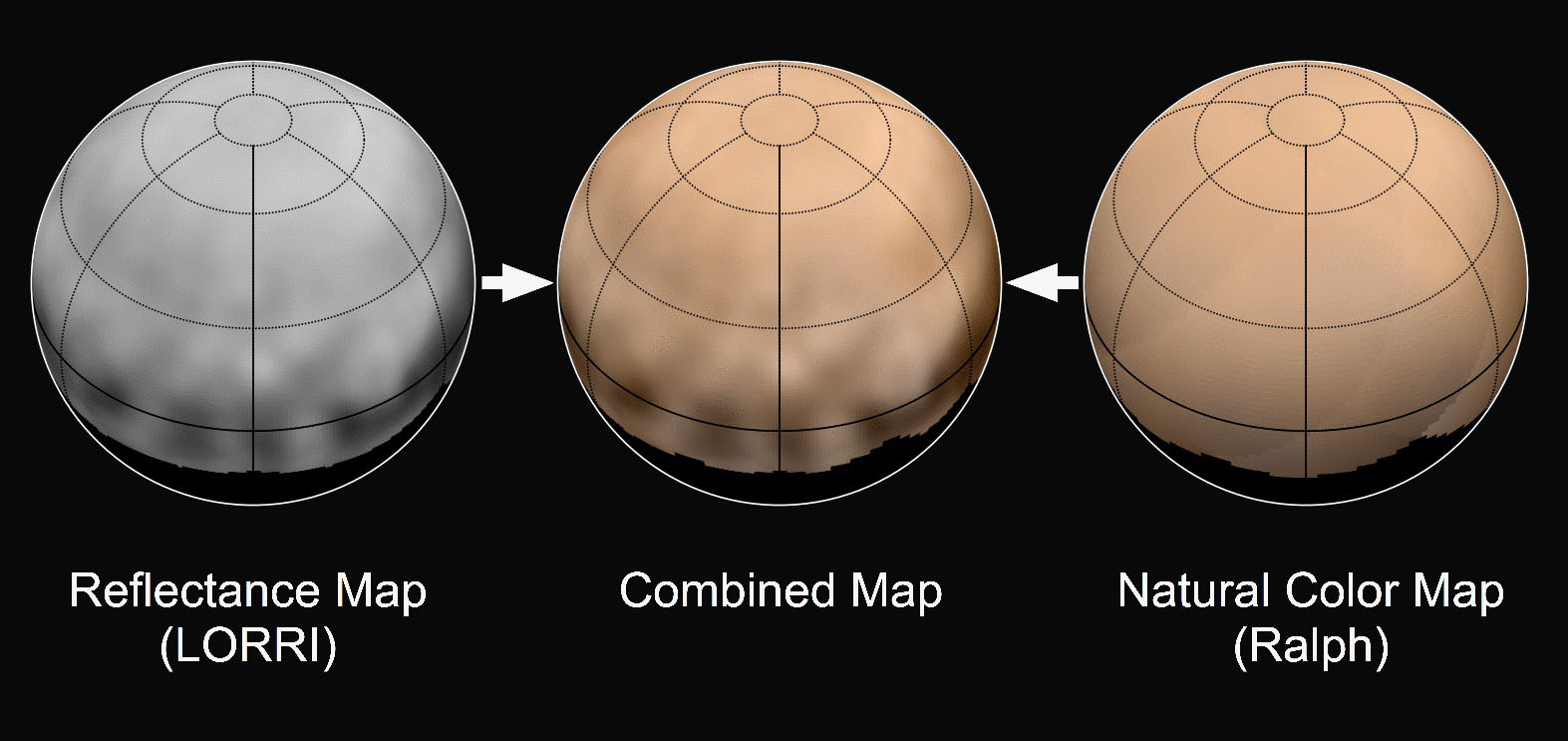
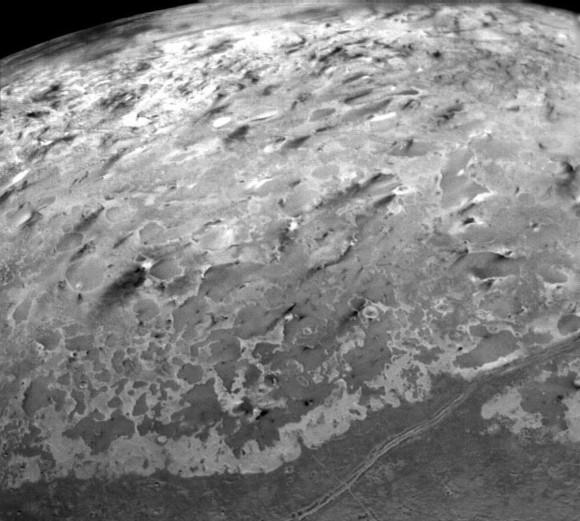
Chasms, craters, and a dark north polar region are revealed in this image of Pluto’s largest moon Charon taken by New Horizons on July 11, 2015. The annotated version includes a diagram showing Charon’s north pole, equator, and central meridian, with the features highlighted. Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SWRI
Story/imagery updated[/caption]
In the final days before humankinds first ever flyby of mysterious and tantalizing Pluto for the history making up close visit on Tuesday, July 14, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft has just delivered the sharpest and most stunning view yet of its binary companion Charon – and unveiled it to be a geologically rich world with colossal chasms, a multitude of craters and a humongous dark splotch in the northern regions. It’s obviously quite different in appearance and varies in composition from its larger planetary host.
Indeed the largest of Charon’s chasms stretches farther than Earth’s Grand Canyon. And it’s taken New Horizons over nine years speeding through space – since launching back in 2006 as the fastest spacecraft departing Earth – to get close enough to see these wonders for the first time.
“The most pronounced chasm, which lies in the southern hemisphere, is longer and miles deeper than Earth’s Grand Canyon,” says William McKinnon, deputy lead scientist with New Horizon’s Geology and Geophysics investigation team, in a NASA statement.
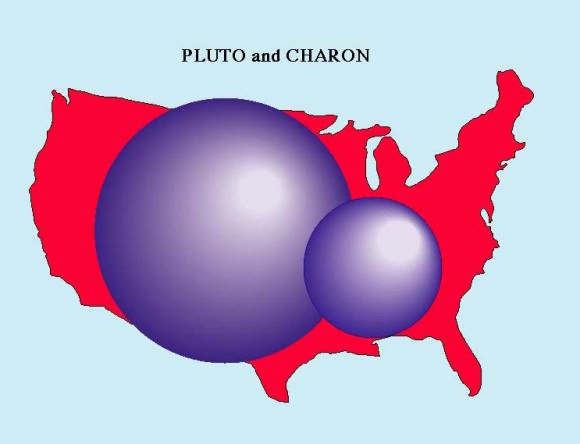
To put that into perspective, consider this; Charon is only about 750 miles (1200 kilometers) across, about half the diameter of Pluto. The Grand Canyon stretches 277 miles (446 km) across the western United States and is up to 18 miles (29 km) wide and attains a depth of over a mile (6093 feet or 1857 meters). Thus Charon’s ‘Grand Canyon’ is truly gargantuan in comparison to its moons size when compared to our Grand Canyon.
At 1471 miles (2368 km) across, Pluto is about half the diameter of the United States. Both Pluto and Charon and largely composed of icy materials, with much less rock compared to the terrestrial planets like Earth.
“This is the first clear evidence of faulting and surface disruption on Charon,” says McKinnon, who is based at the Washington University in St. Louis.
“New Horizons has transformed our view of this distant moon from a nearly featureless ball of ice to a world displaying all kinds of geologic activity.”
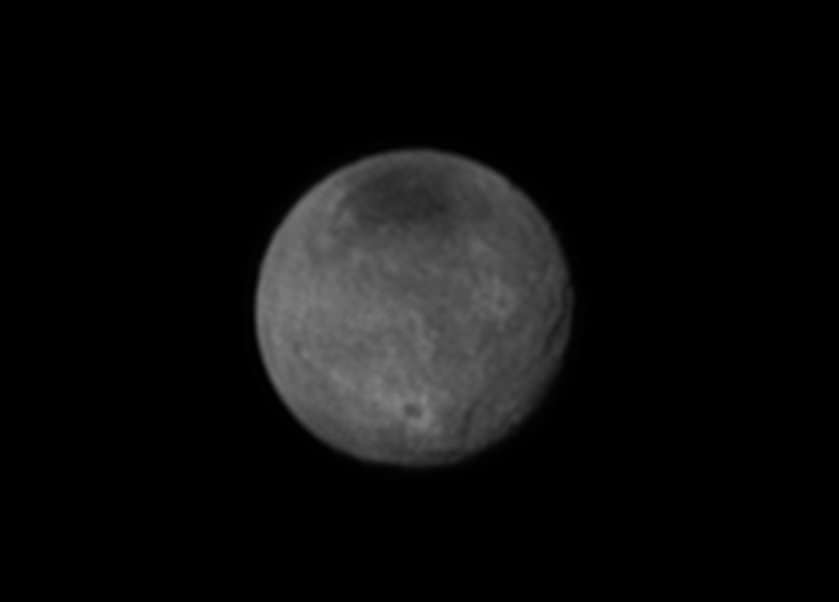

The exquisite new image of Charon’s chasms and canyons was just released by NASA this evening, Sunday, July 12. It was taken yesterday, Saturday, July 11, by New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) at a distance of 2.5 million miles (4 million kilometers) from Pluto and Charon, and radioed back to Earth today.
The largest crater seen in the July 11 images lies near Charon’s south pole and is about 60 miles (96.5 kilometers) across.
“The brightness of the rays of material blasted out of the crater suggest it formed relatively recently in geologic terms, during a collision with a small body some time in the last billion million years,” says the team.
“The darkness of the crater’s floor is especially intriguing,” says McKinnon.
“One explanation is that the crater has exposed a different type of icy material than the more reflective ices that lie on the surface. Another possibility is that the ice in the crater floor is the same material as its surroundings but has a larger ice grain size, which reflects less sunlight. In this scenario, the impactor that gouged the crater melted the ice in the crater floor, which then refroze into larger grains.”
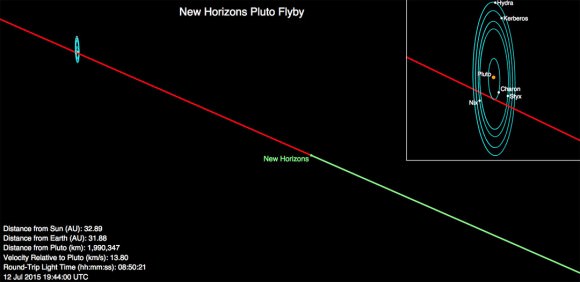
New Horizons is now merely one day and one million miles (1.6 million km) out from its history making encounter with the Pluto planetary system – some three billion miles (4.8 billion km) from Earth. It passed the million mile milestone at 11:23 p.m. EDT, Sunday night July 12.
And its closing in fast on its quarry at a whopping 31,000 mph (49,600 kph) after a nine year interplanetary voyage.

The high resolution LORRI imager is achieving an image resolution of 5 mile per pixel at this moment at a million miles away. And it will gets thousands of times better during the closest approach.
“Features as small as the lakes in New York’s Central Park and wharfs on the Hudson will be resolved,” said New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute, Boulder, Colorado, during a live mission update today, July 12. The image resolution will reach a maximum of about 230 feet (70 meters).
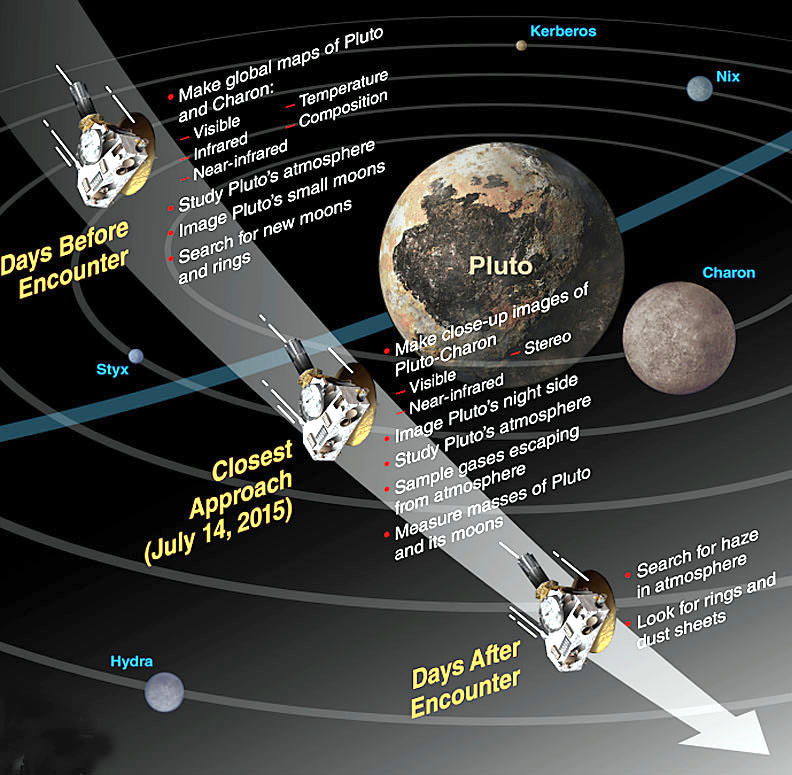
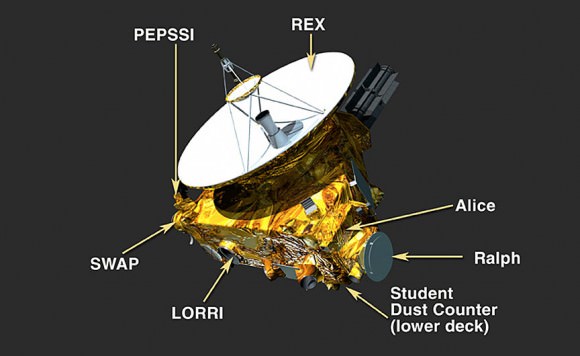
New Horizons suite of seven science instruments will collected 44 gigabits of data during the flyby encounter period lasting from July 7 to July 16, from Pluto, Charon and the four tiny moons – Hydra, Styx, Nix and Kerberos.
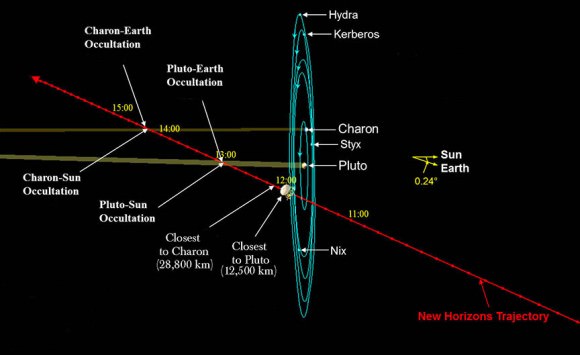
New Horizons will swoop to within about 12,500 kilometers (nearly 7,750 miles) of Pluto’s surface and about 17,900 miles (28,800 kilometers) from Charon during closest approach at approximately 7:49 a.m. EDT (11:49 UTC) on July 14.
Pluto and Charon are gravitationally locked with an orbital period of 6.4 days, so they always show the same face to one another. They orbit about 12,160 mi (19,570 kilometers) apart but about a center of gravity, or barycenter, above the surface of Pluto, unlike any of the other major bodies in our solar system.

Charon is by far the largest of Pluto’s five moons. The new July 11 image also shows that it sports a “mysterious dark region” stretching some 200 miles across near the north pole.
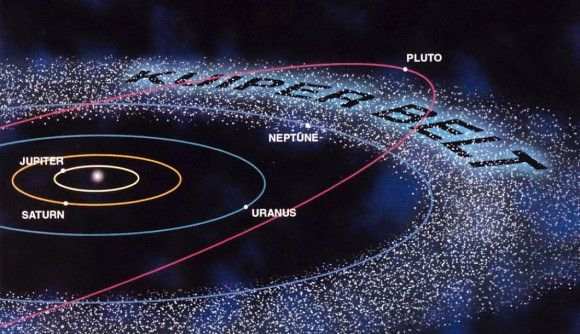
Pluto is the last of the nine classical planets to be explored up close and completes the initial the initial reconnaissance of the solar system nearly six decades after the dawn of the space age. It represents a whole new class of objects known as the ice dwarfs, located in the Kuiper Belt – a relic of solar system formation replete with countless bodies.
It has been three decades since we last visited planetary bodies at the outer reaches of our solar system when Voyager 2 flew past Uranus and Neptune in 1986 and 1989.
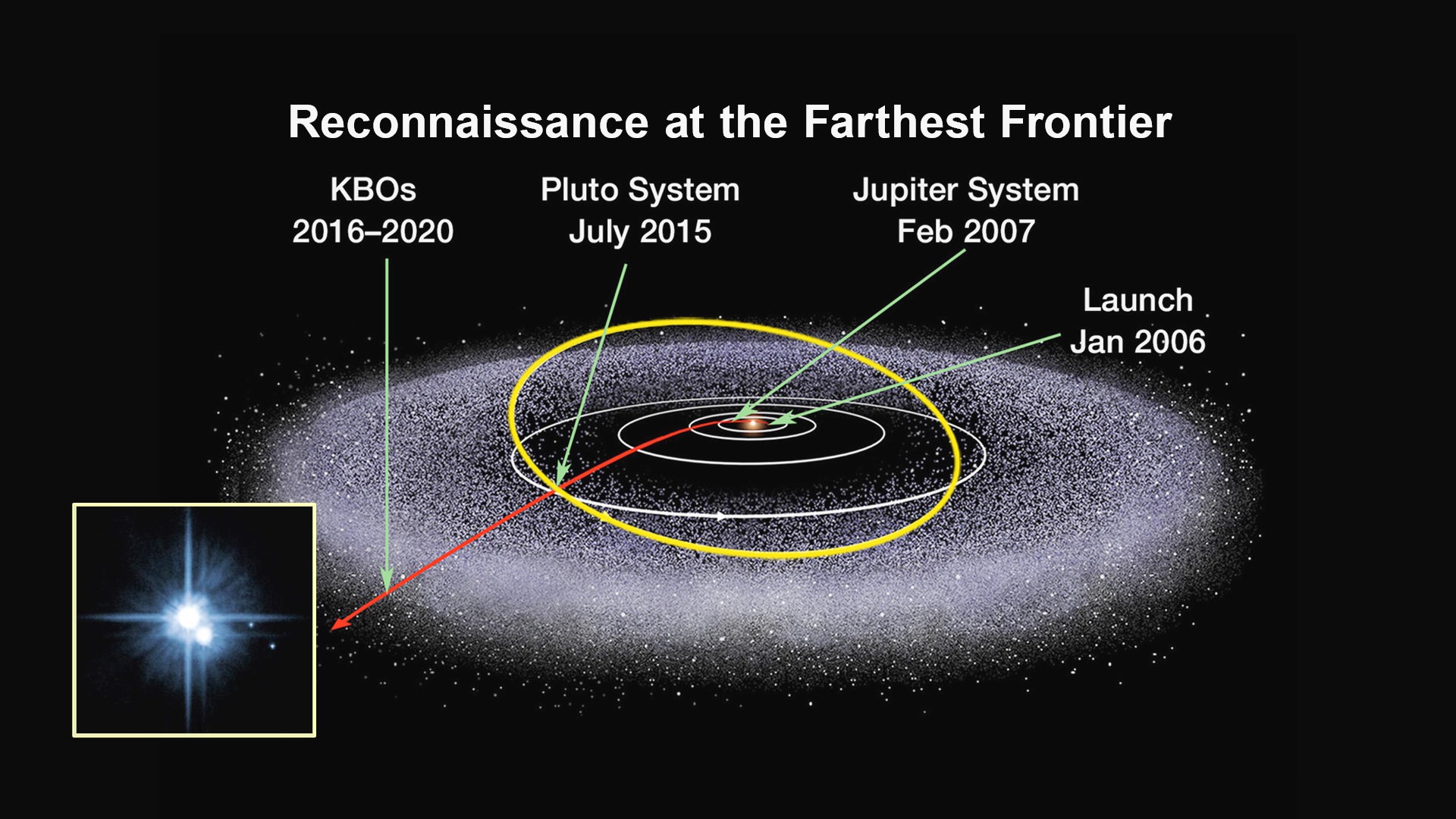
The New Frontiers spacecraft was built by a team led by Stern and included researchers from SwRI and the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. APL also operates the New Horizons spacecraft and manages the mission.
Watch for Ken’s continuing onsite coverage of the Pluto flyby on July 14 from the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL).
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.